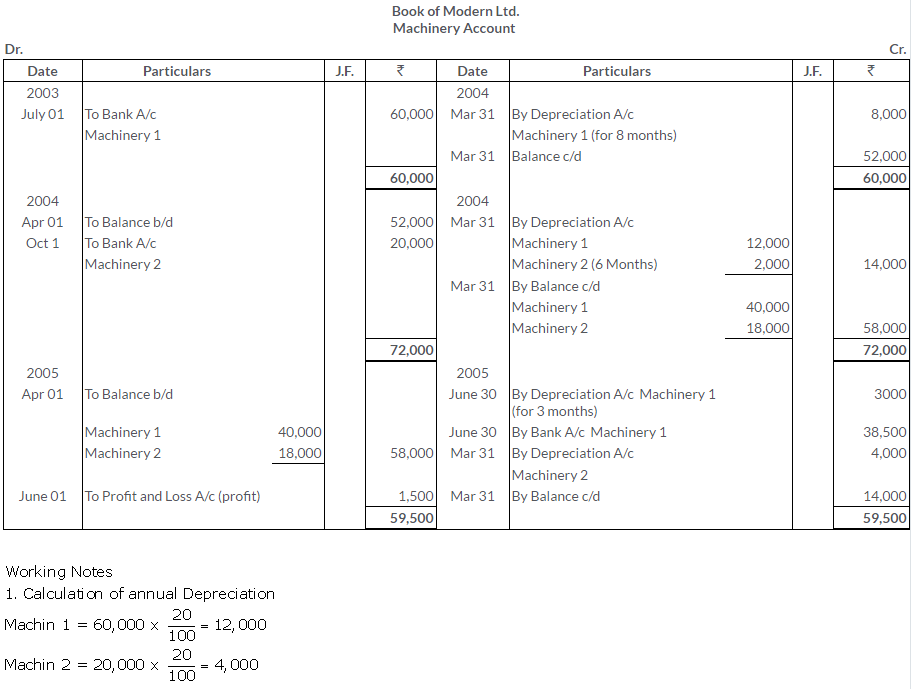
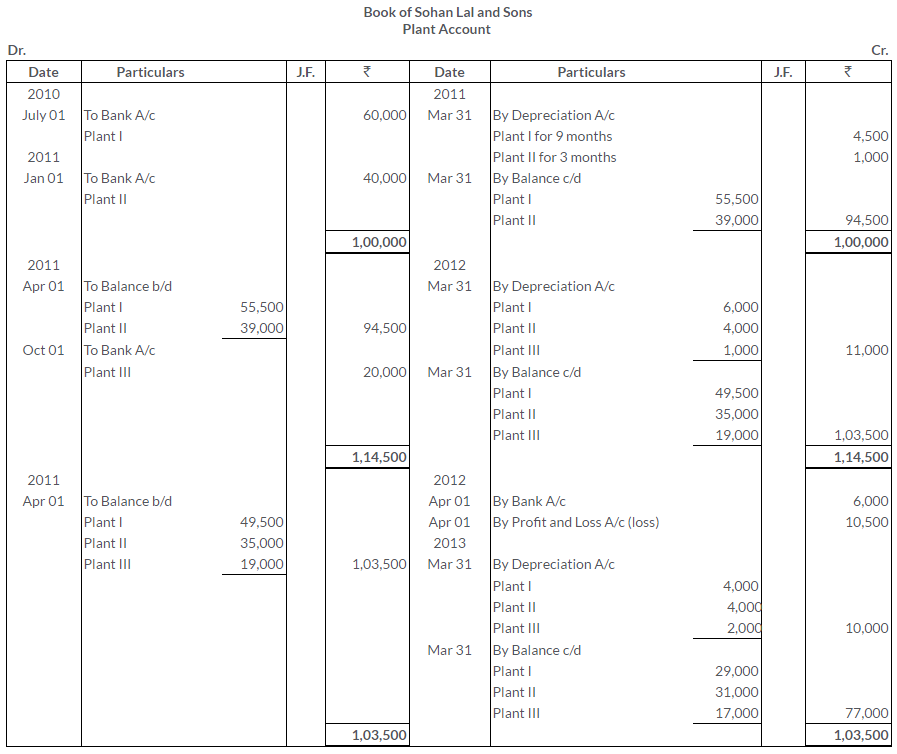
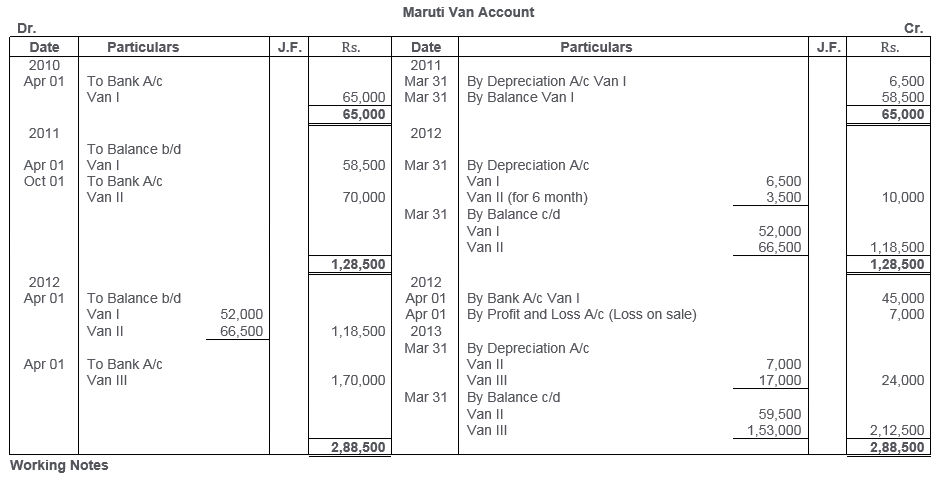
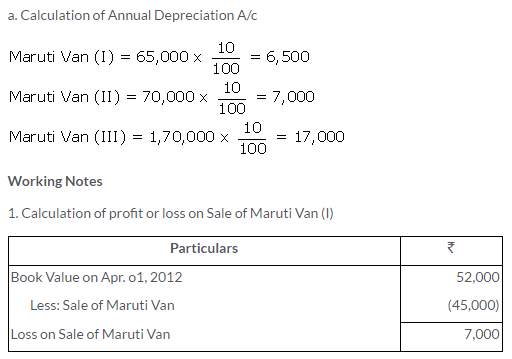
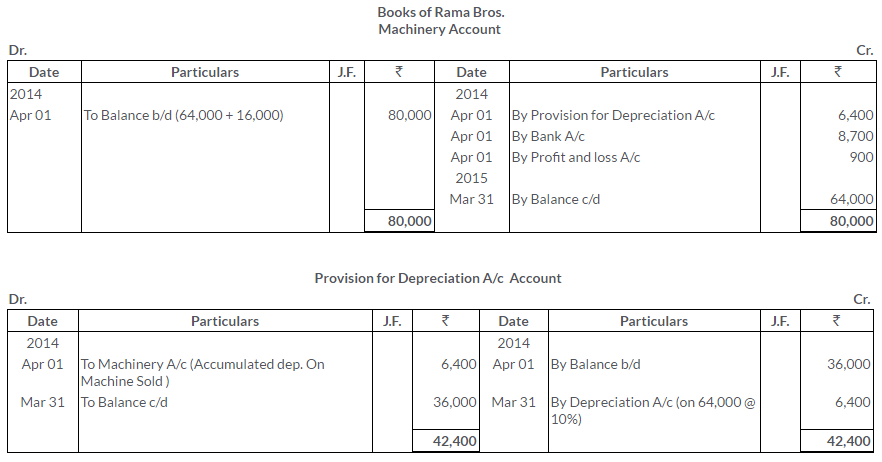
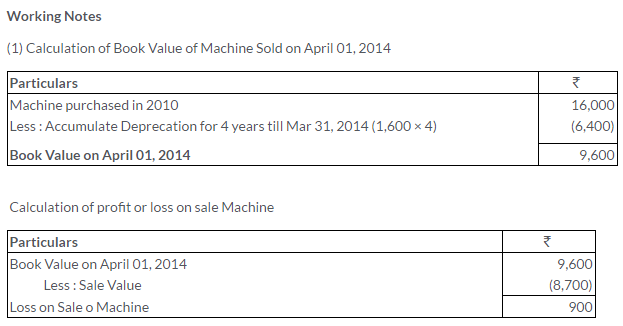
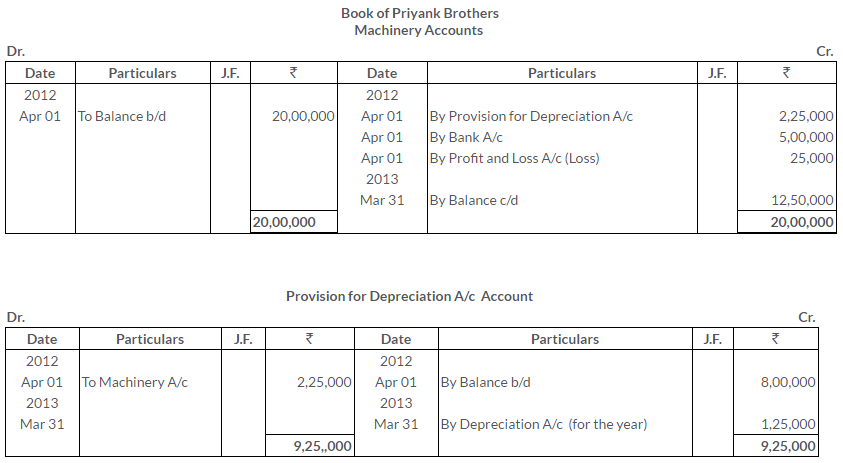
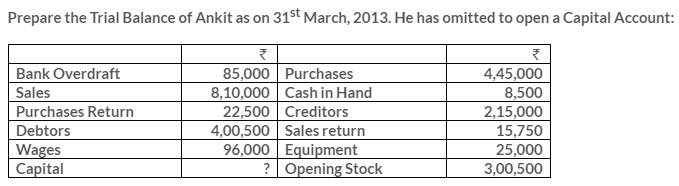
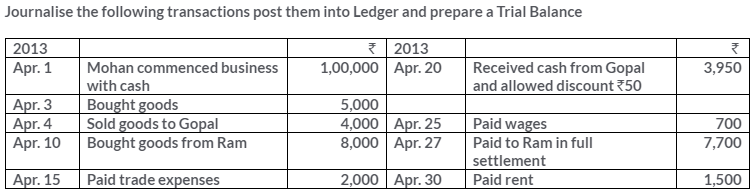
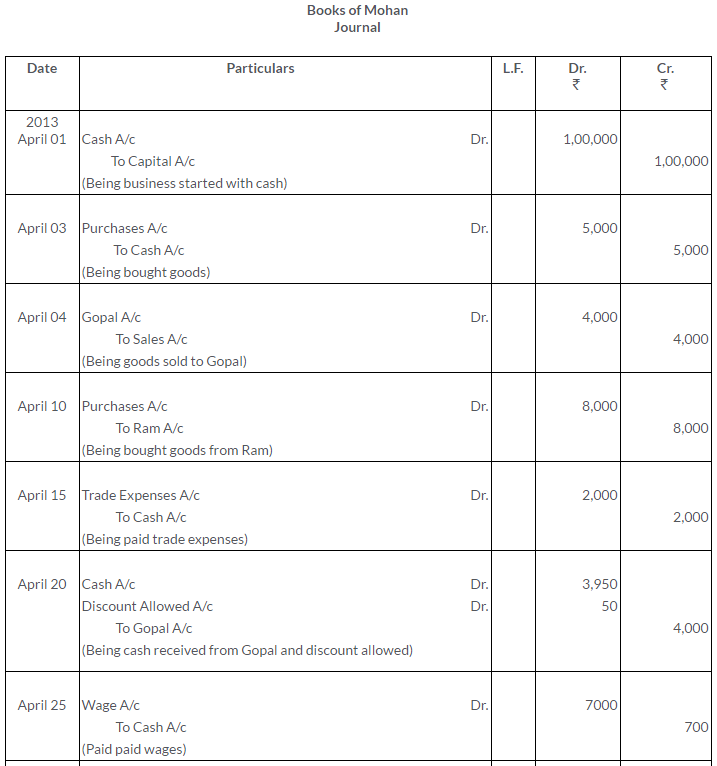
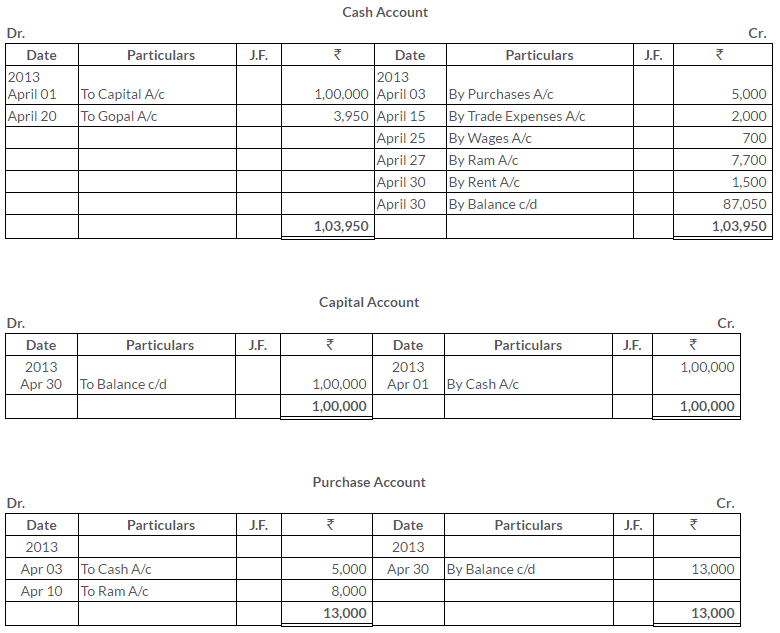
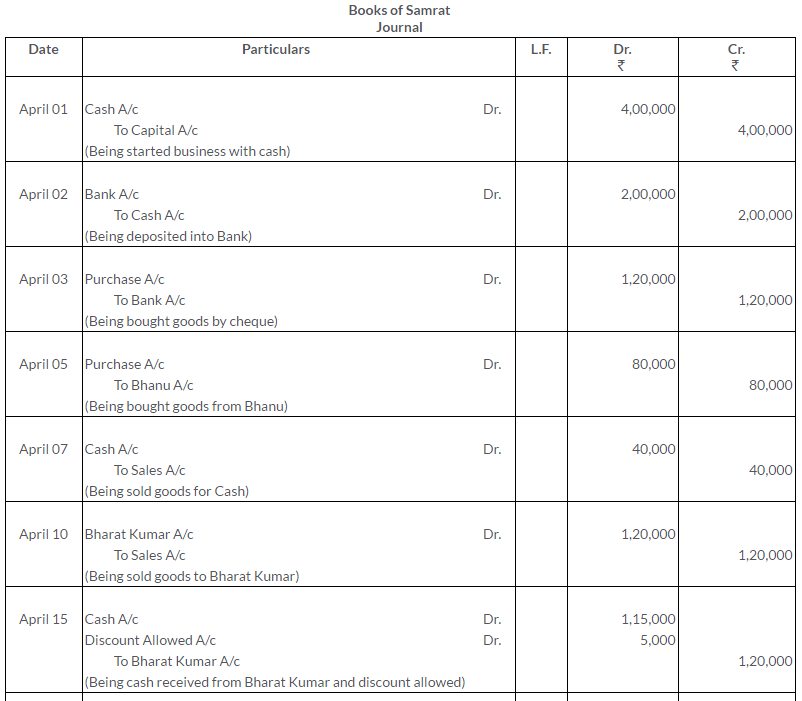
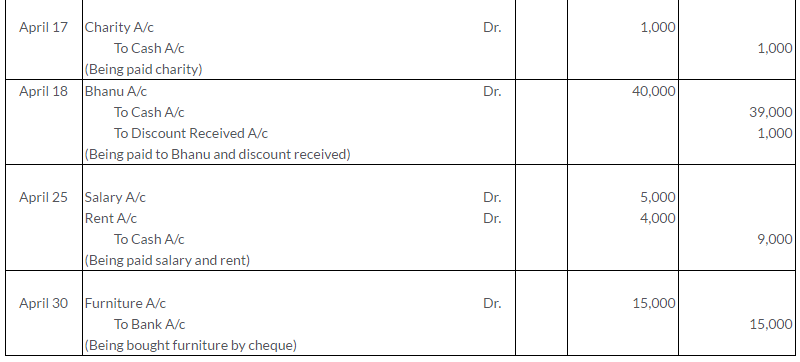
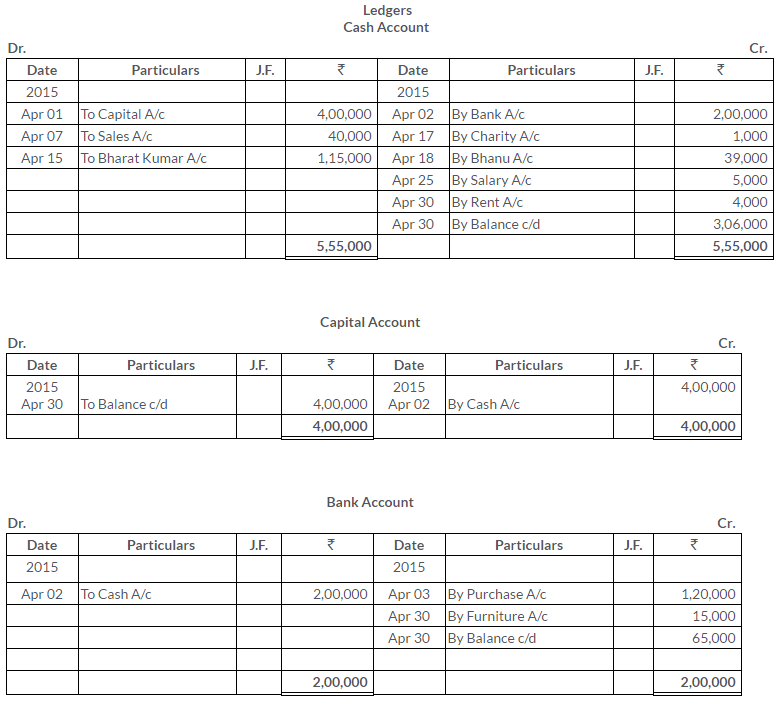
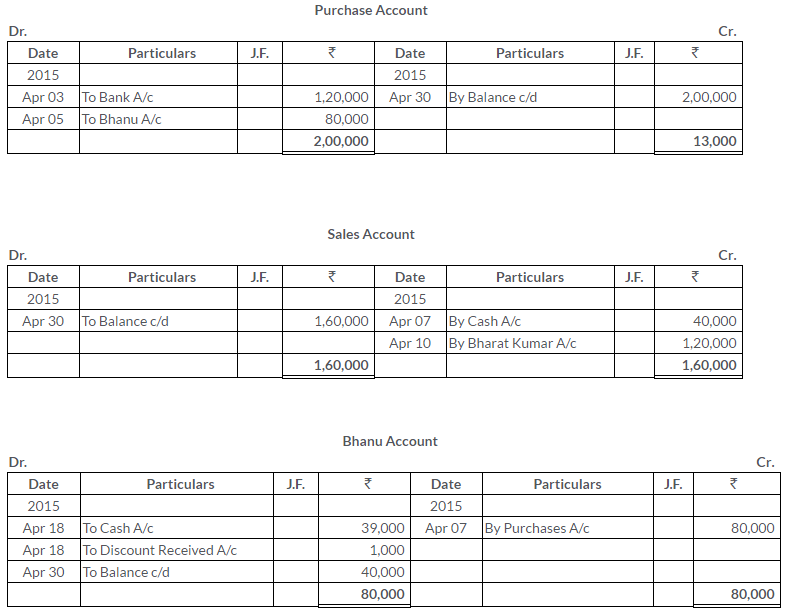
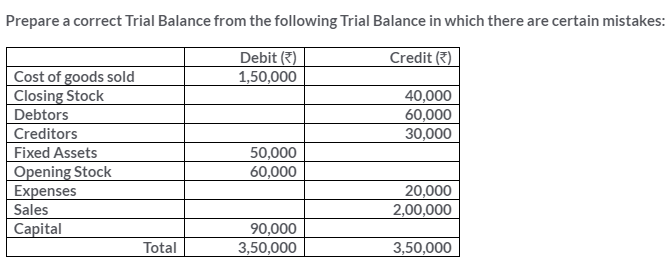
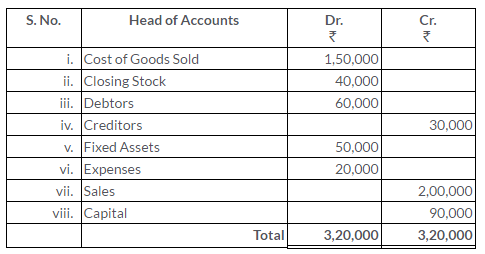
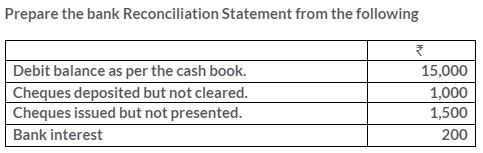
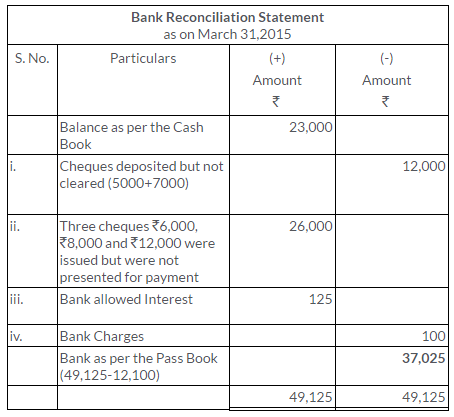
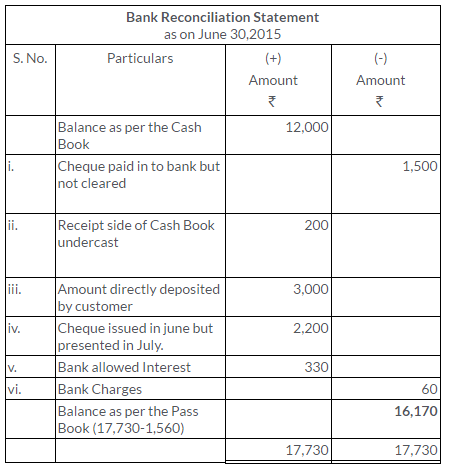
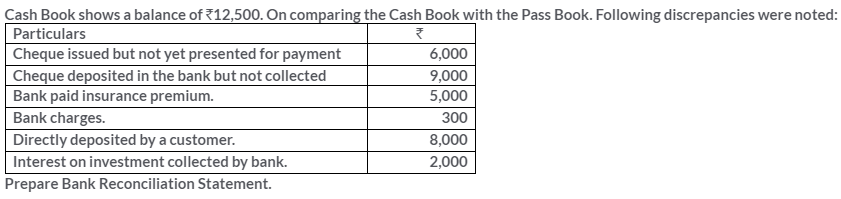
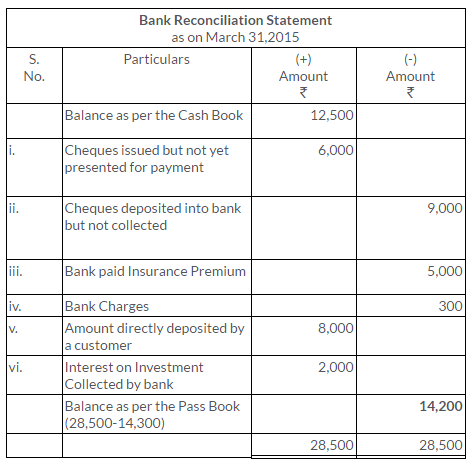
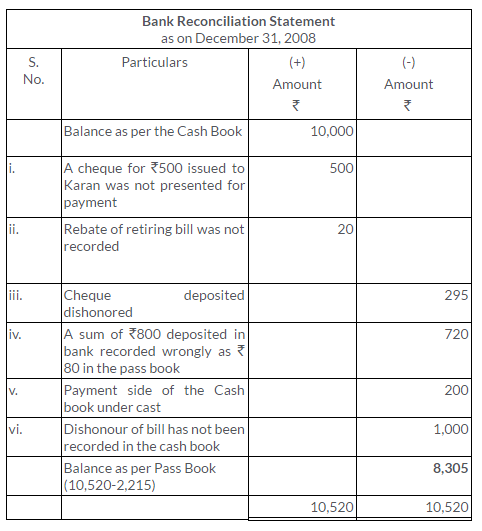
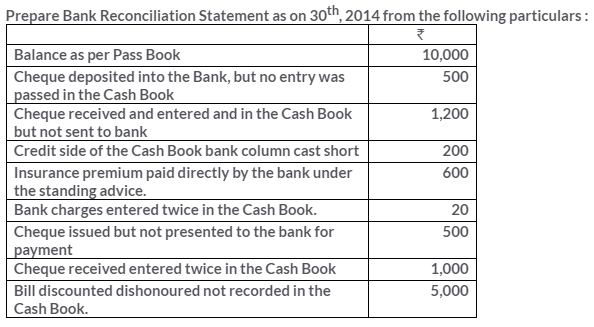
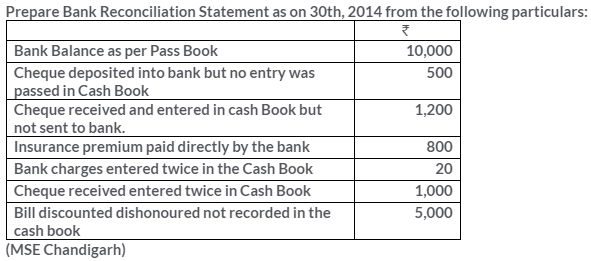
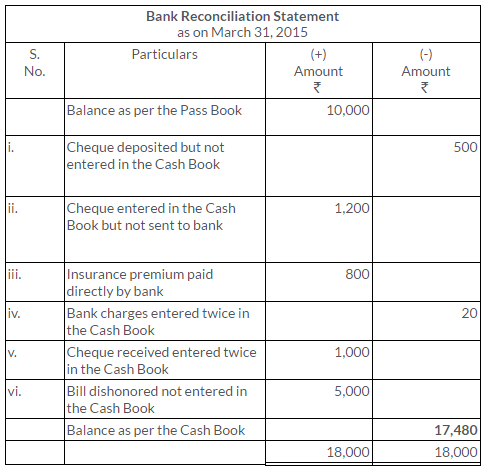
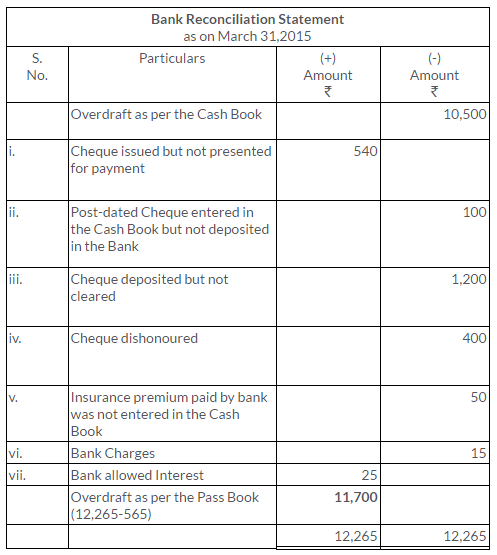
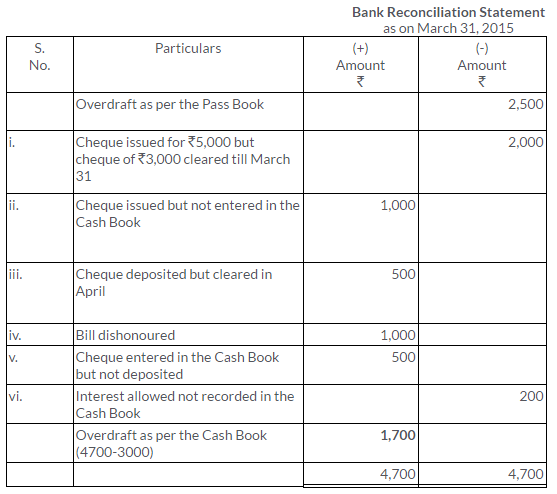
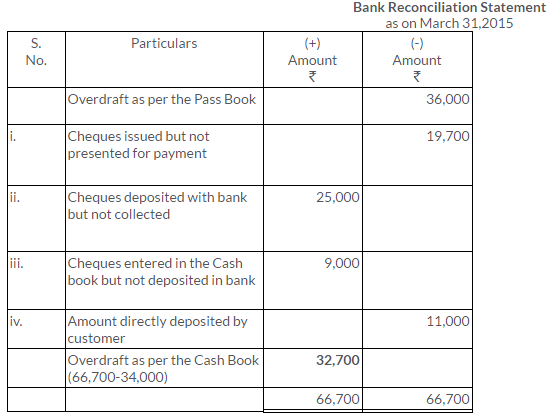
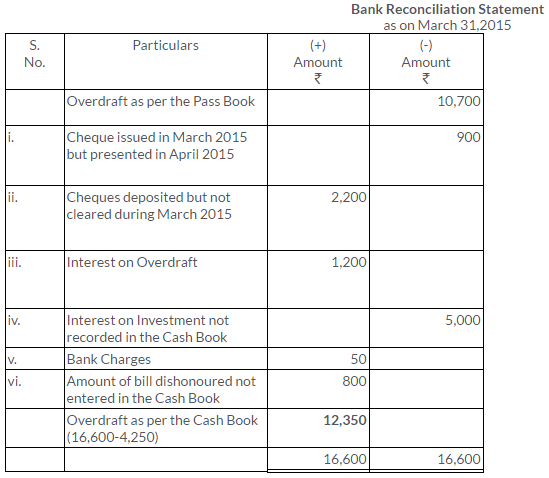
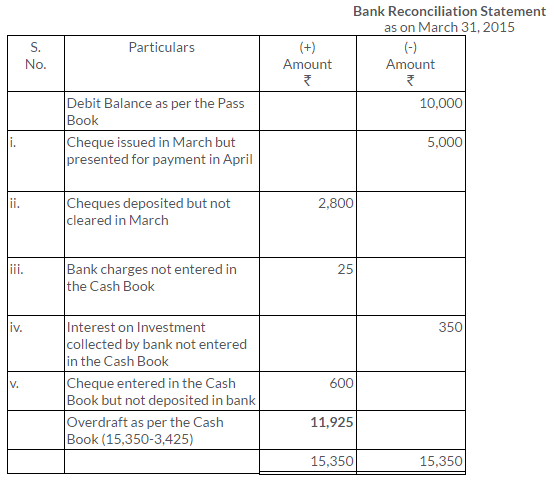
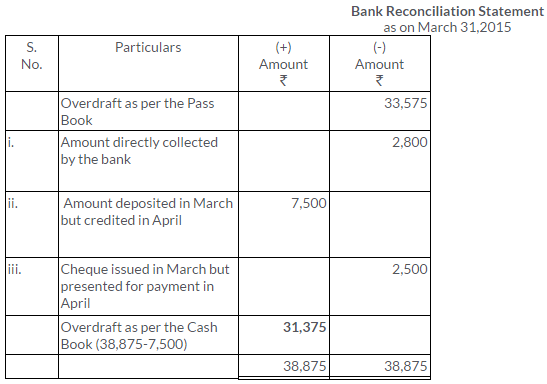
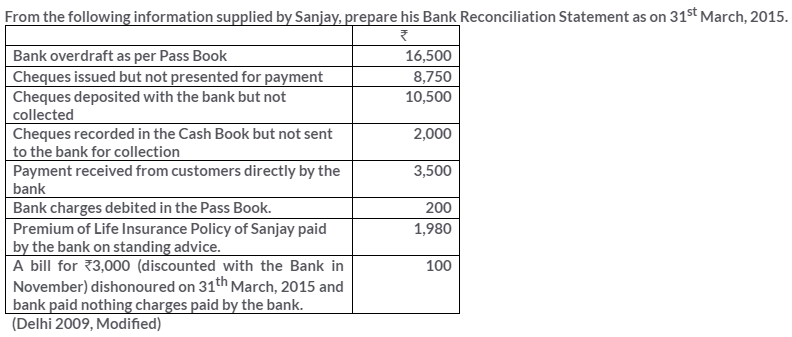
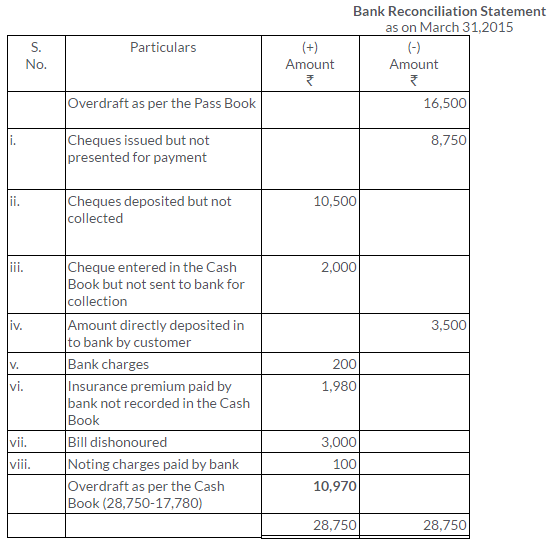
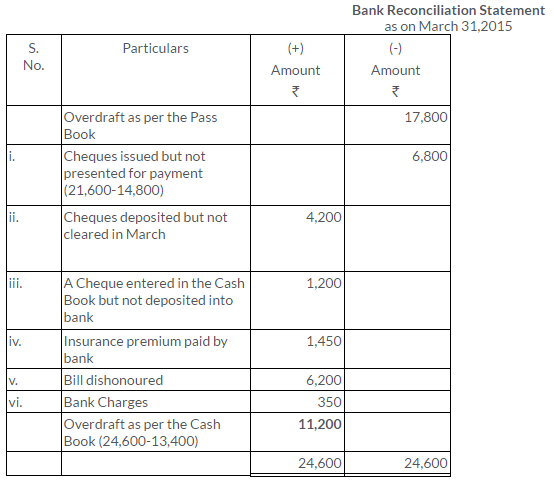
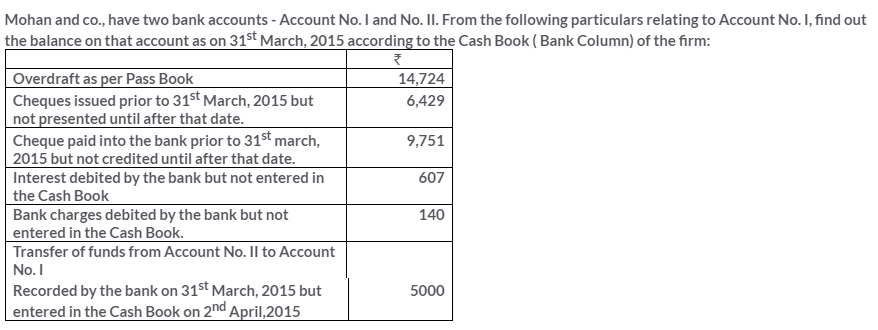
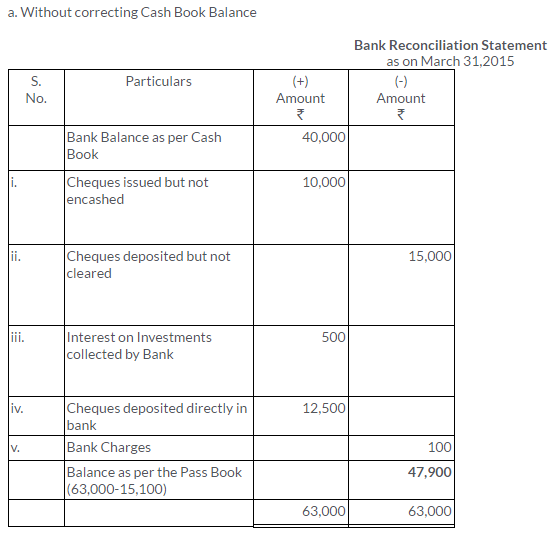
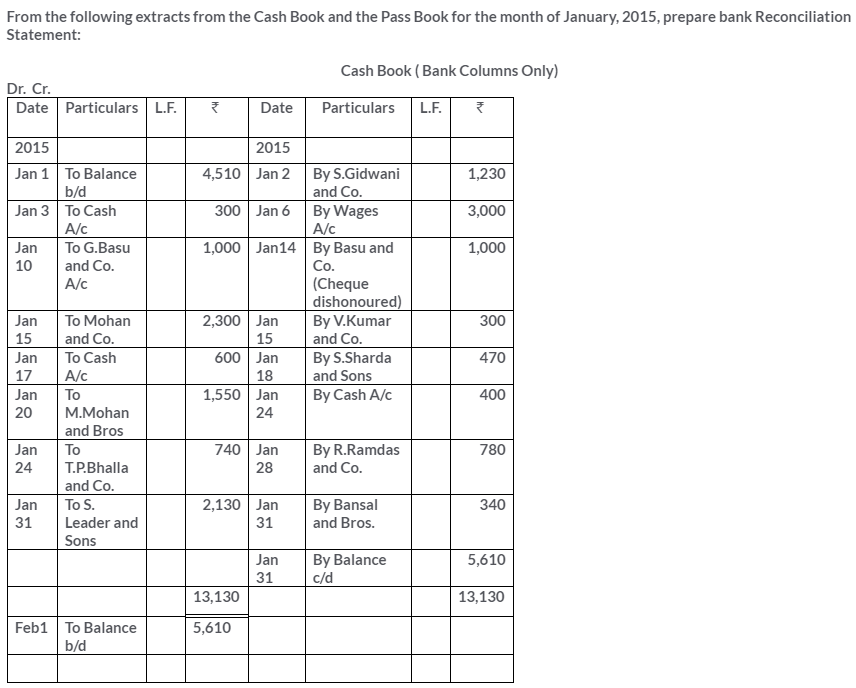
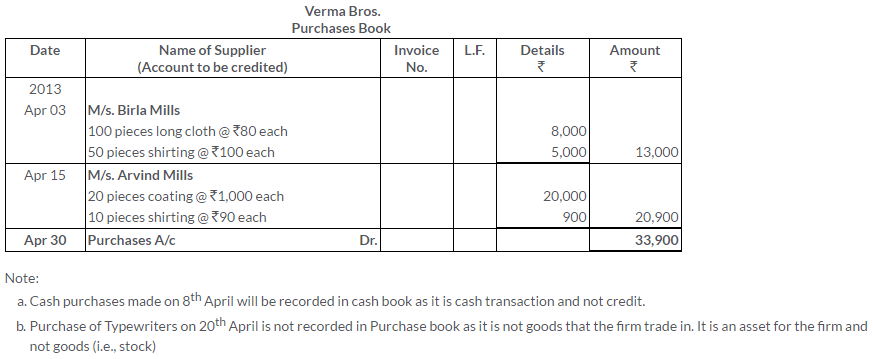
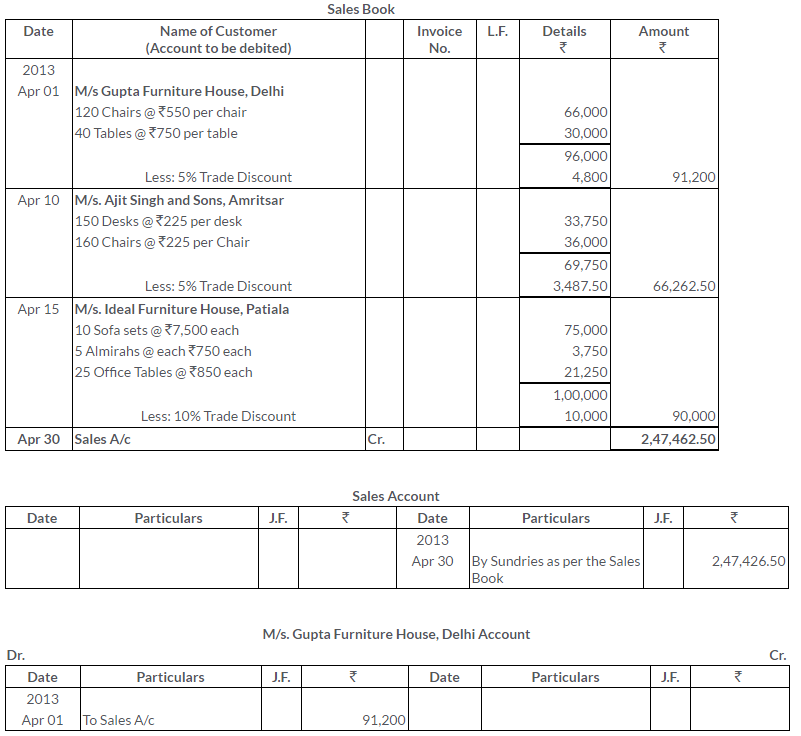
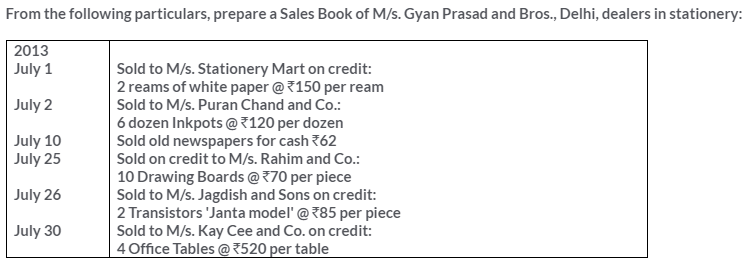
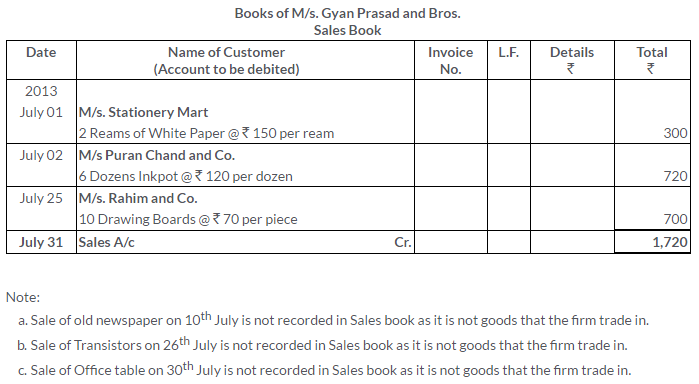
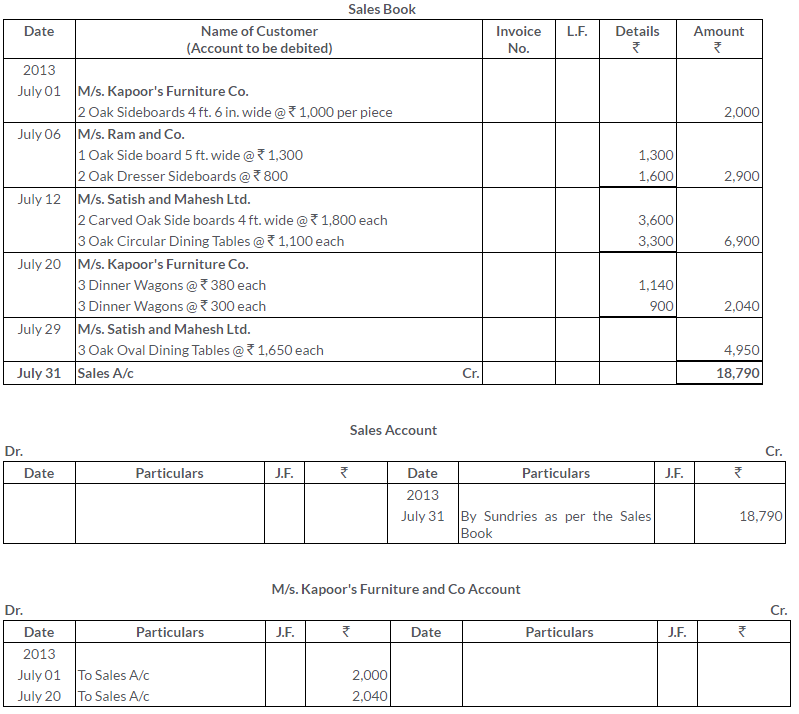
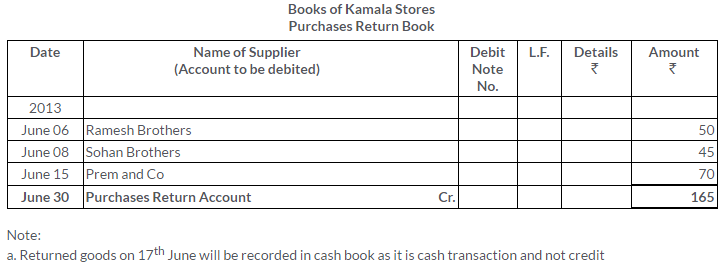
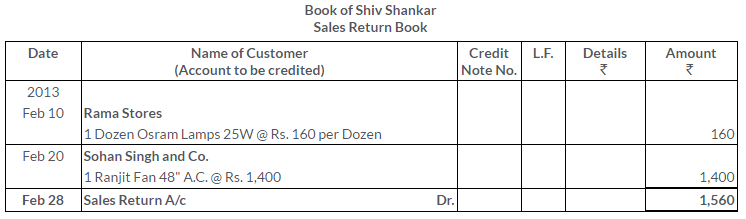
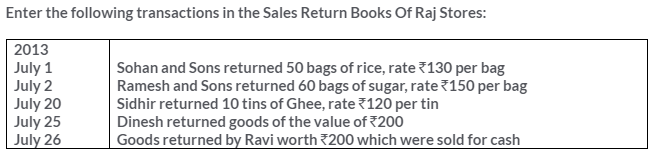
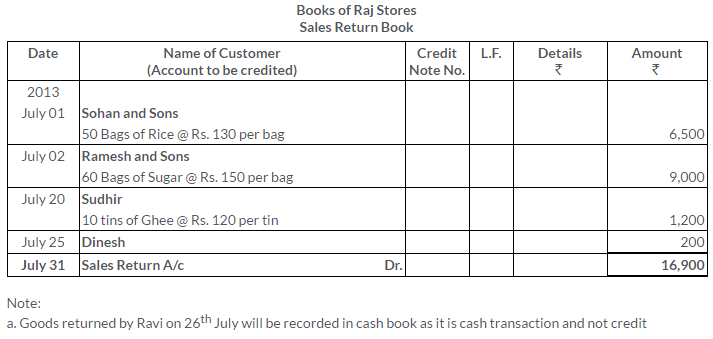
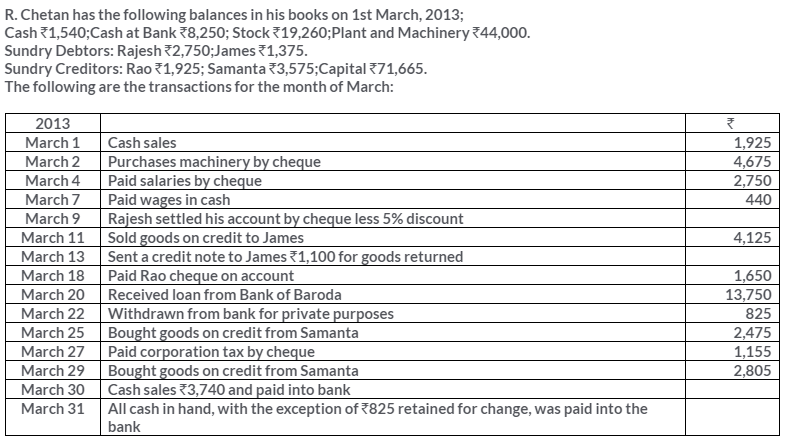
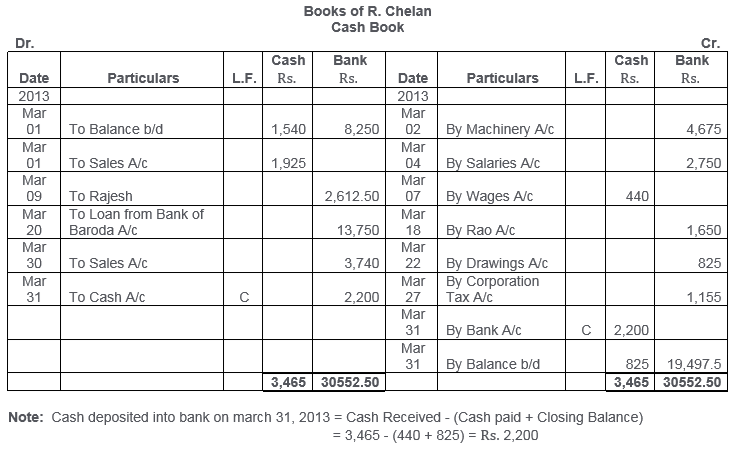
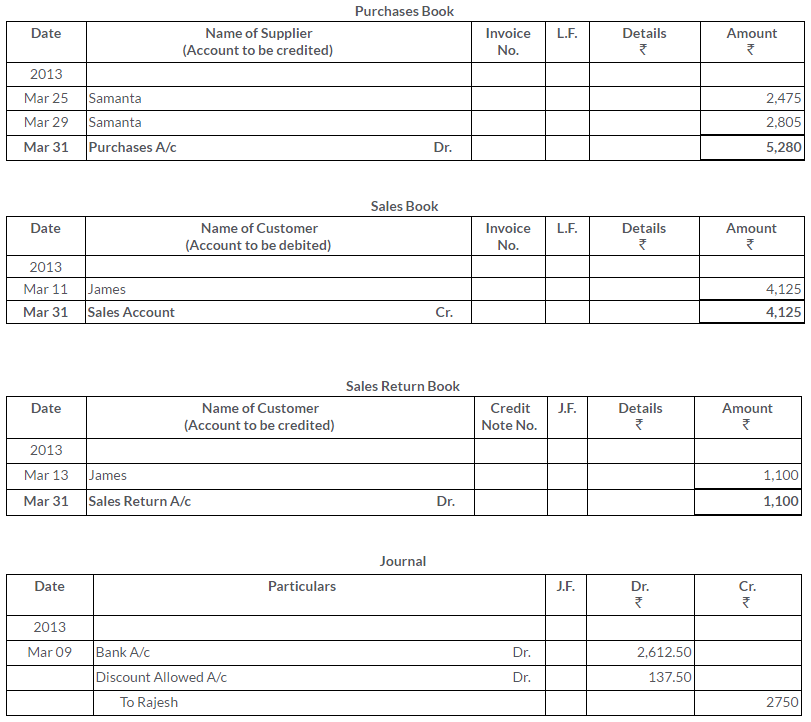
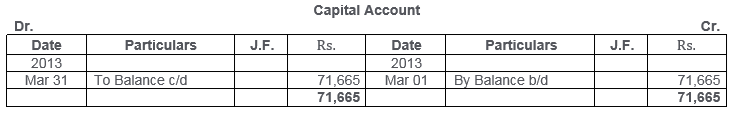
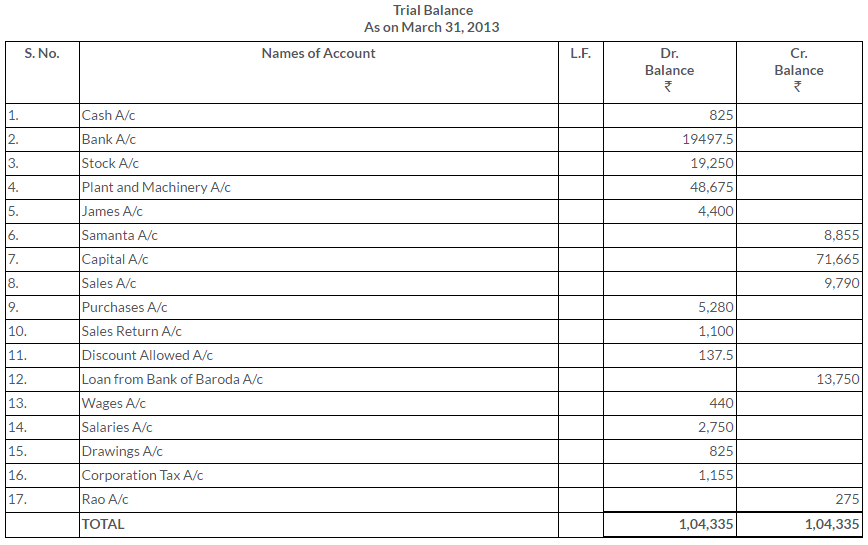
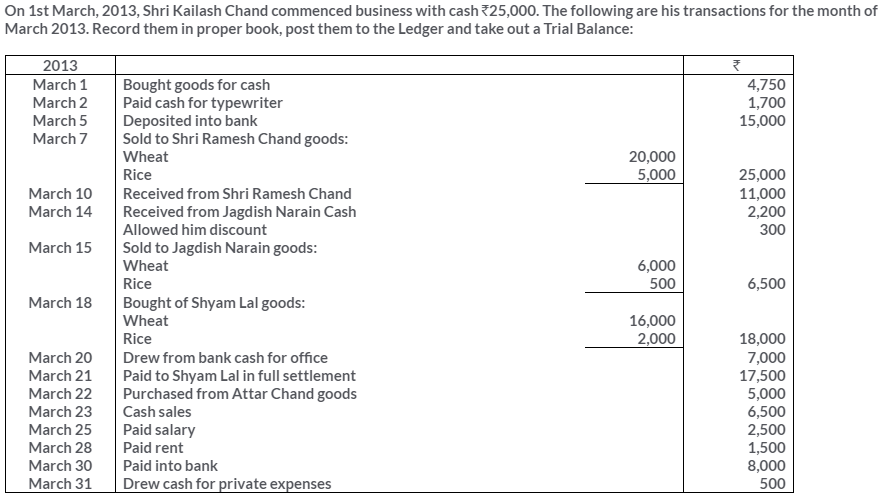
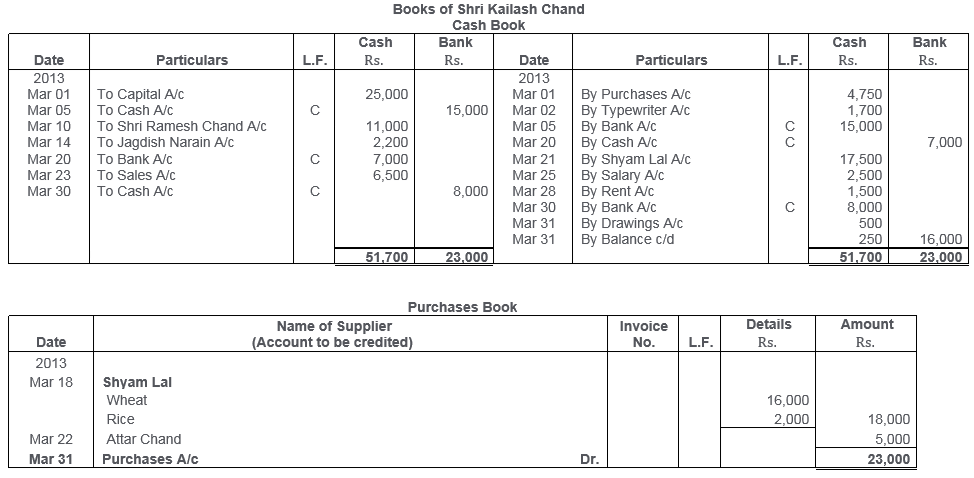
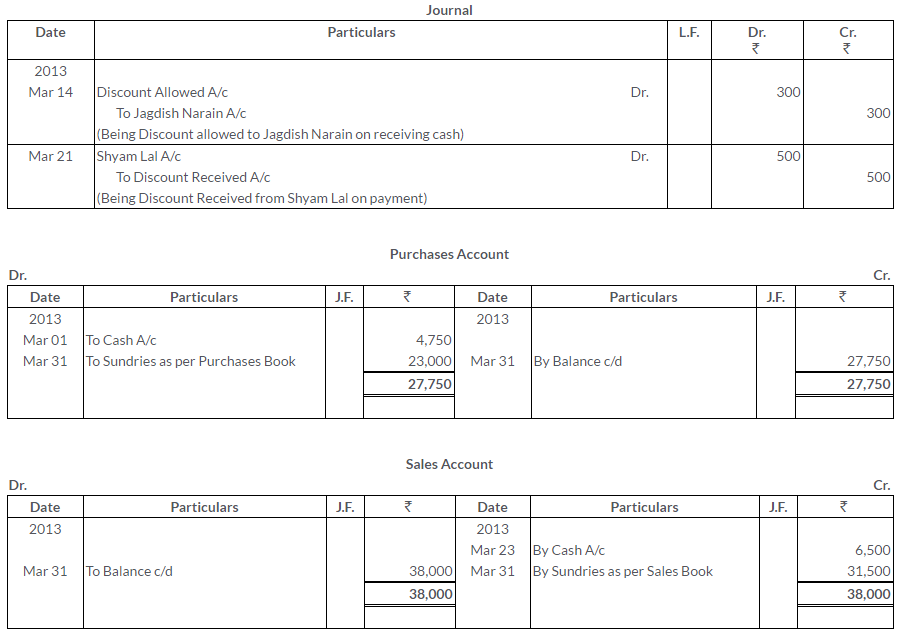
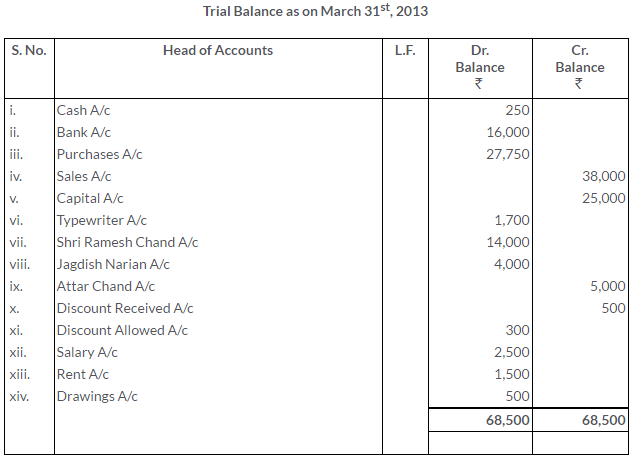
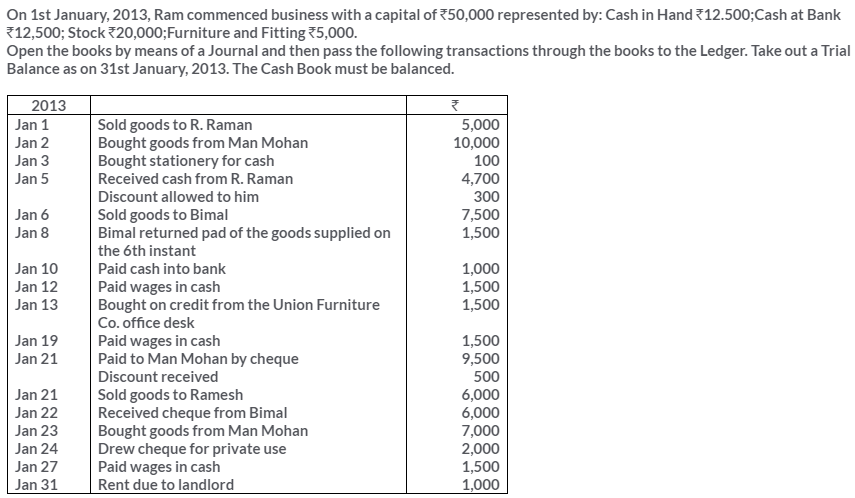
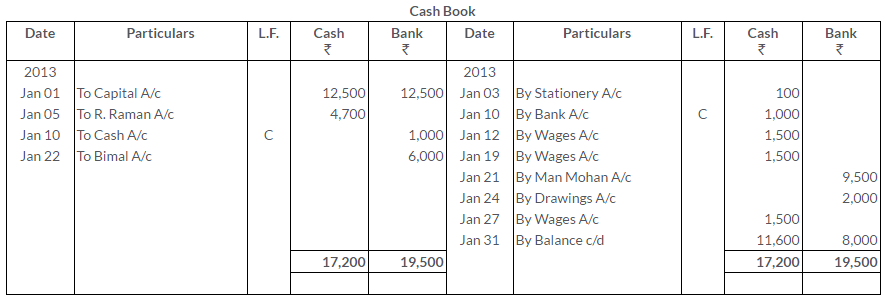
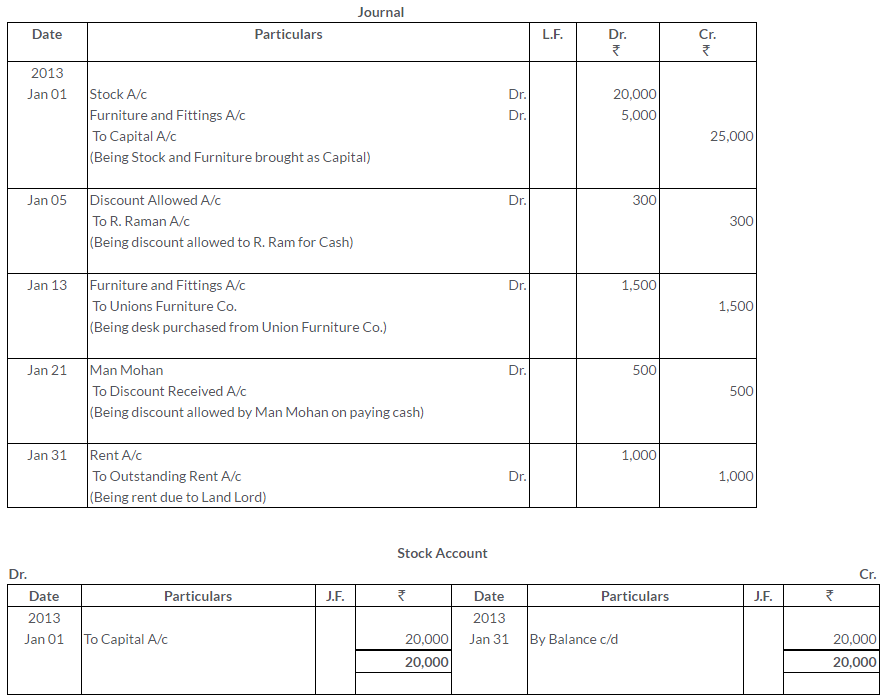
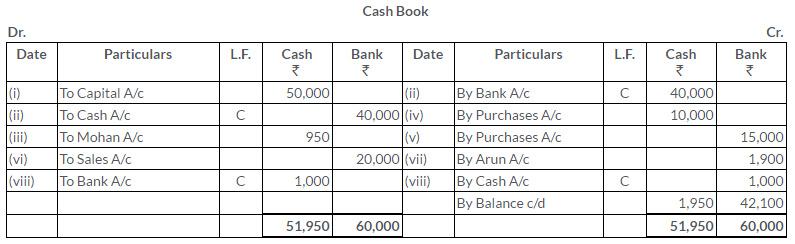
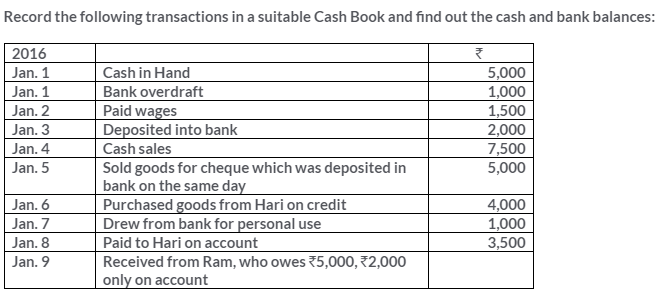
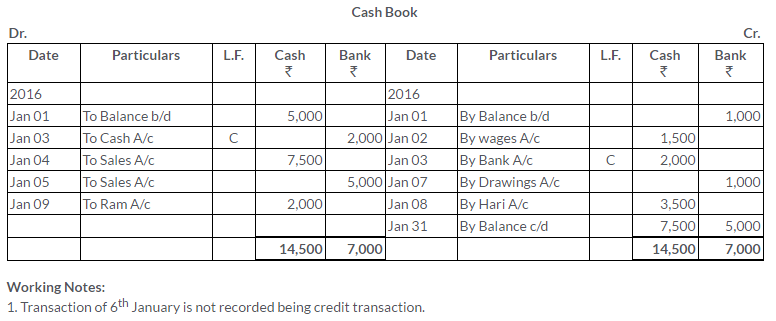
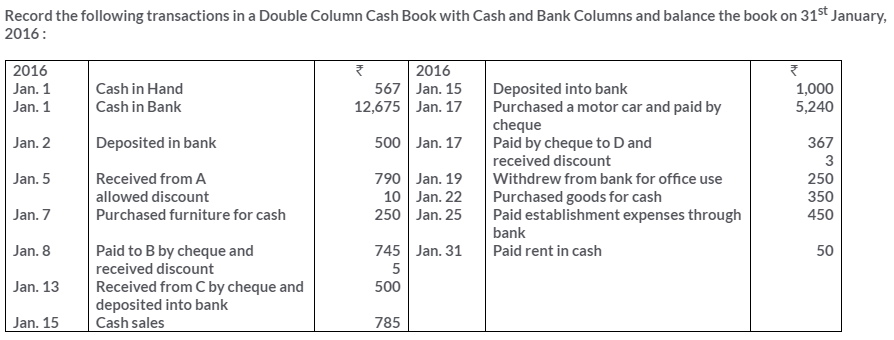
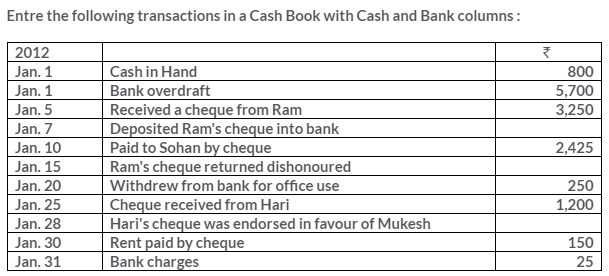
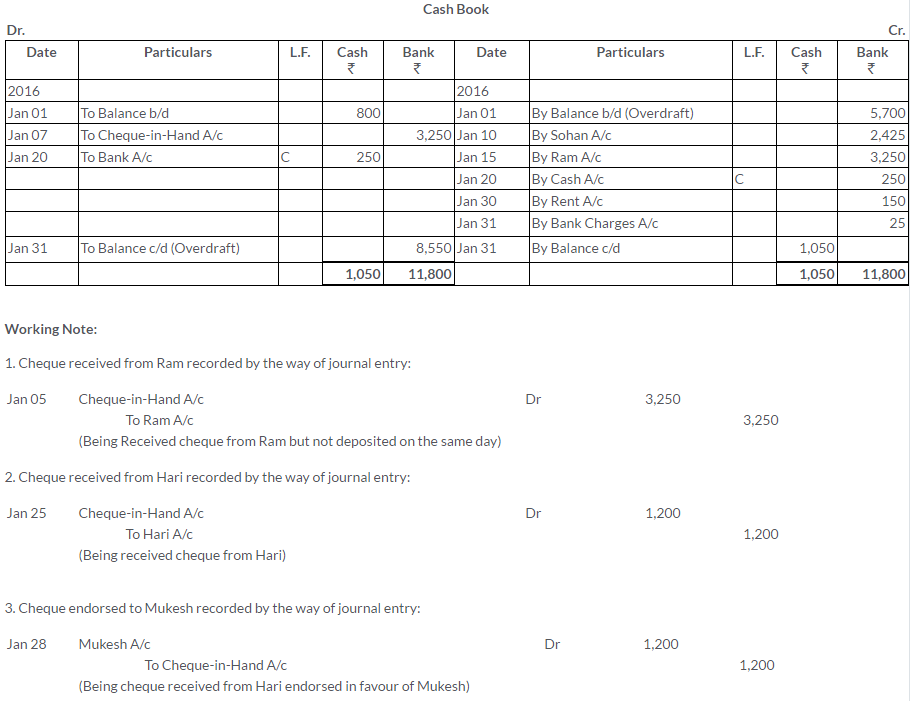
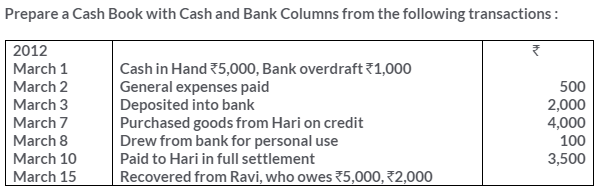
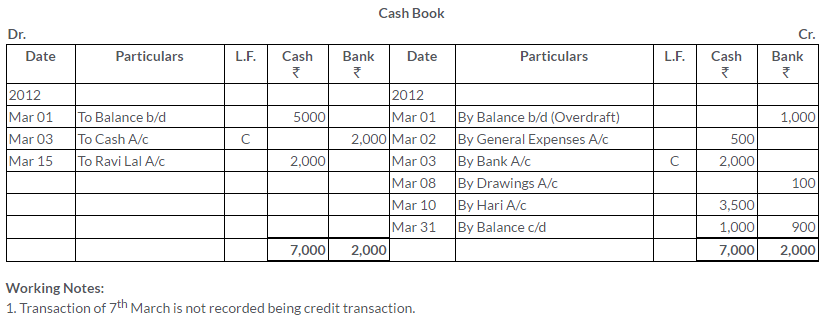
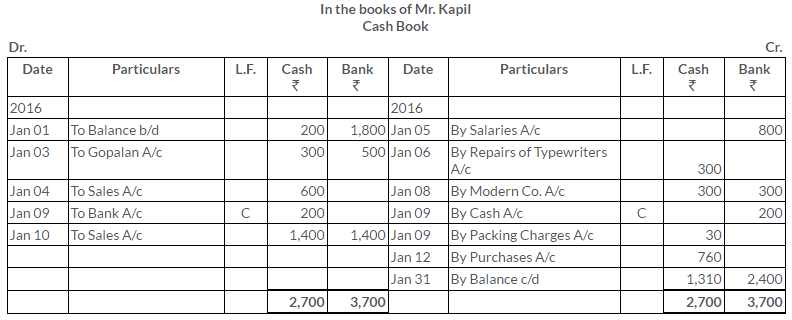
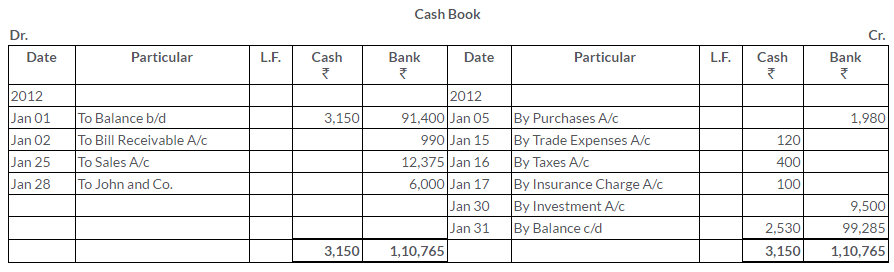
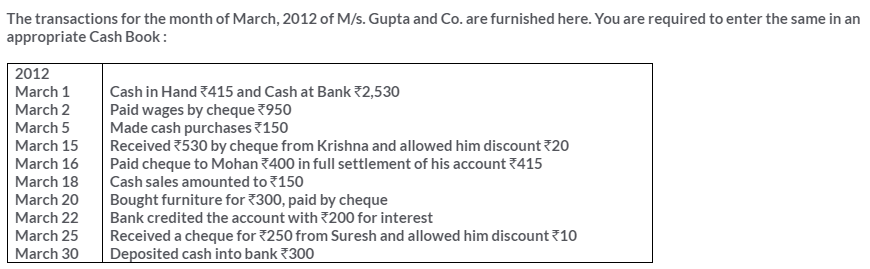
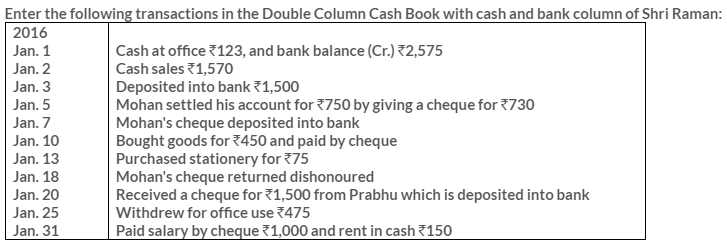
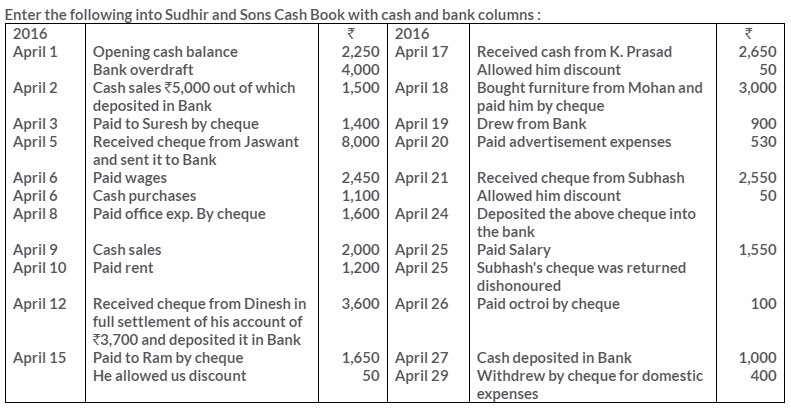
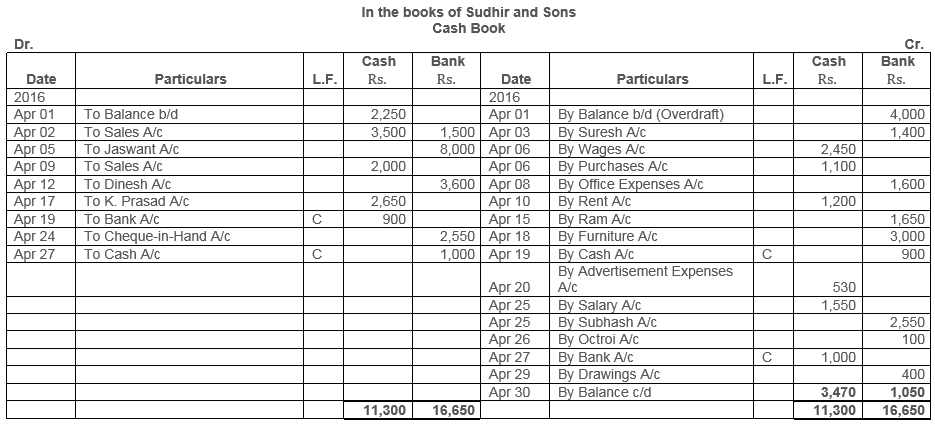
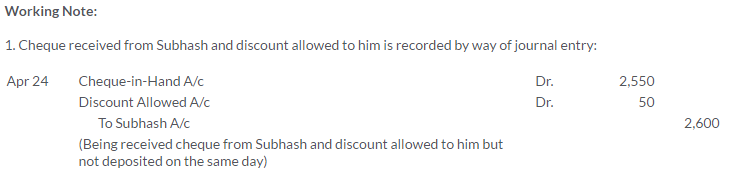
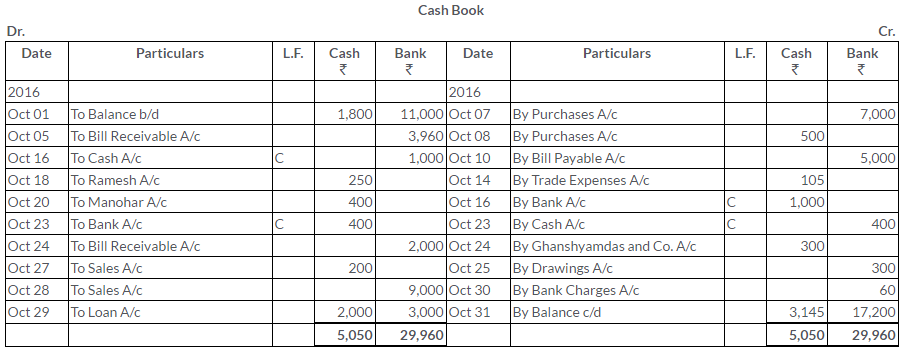
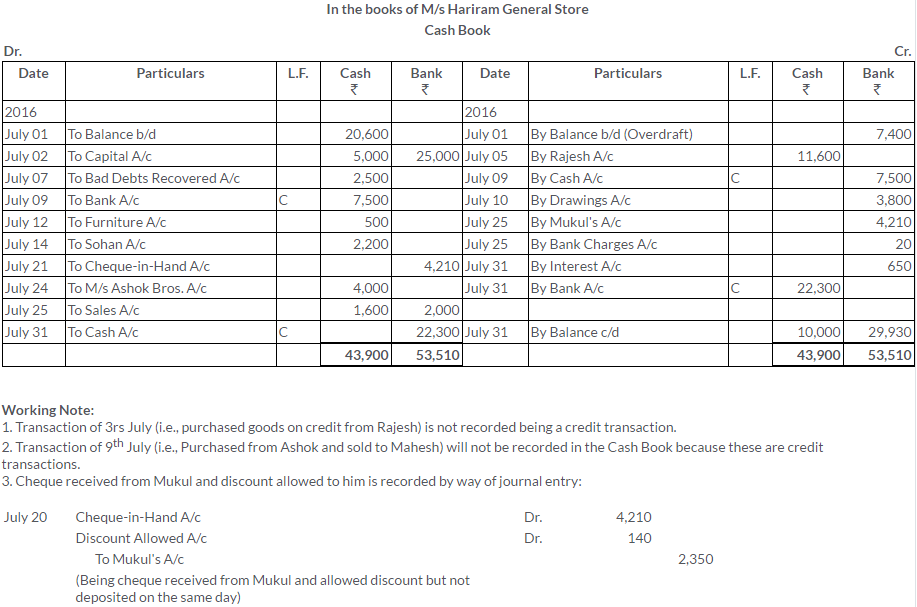
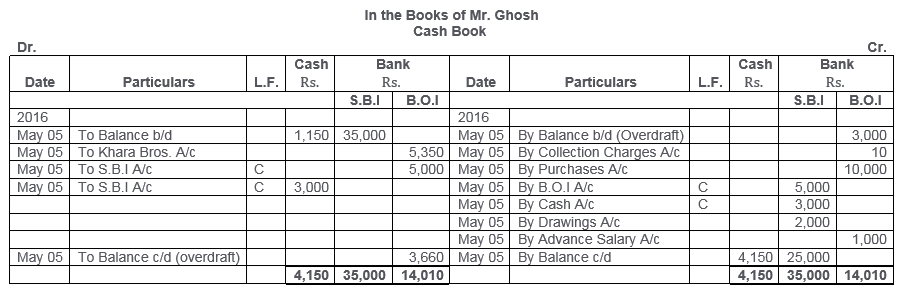
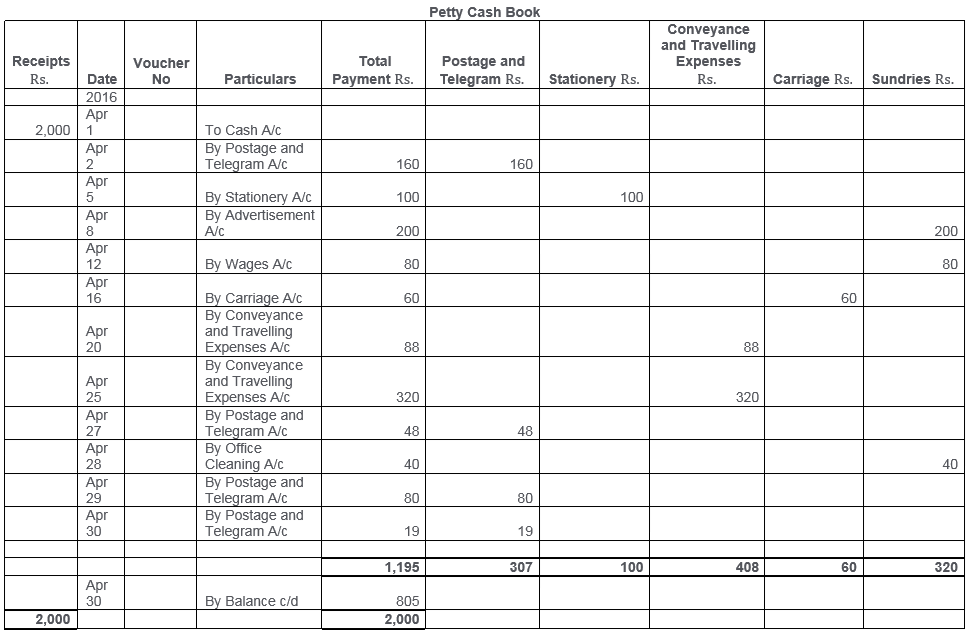
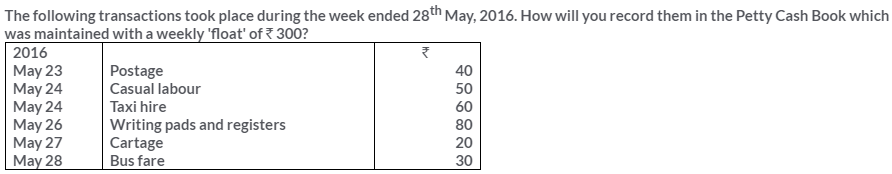
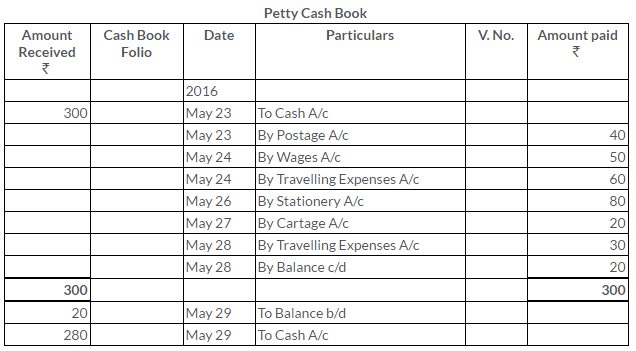
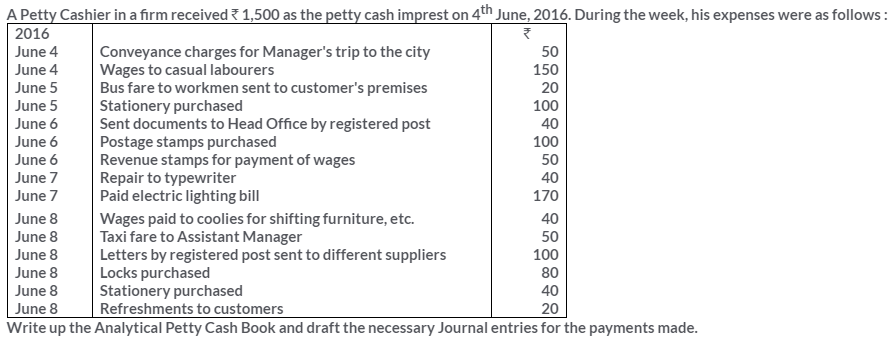
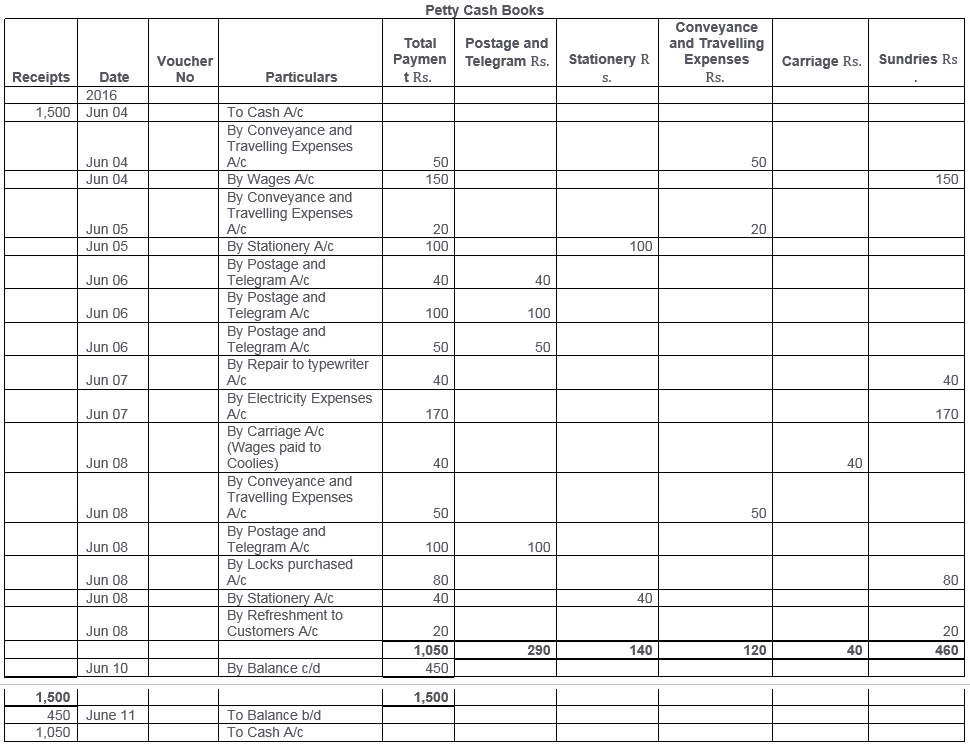
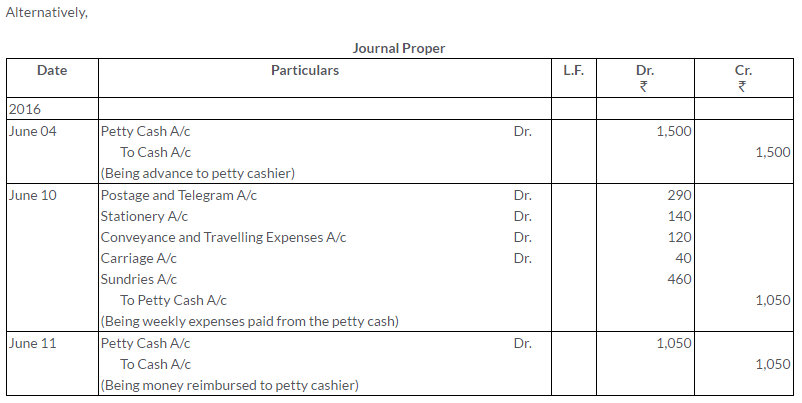
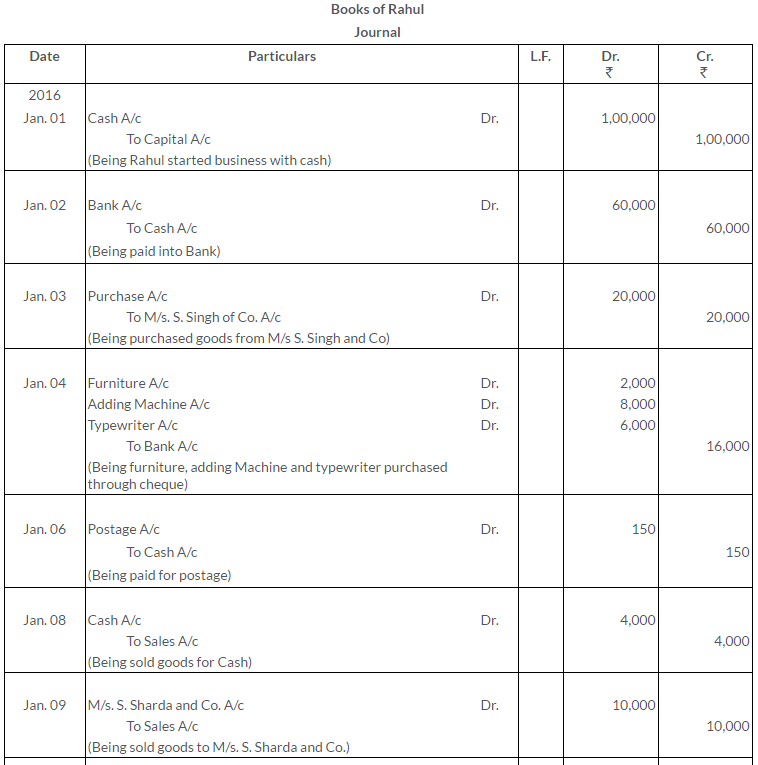
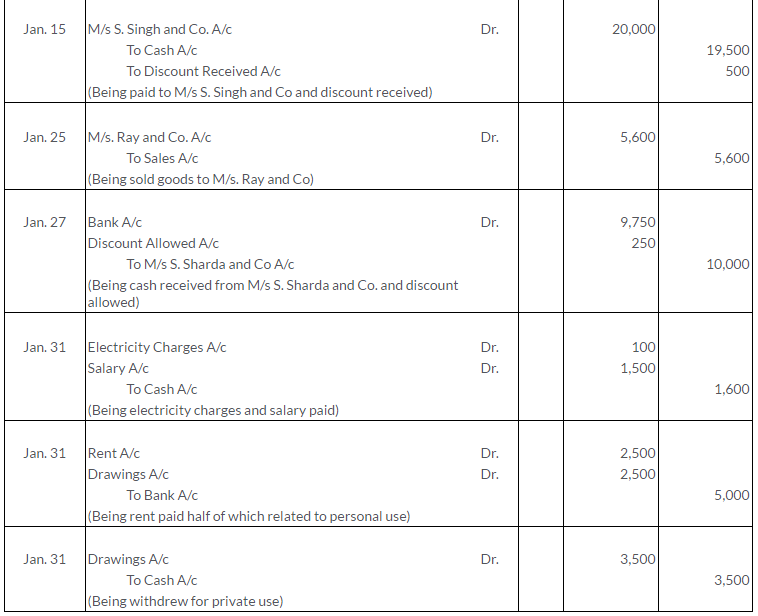
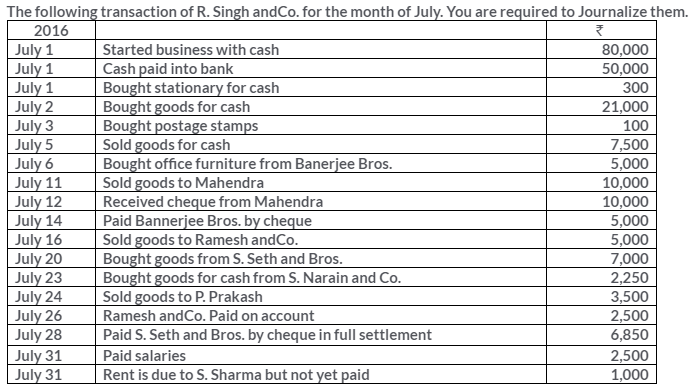
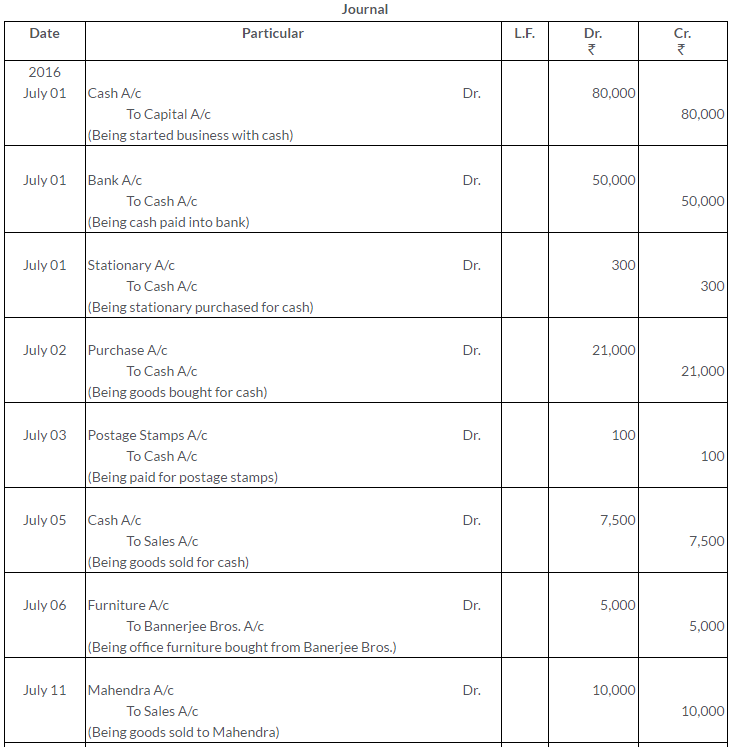
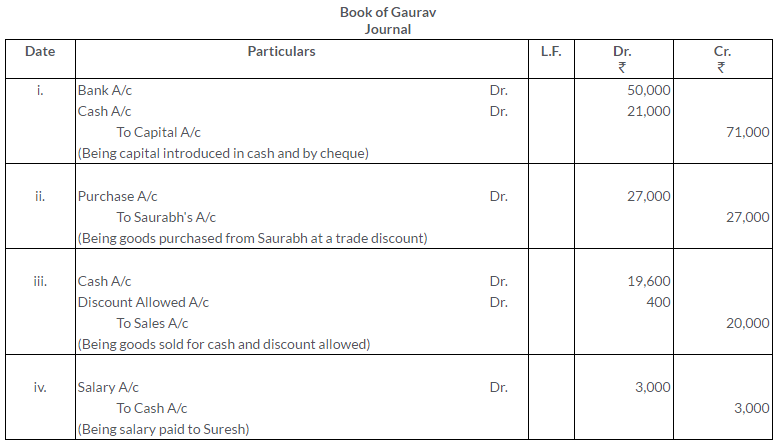
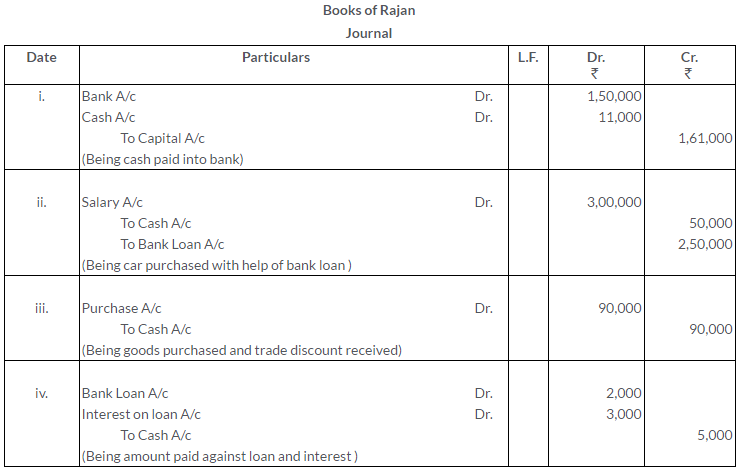
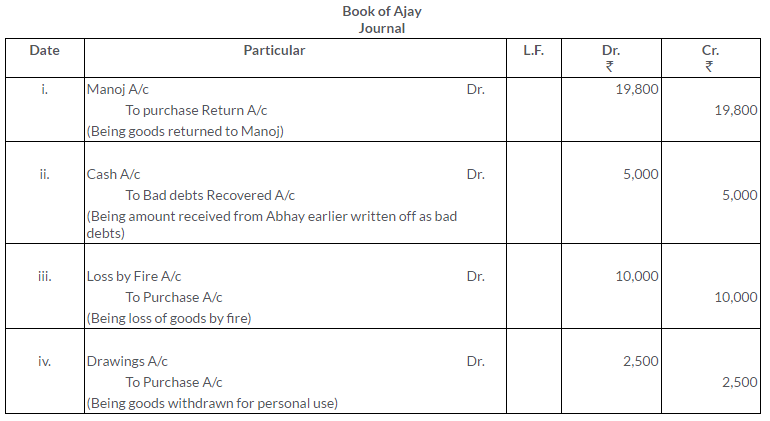
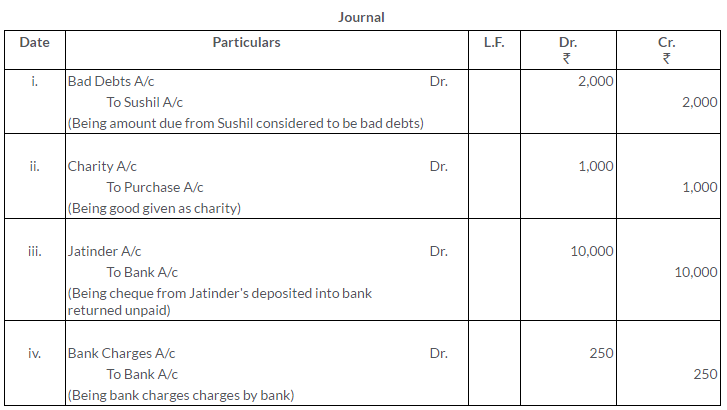
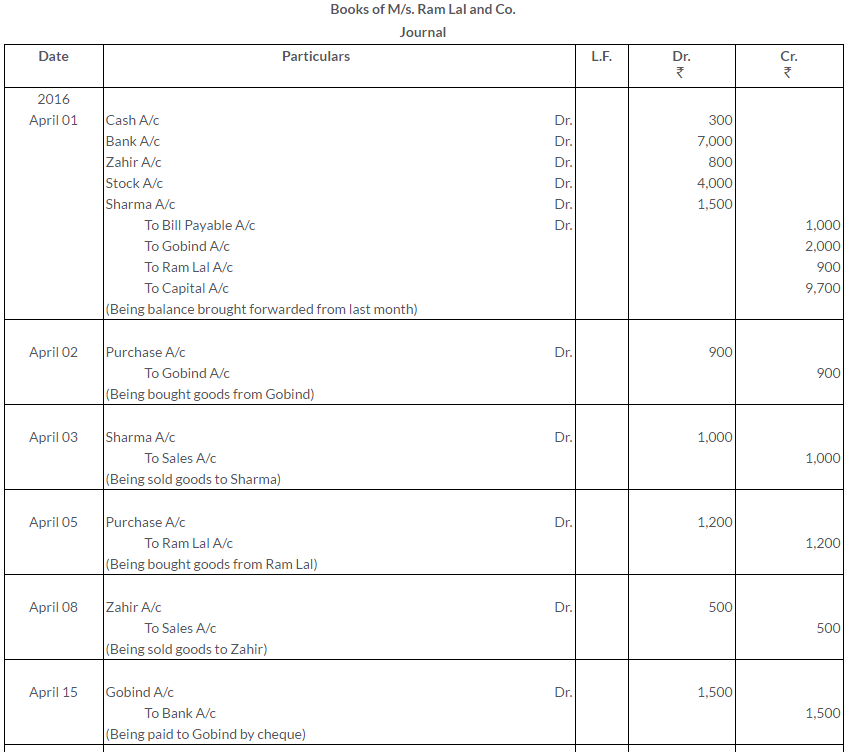
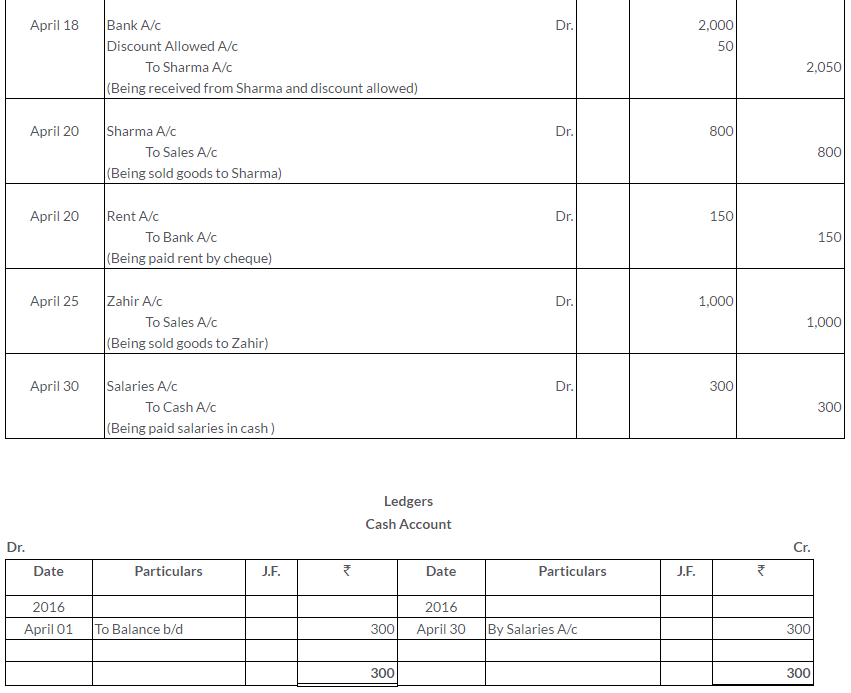
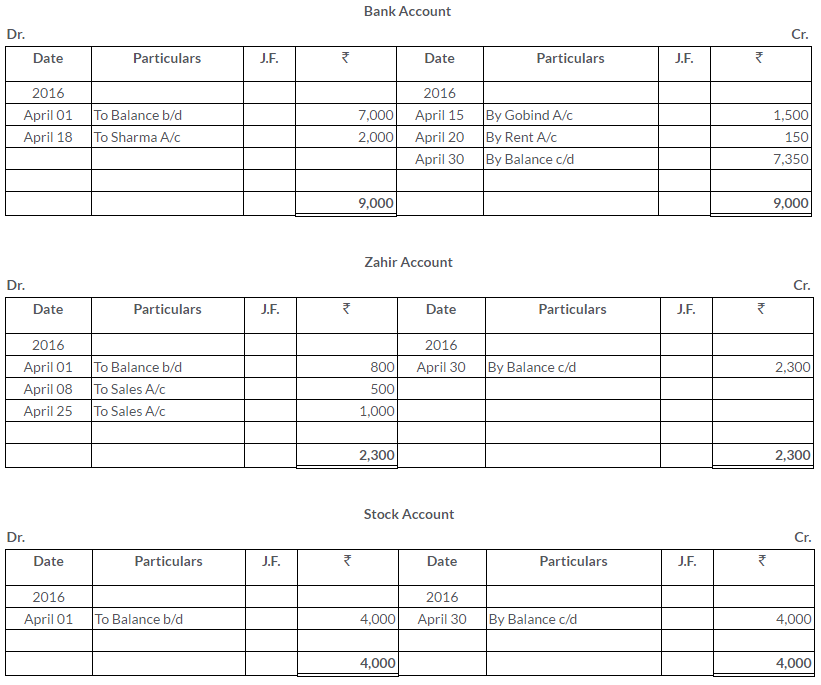
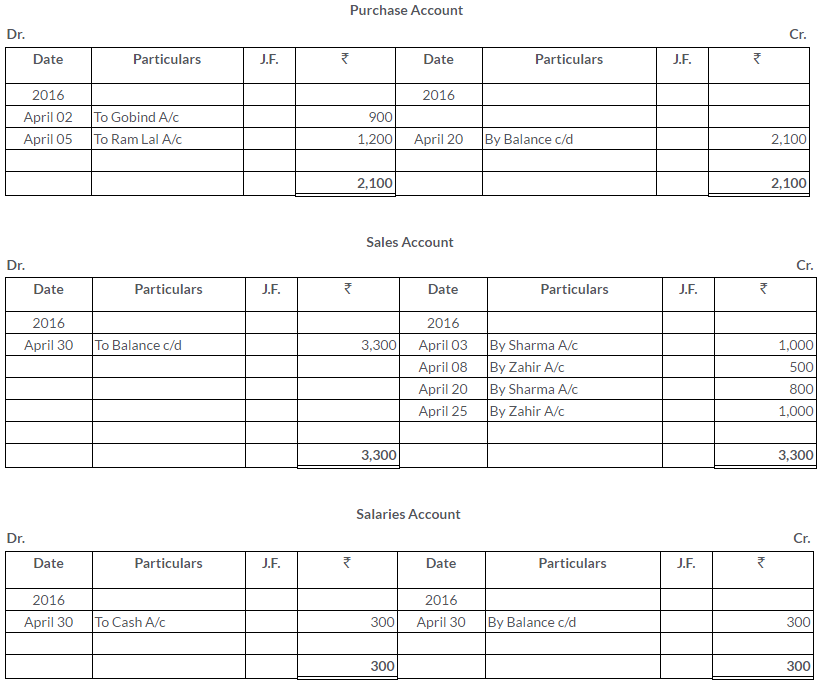
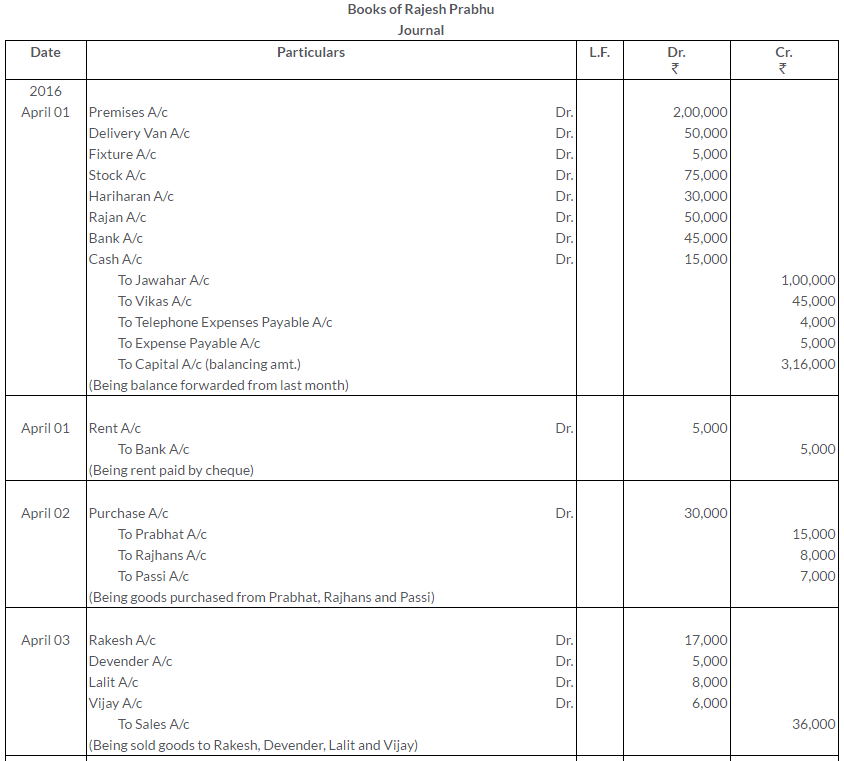
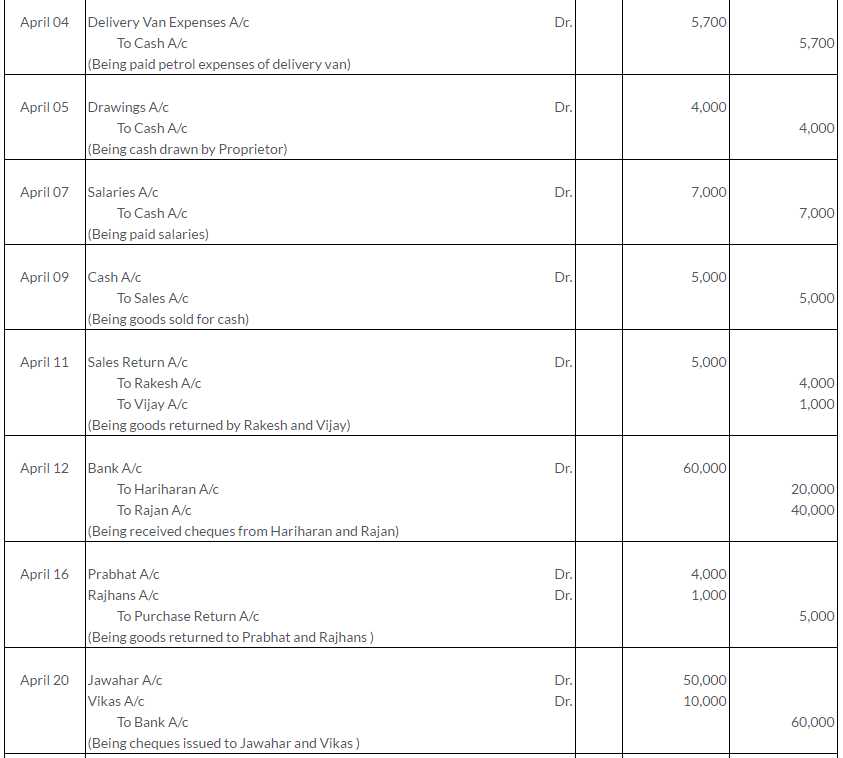
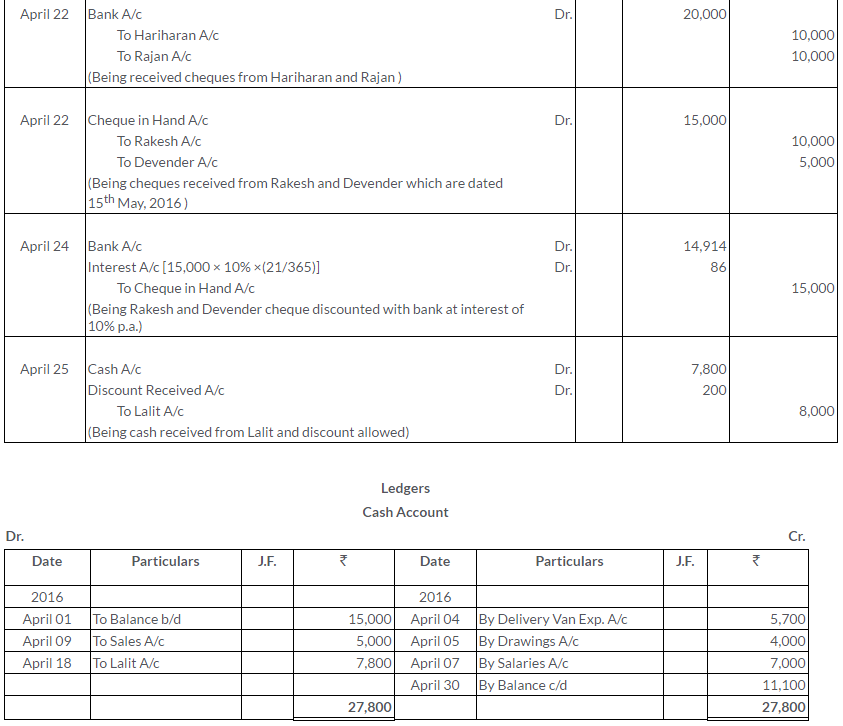
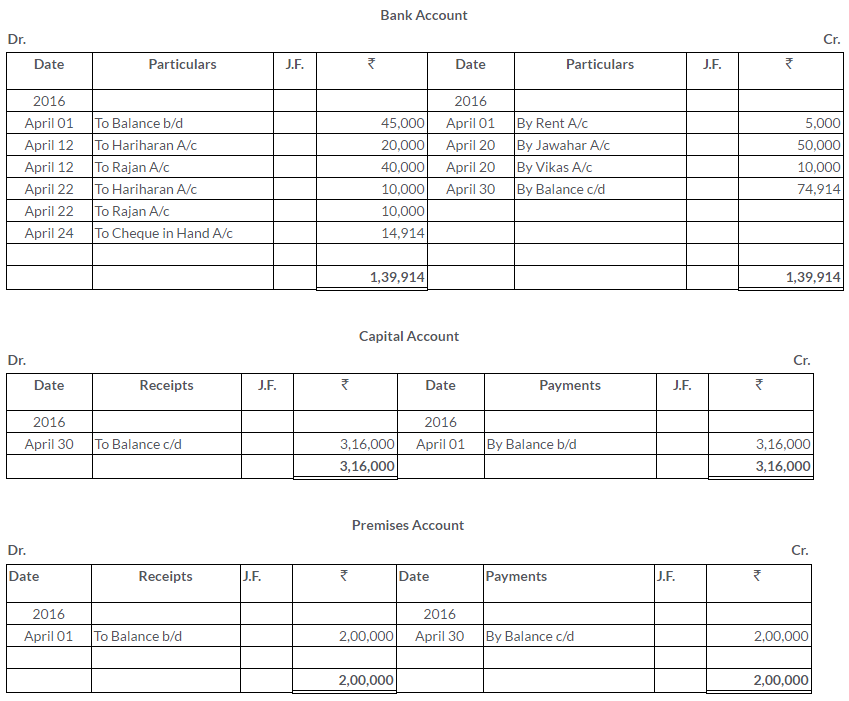
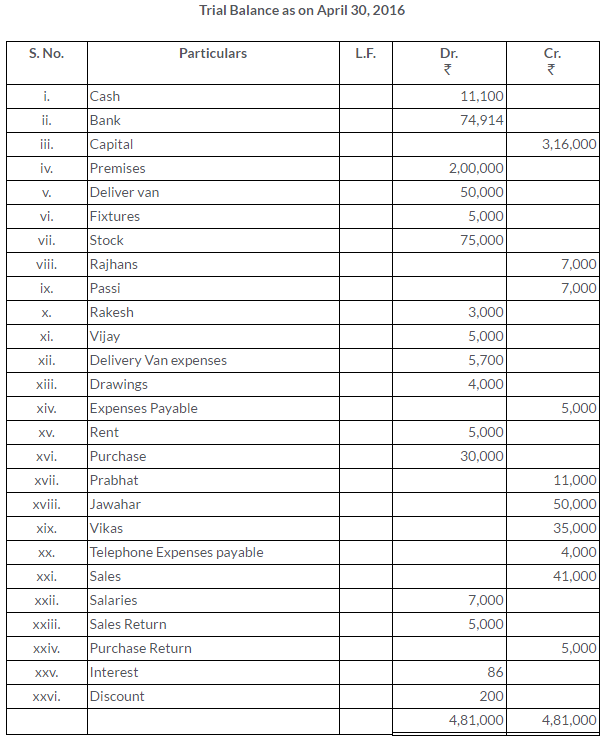
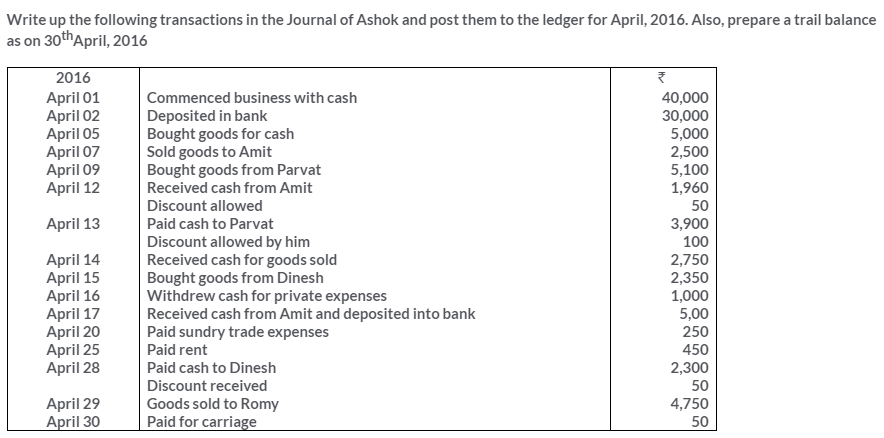
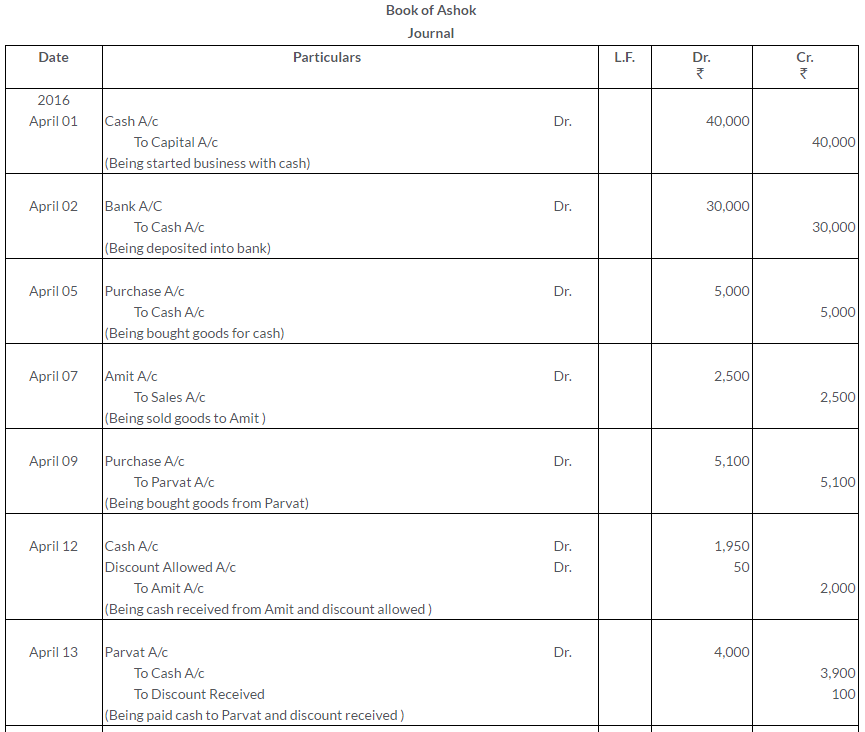
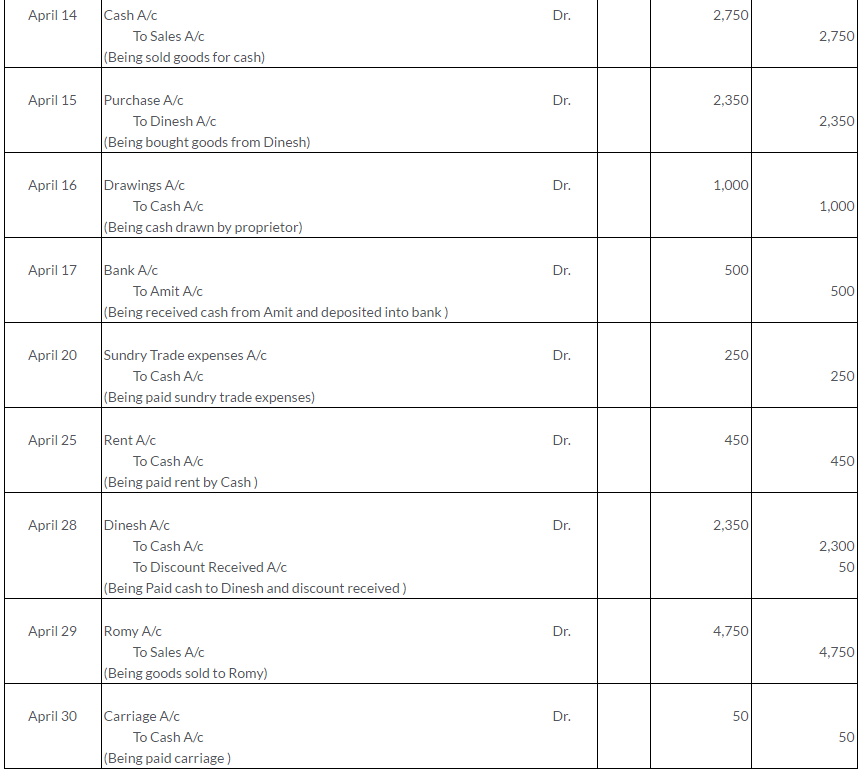
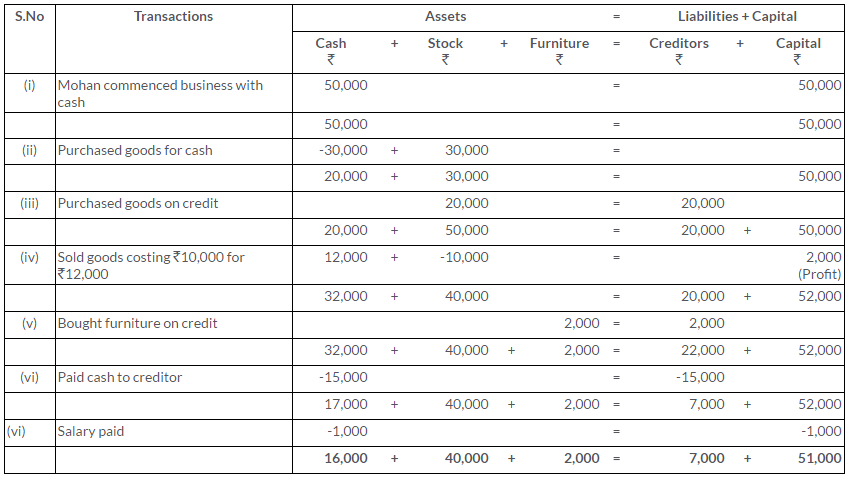
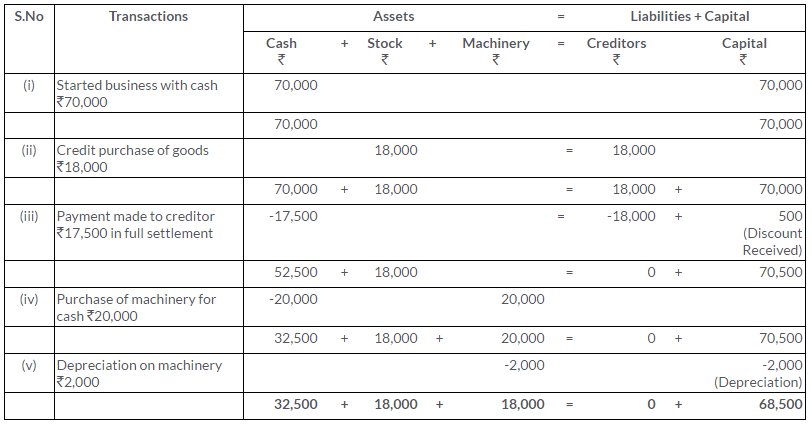
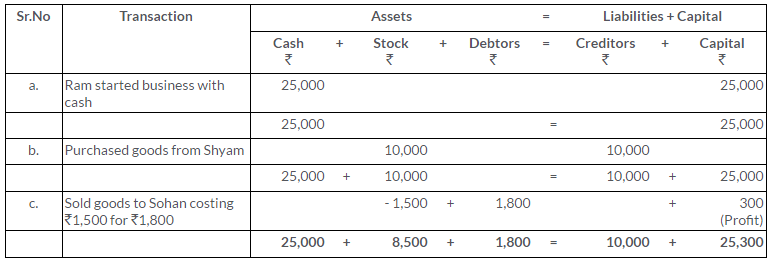
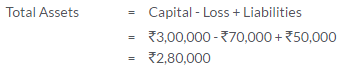
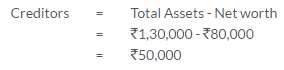
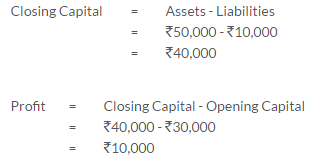
TS Grewal Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 15 – Accounting for Bills of Exchange
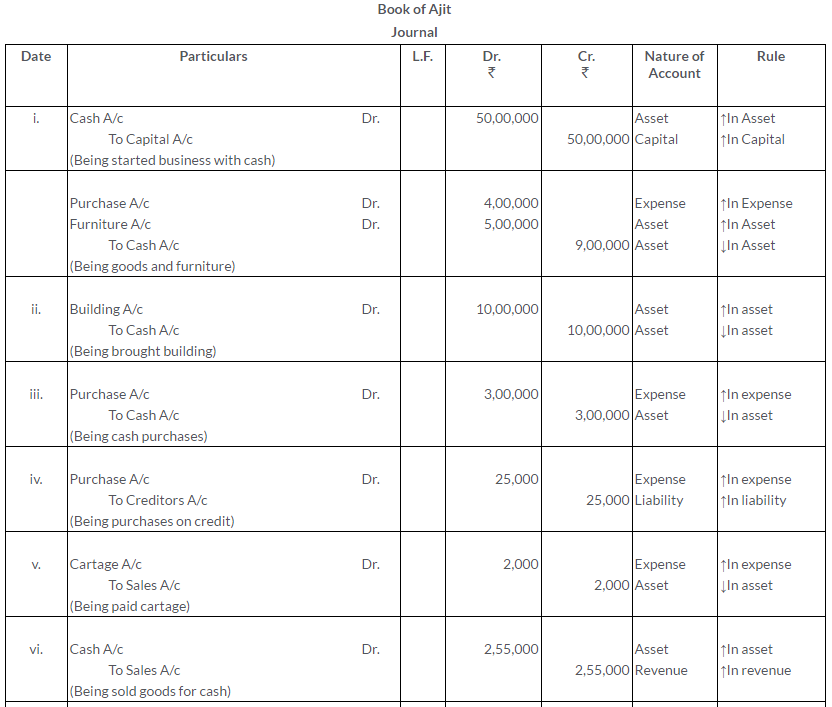
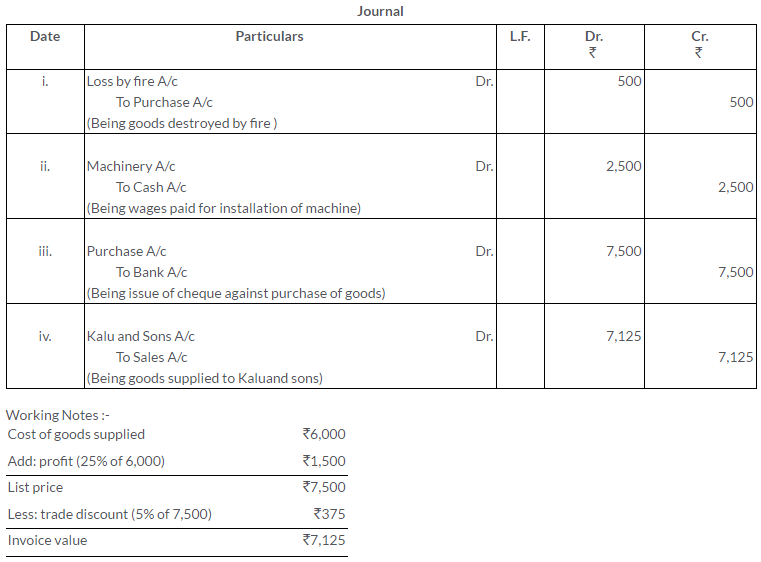
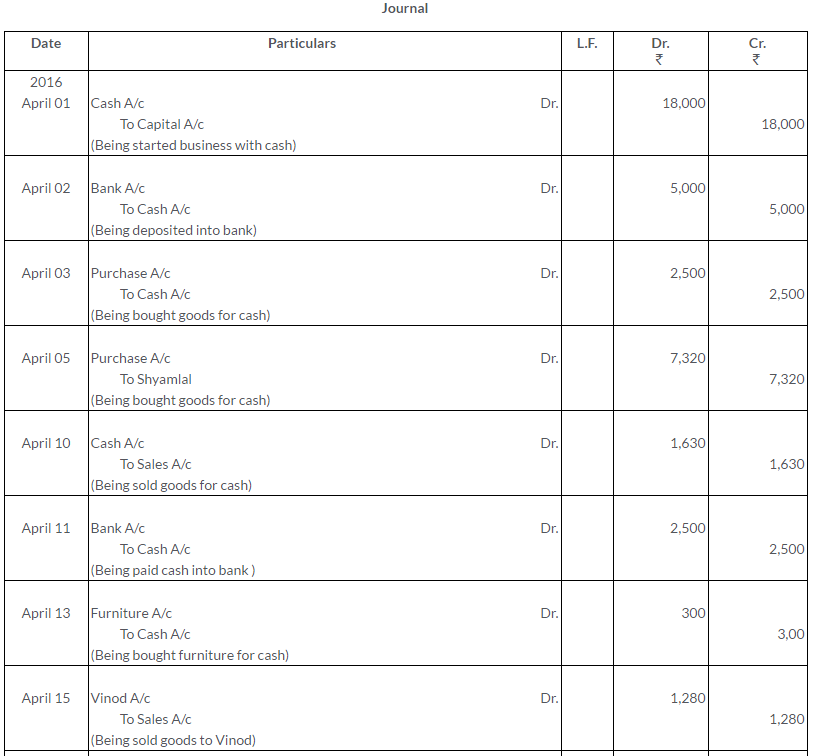
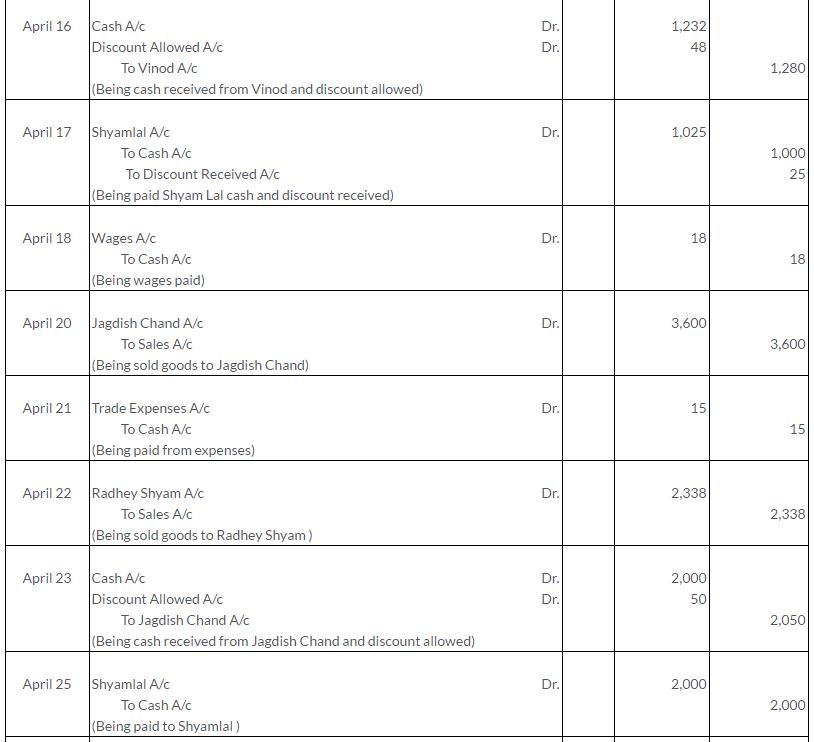
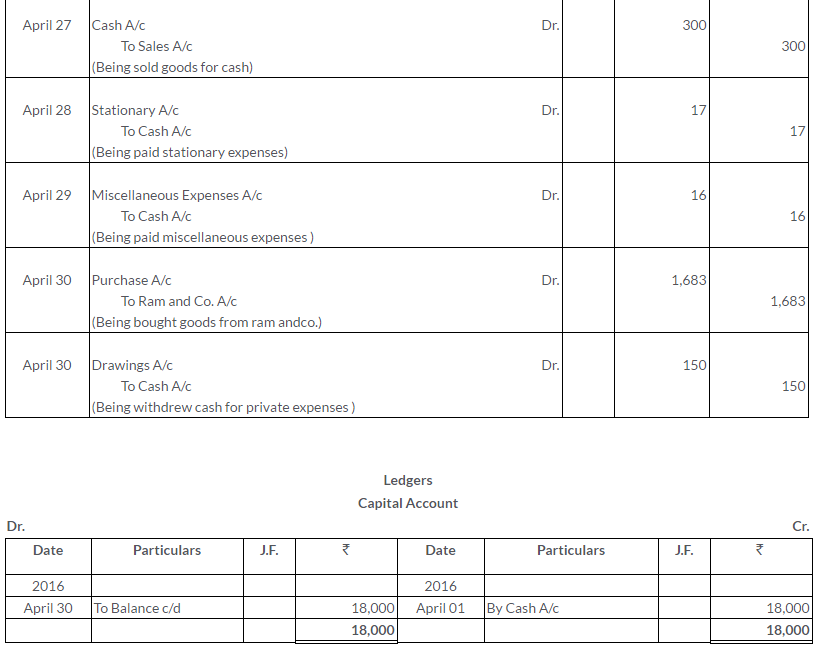
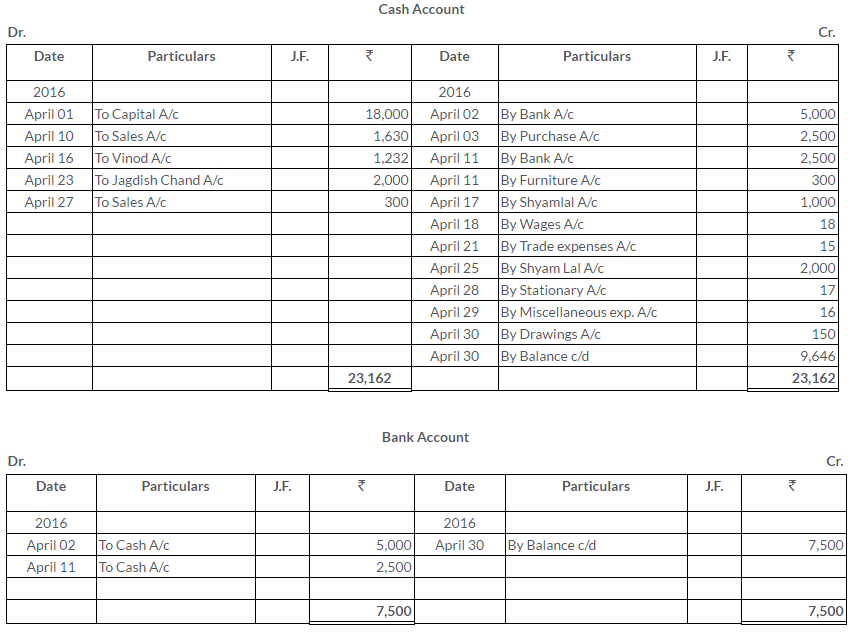
Question 1.
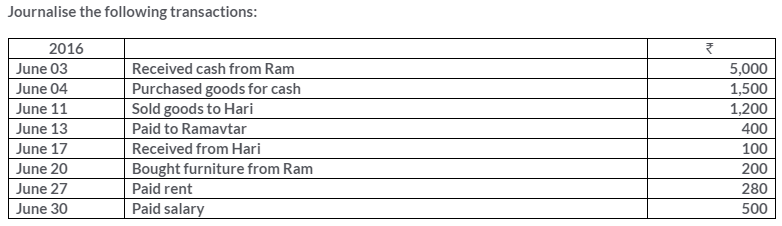
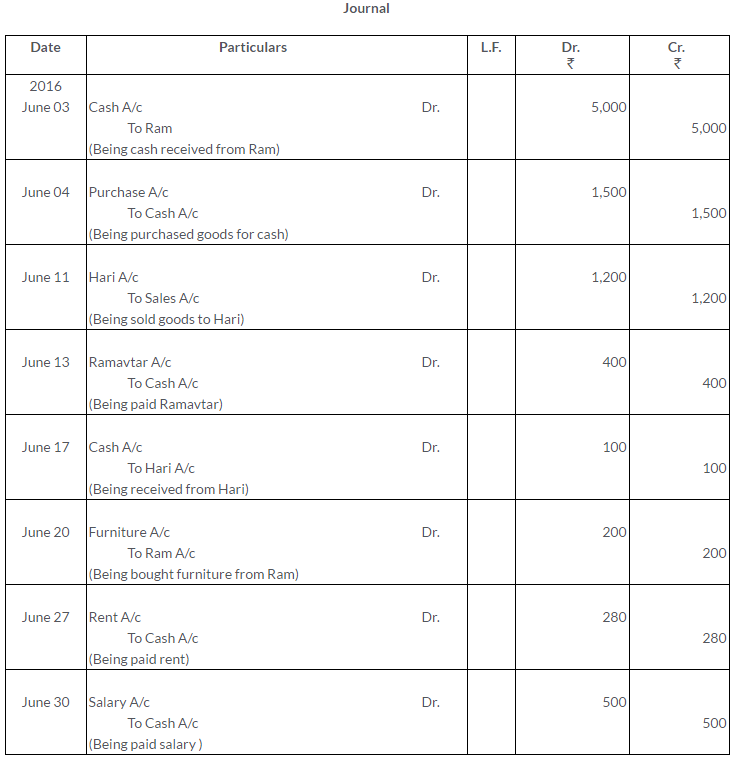
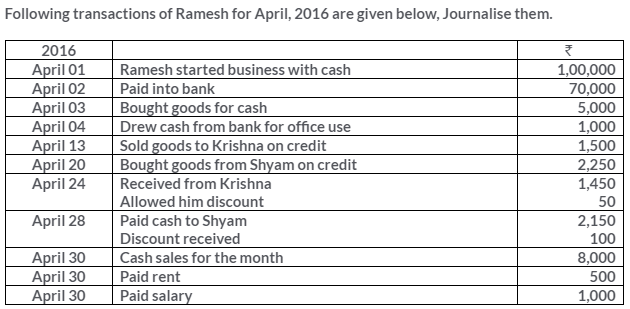
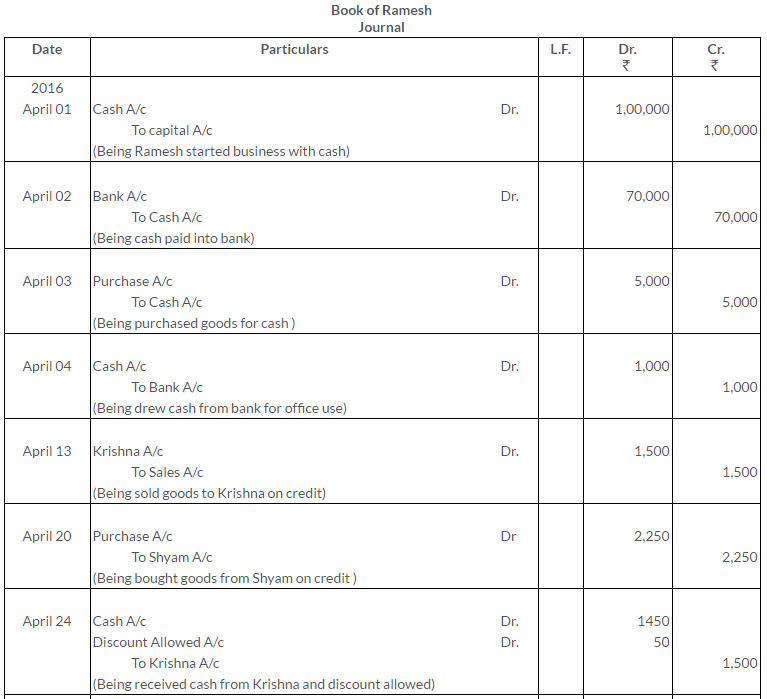
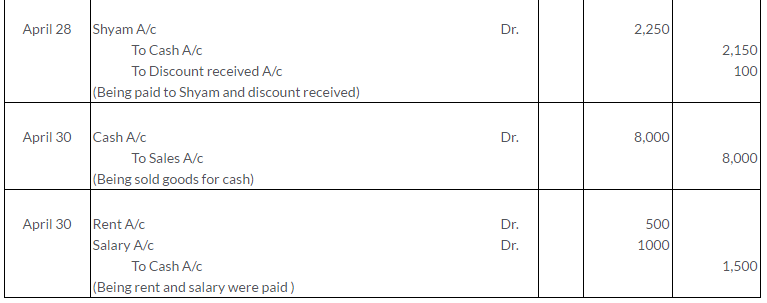
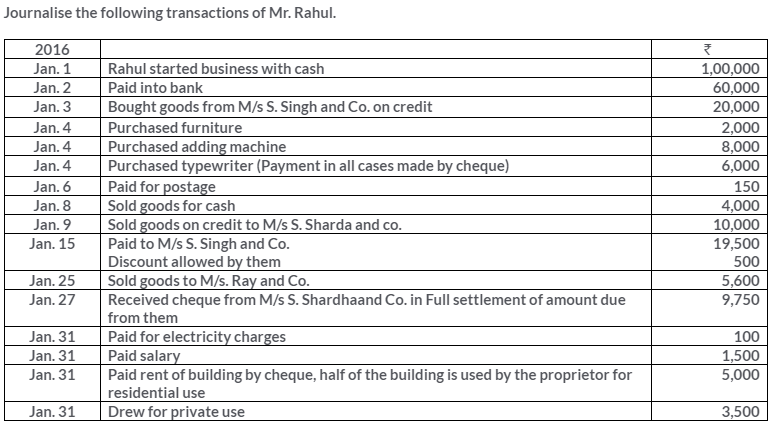
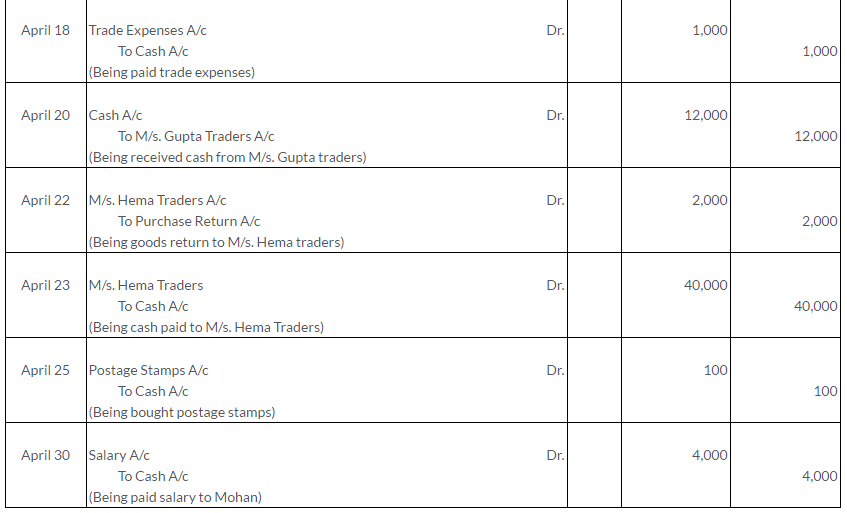
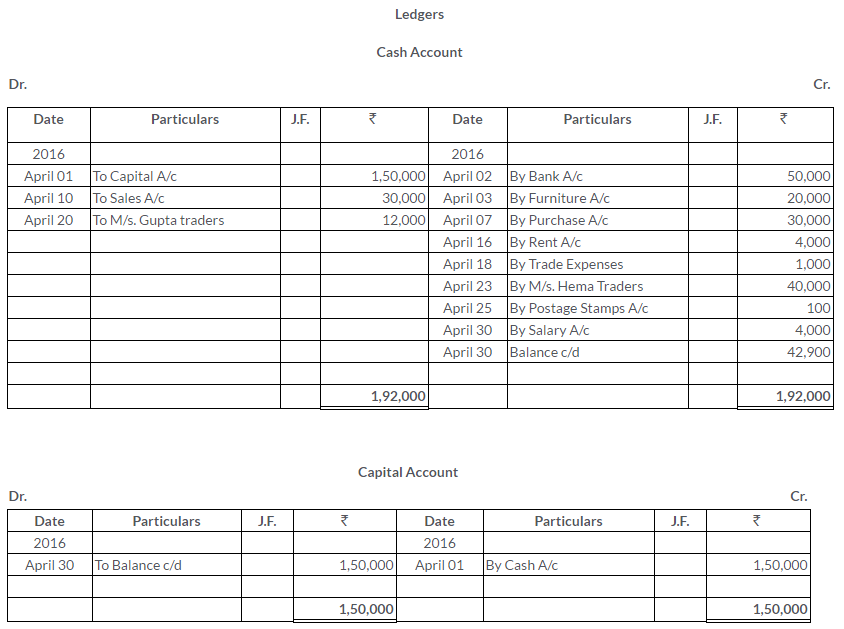
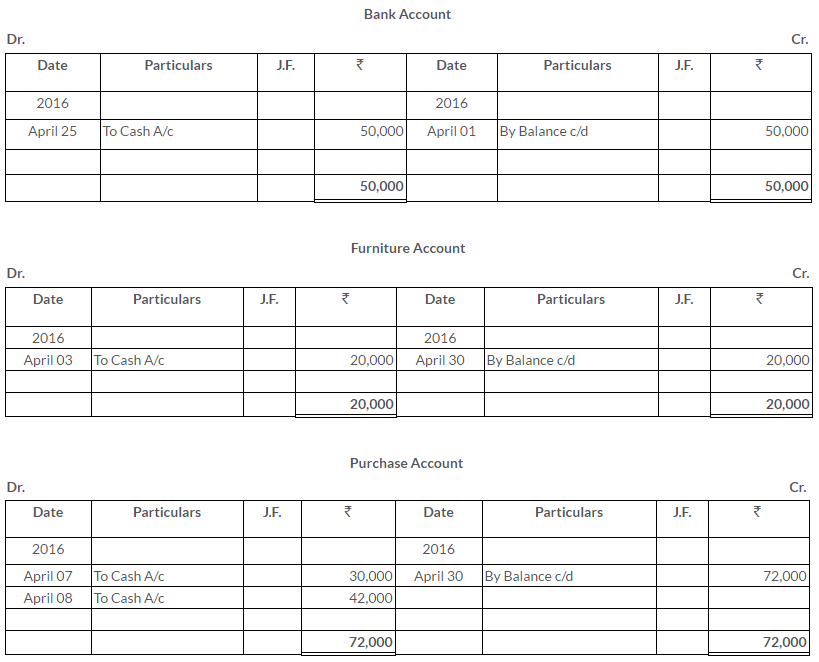
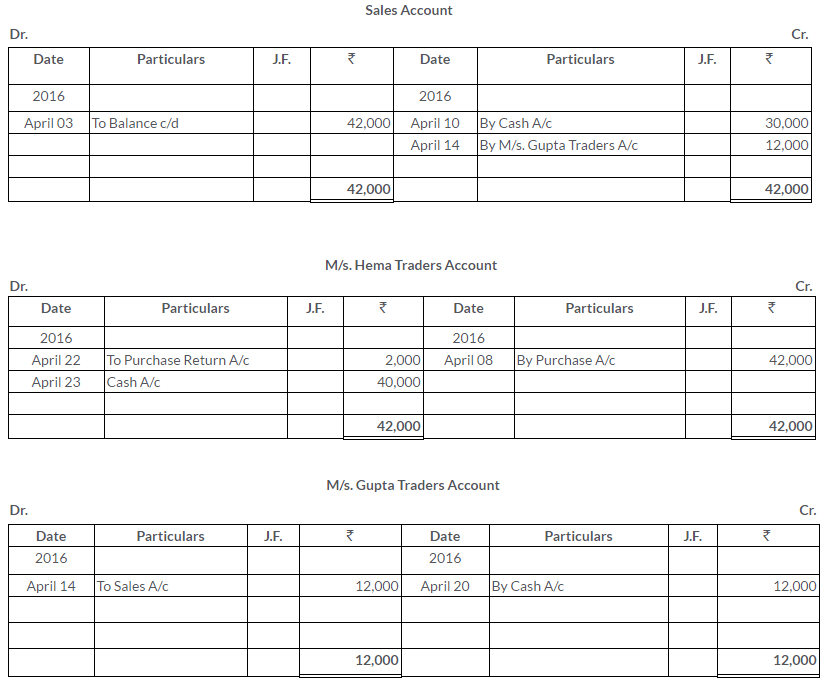
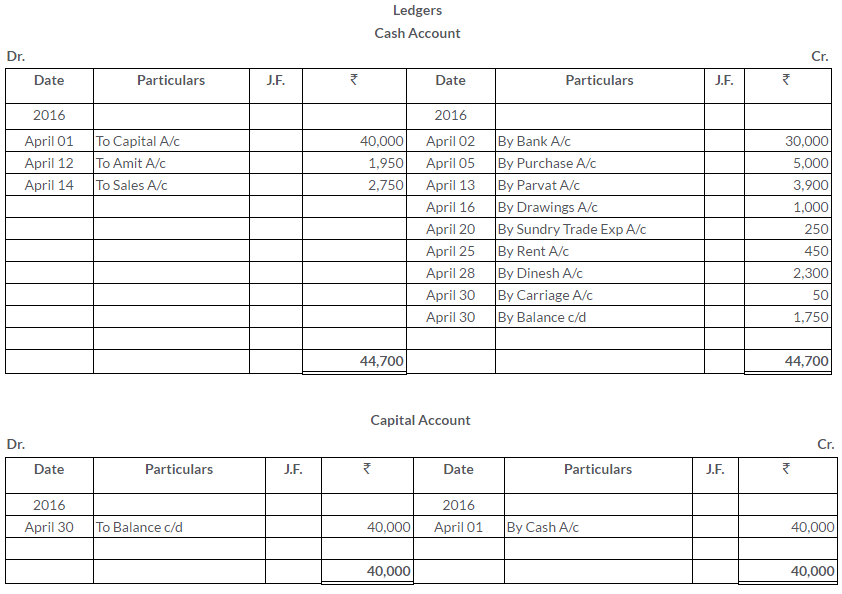
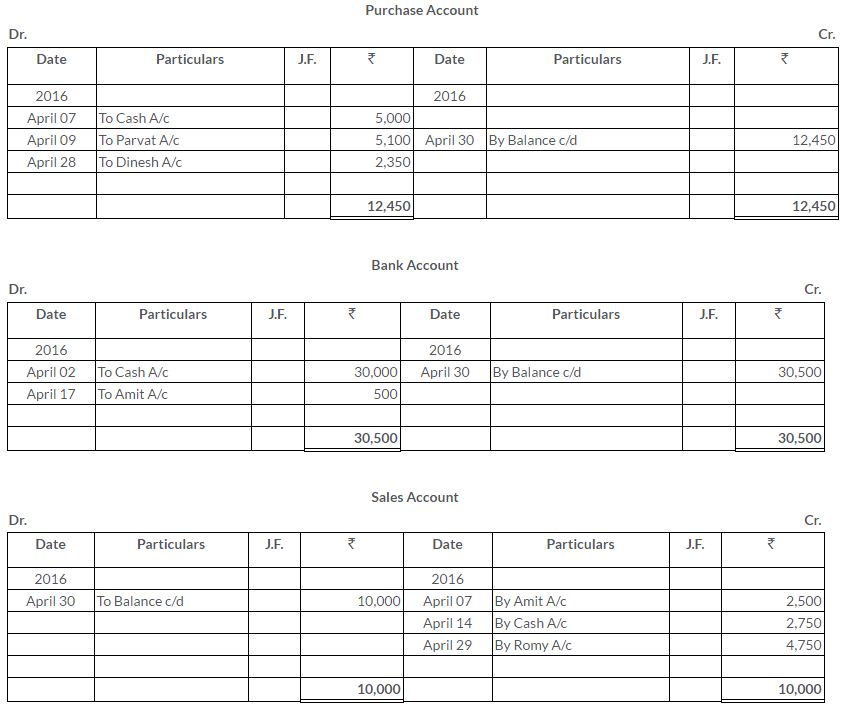
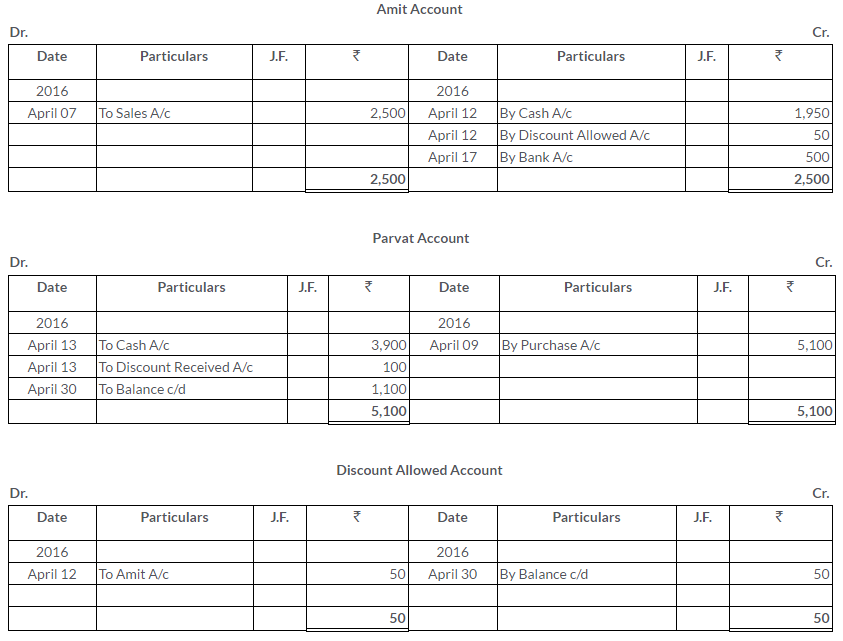
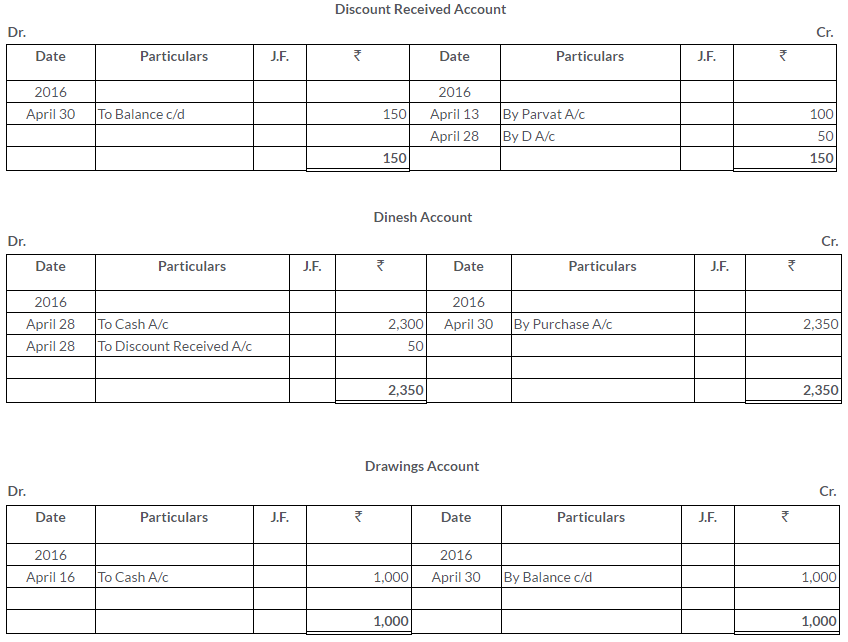
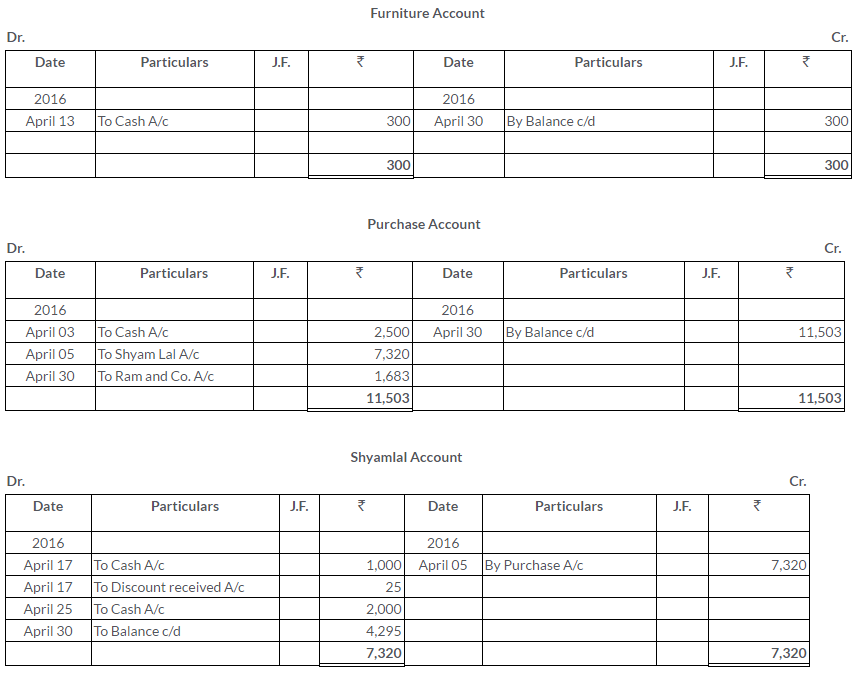
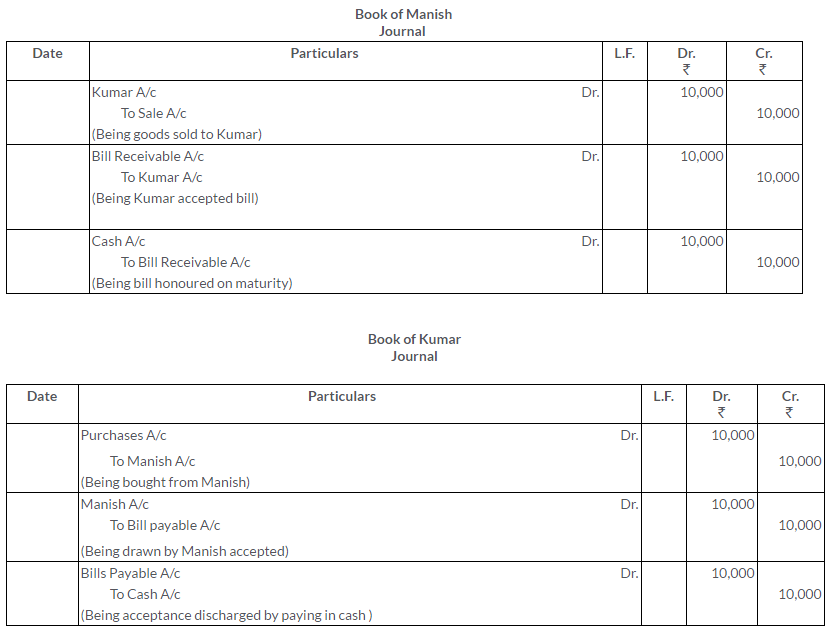
Manish sold goods to Kumar to the value of Rs.10,000 drawing upon him a bill for the amount payable 3 month after date. Kumar accepted the bill and returned it to Manish. On the due date, Manish presented the bill to Kumar who honoured it. Pass the Journal entries in the books of both the parties.
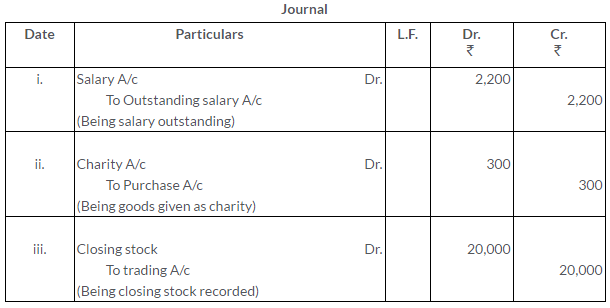
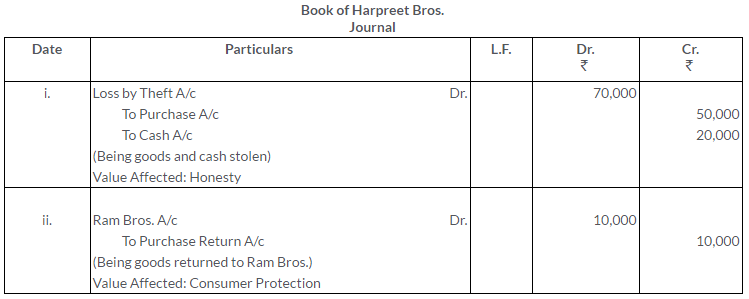
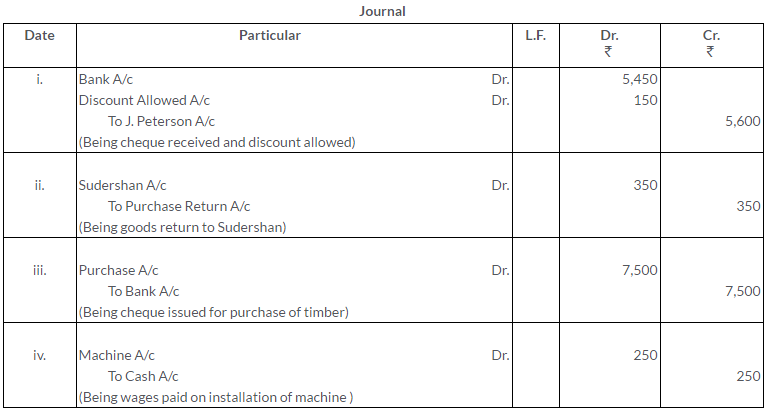
Solution:
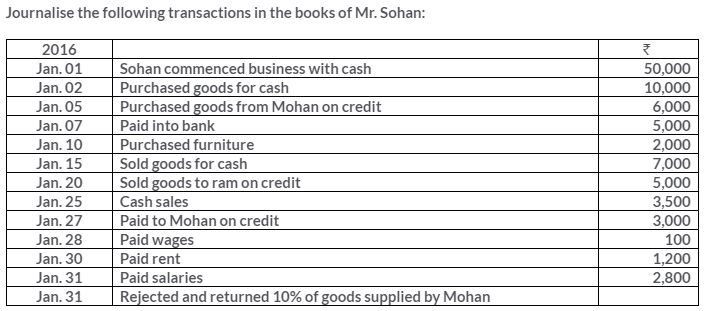
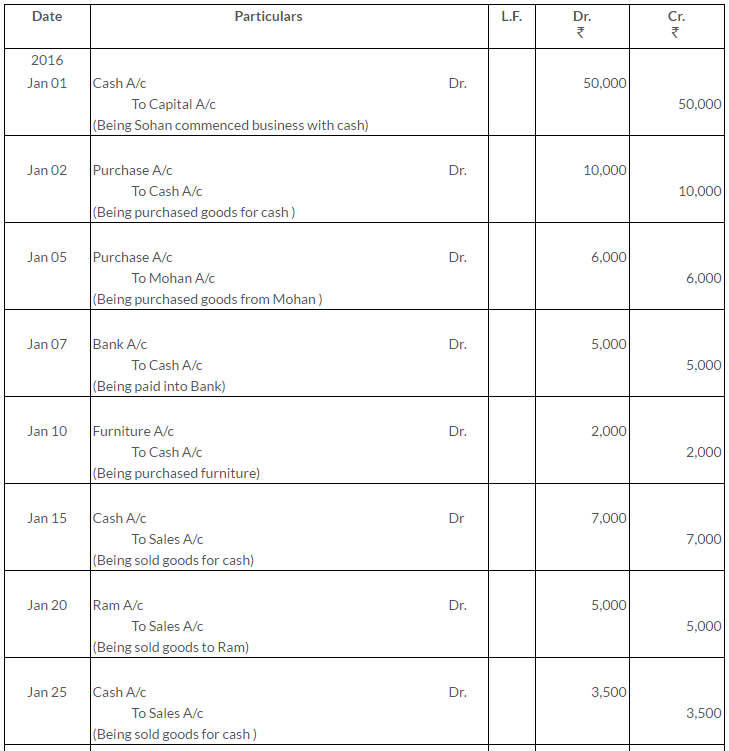
Question 2.
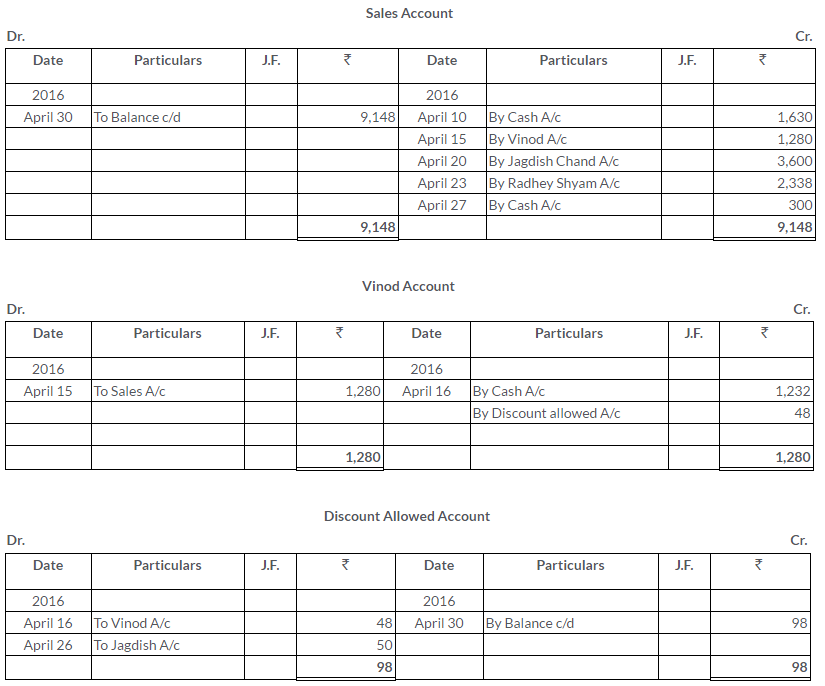
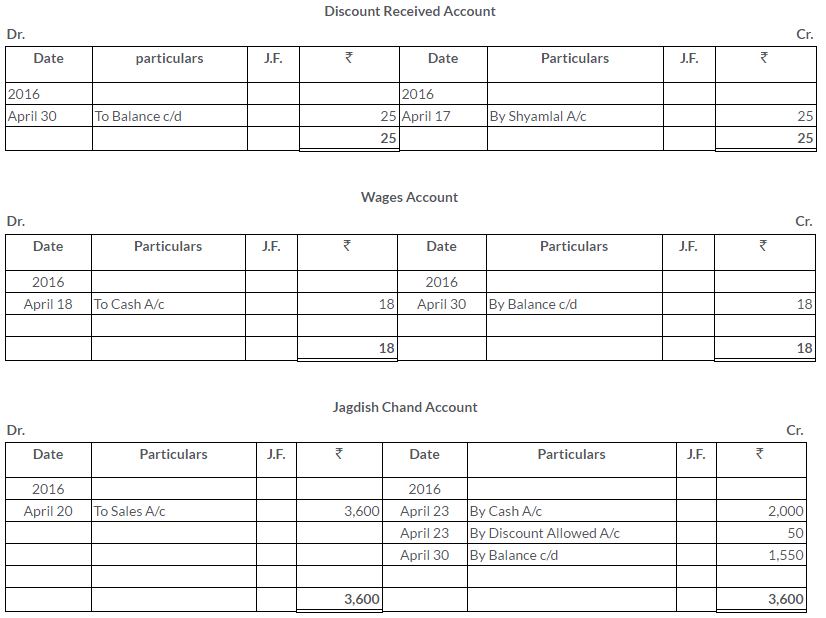
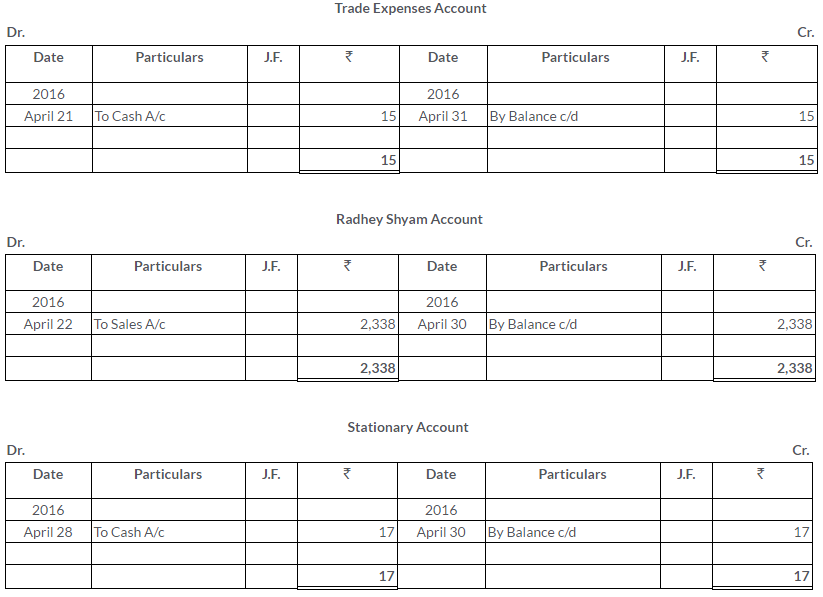
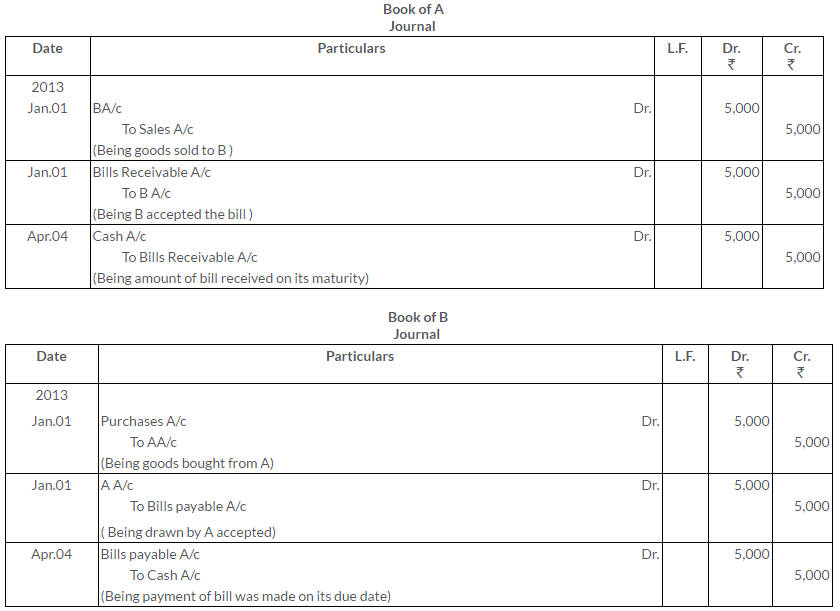
On 1stJanuary2013, A sold goods to B for Rs.5,000 and drew upon him a bill for this amount payable 3 month after date. The bill was duly accepted by B.A retained the bill due date. On the due,the bill was paid.
Pass the Journal entries in the books of A And B. Also, show the necessary accounts in the books of both the parties.
Solution:
Question 3.
Vinod sold goods to Darbara Singh for Rs. 1,000. He drew on the latter a bill for the amount payable 3 month after date. He discounted the bill with his bankers for Rs.990. On maturity, the bill is duly met. Make the journal entries in the books of Vinod and Darbara Singh.
Solution:

Question 4.
Dinesh received from Shridhar an acceptance for Rs.3,000 on 1stSeptember, 2012 at 3 month. Dines got the acceptance discounted at 9% p.a.from his bank. On the due date, Shridhar paid the required amount. Give the Journal entries in the books of Dinesh and Shridhar.
Solution:

Question 5.
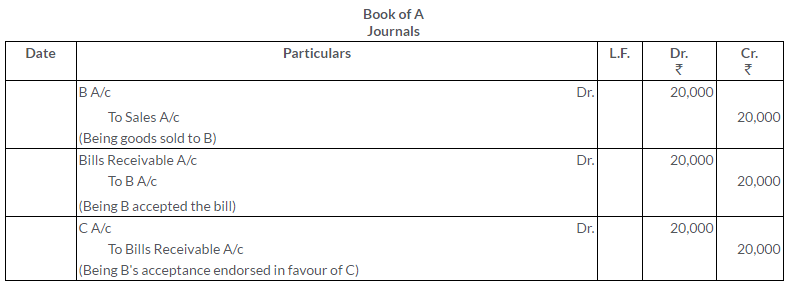
A sold goods to B for Rs.20,000 on credit of 3 moths. He drew on the latter a bill for the amount. The bill was endorsed in favour of C, who got the payment on maturity. Give the journal entries in the books of A.
Solution:
Question 6.
On 10thJuly, 2013, A sold goods to B for Rs.3,500 and drew upon him a bill at 3 month of the amount. B accepted the bill. After 10 days, A endorsed the bill to his credit C. On the due date, acceptance is duly met.
Show the entries in the books of A, B and C.
Solution:

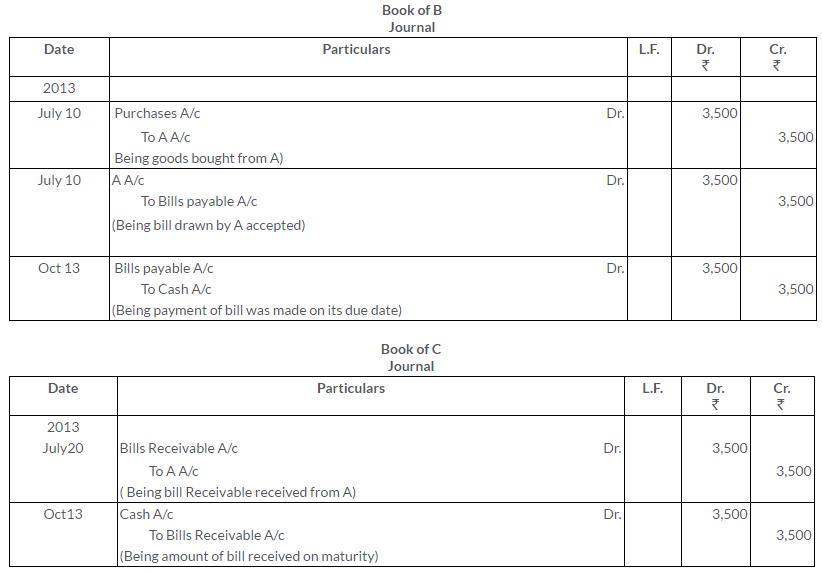
Question 7.
A owed a bill of Rs.1,000 on B for 3 month which was duly accepted by the latter. A endorsed the to C in full payment of his own acceptance to C for like amount. C endorsed the bill to B.
Pass the journal entries in the book of A,B and C.
Solution:
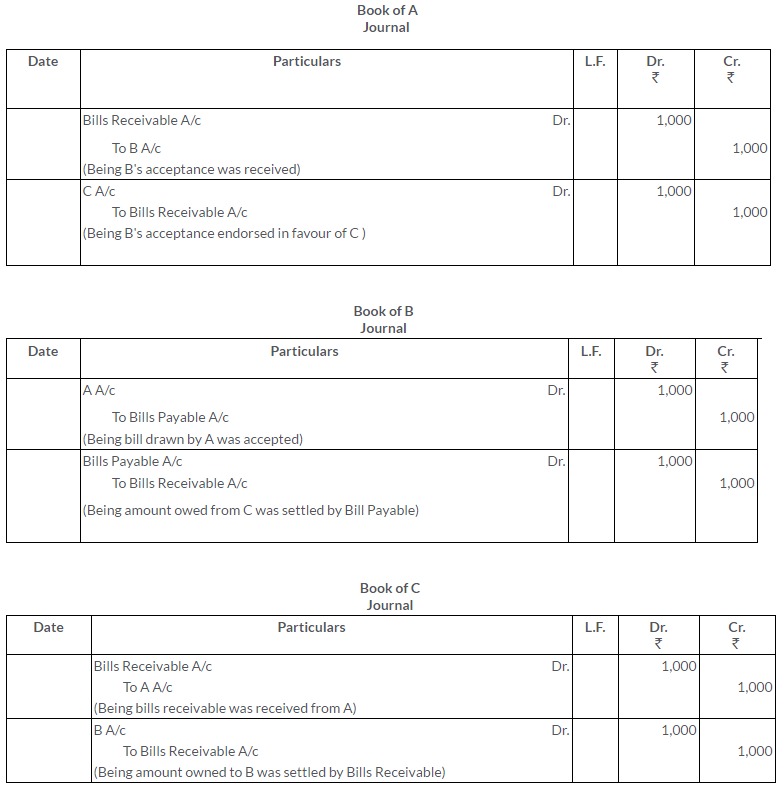
Question 8.
A owed B Rs.8,000.He gave a bill for the same on 1st August,2011 payable after 4 months at the Bank of India, ChandniChowk, Delhi. Immediately after receiving the bill of endorsed it C in payment of his debt. On 1st September, C discounted the bill the at 12% p.a. The bill is met on due date.
Pass the journal entries in the books of A,B and C.
Solution:
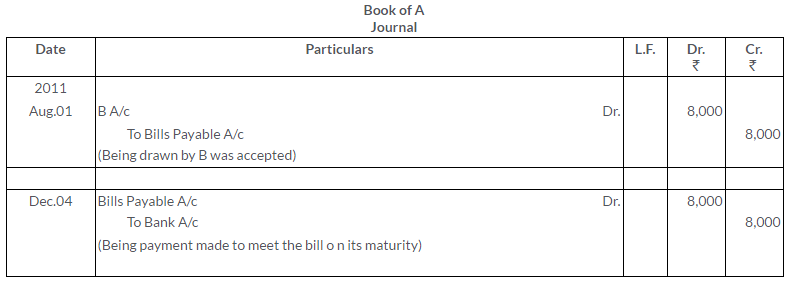
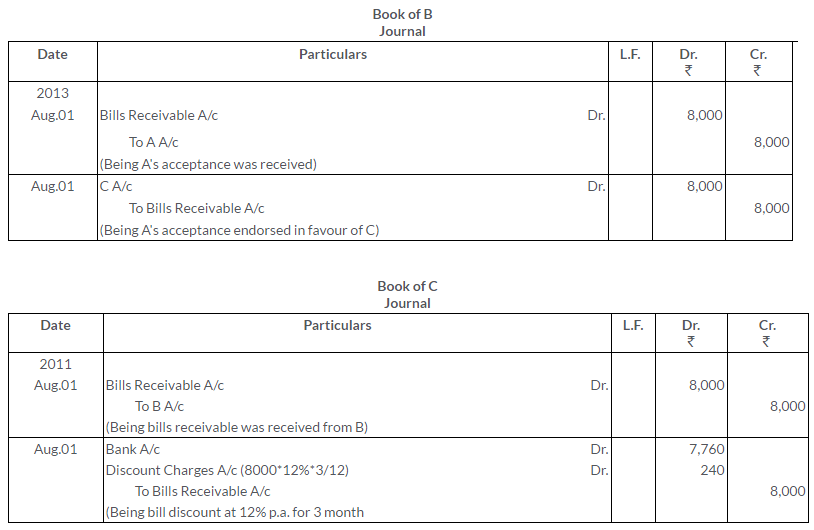
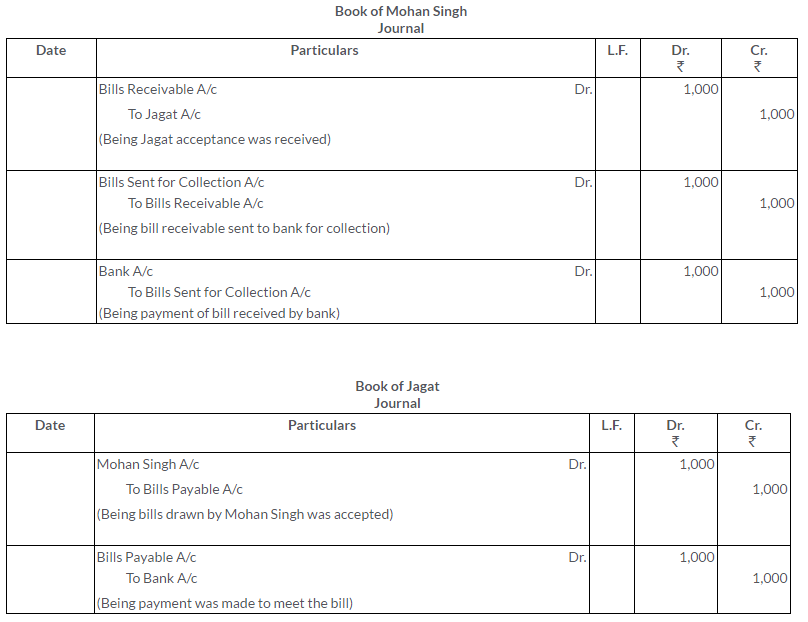
Question 9.
Mohan Singh draws a bill on Jagat for Rs.1,000 payable 2 month after date. Immediately after its acceptance, Mohan Singh sends the bill to his Bank for collection . On due date bank gets the payment.Make the entries in the books of all the parties.
Solution:
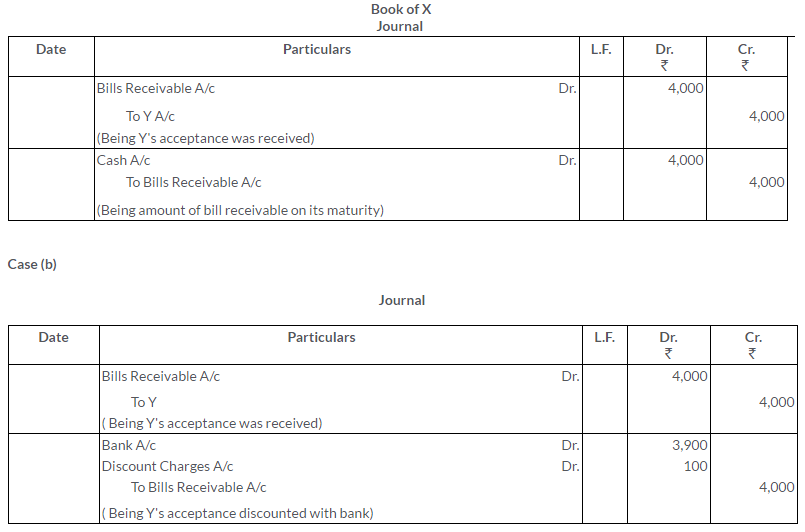
Question 10.
X draws on Y a bill for Rs.4,000 which was duly accepted by Y. Y meet the bill on its due date show what entries would be passed in the books of X under each of the following circumstance.
a. If X retainthe bill till due date.
b. If X discounts the same with his banker paying Rs.100 for discount.
c. If Xendorses the same to his creditors Z in full settlement of this debtofRs.4,080.
d. If X sends the bill to his banker for collection the next day bank.
Solution:

Question 11.
Ram draws a bill forRs.2,000 on Shyam on 15th September, 2011 for the 3 months on maturity, Shyam failed to honour the bill.
Solution:

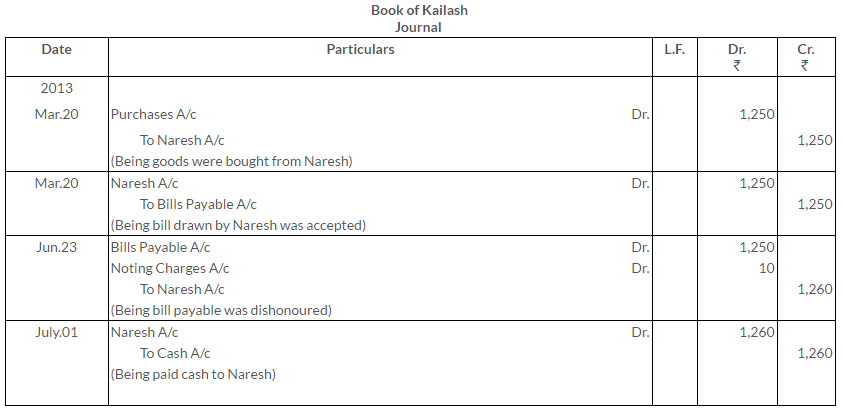
Question 12.
On 20thmarch,2013, Naresh sold goods to Kailash to the value of Rs.1,250, taking a bill of 3 months for the amount. On maturity, the bill was dishonoured. Rs.10of noting charges. On 1stJuly, Kailash cleared his account by paying Rs. 1,260.
Make the entries in the books of both the parties to record the above transaction.
Solution:

Question 13.
On 1stJuly, 2011, A drew a bill for Rs.500. On B payable after 3 months. A discounted it the Bank for Rs.485. On maturity B failed to pay the amount of his acceptance and had to pay Rs.5 as noting charges.
Draw up the necessary Journal entries in the books of A and B.
Solution:

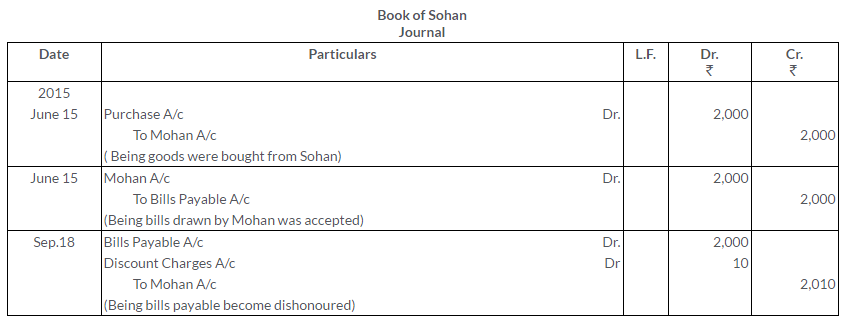
Question 14.
On 15thJune, 2015, Mohan sold goods to Sohan valued at Rs.2,000. He drew a bill 3 month for the amount and discounted the same with his bankers atRs.1,960.On the due date the bill was dishonoured and Mohan paid to the bank the amount due plus noting charges of Rs.10.
Draft the journal entries in the books of all parties.
Solution:

Question 15.
On 1stMarch ,2015, R accepted a Bill of Exchange of Rs.20,000 from S payable 3month after date in full settlement of his dues. On the same day S endorsed the Bill of Exchange to T together with a cheque for Rs.5,000 in settlement of his debt to the latter. On 2ndMarch, 2015, T discounted the Bill of exchange @ 6% p.a. with his bankers. On maturity the Bill of Exchange was dishonoured.
Journalise the transaction in the books of R and T.
Solution:

Question 16.
On 1st January, 2015, A drew a bill on B for Rs.1,000 payable after 3 months. B accepted the bill and returned it to A. After 10 days, A endorsed the bill to his creditor C. On the due date, the bill was dishonoured and C paid Rs.5 as noting charges.Record the transactions in the books of A, B and C.
Solution:

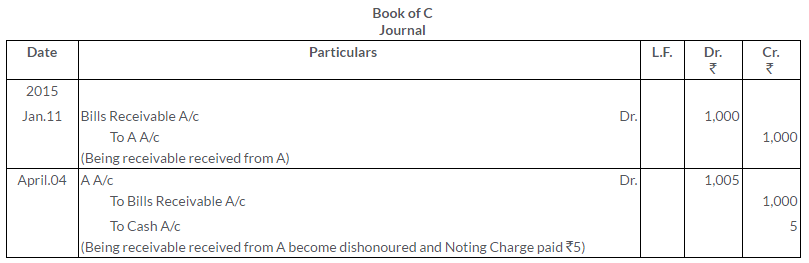
Question 17.
B owes A Rs.4,000 on 1st January, 2015. B accepts a 3 months bill for Rs.3,900 being in full settlement of the claim. At its due date the bill is dishonoured. Noting charges Rs.50 are paid by A. Give the Journal entries in the books of A and B.
Solution:
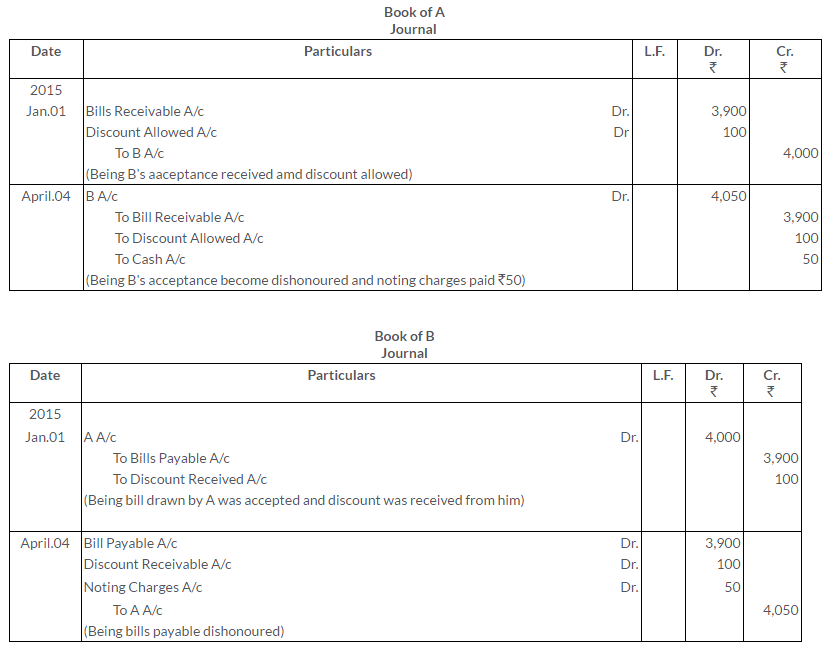
Question 18.
Y owesX Rs.4,000. On 1st January, 2015, Y accepts a 3 months bill for Rs.3,900 in satisfaction of his full claim. On the same date, it was endorsed by Xto Z in satisfaction of his claim of Rs.3,980. The bill is dishonoured on the due date. Give the Journal entries in the books of X.
Solution:
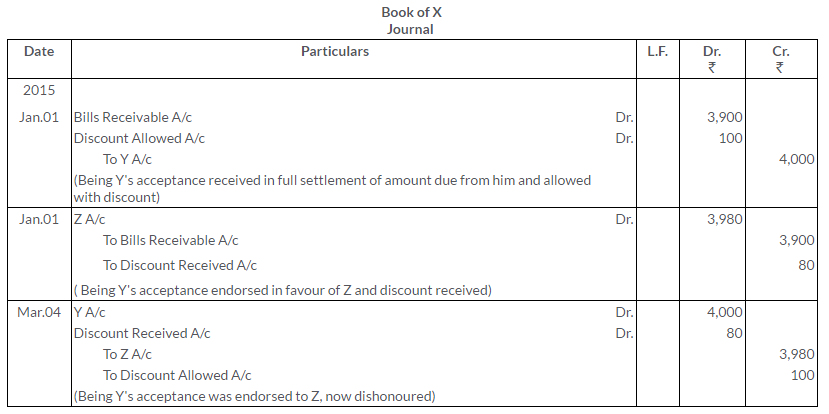
Question 19.
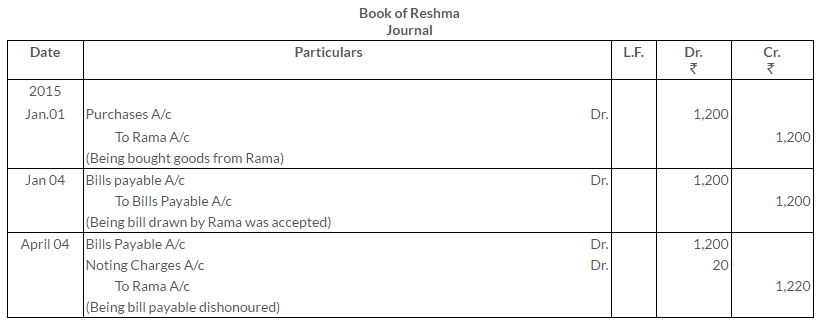
Rama sold goods worth Rs.1,200 to Reshma on 1st January, 2015. On the same date Rama draws a bill on Reshma for Rs.1,200 for a period of 3 months. On receipt of the bill on 1st January, duly accepted by Reshma. Ramadiscounts it with a bank at 6% p.a. On the date of maturity, the bill was dishonoured, the bank having to pay Rs.20 as noting charges. Rama was compelled to make the settlement. Show the Journal entries arising from the above in the books of both Rama and Reshma.
Solution:
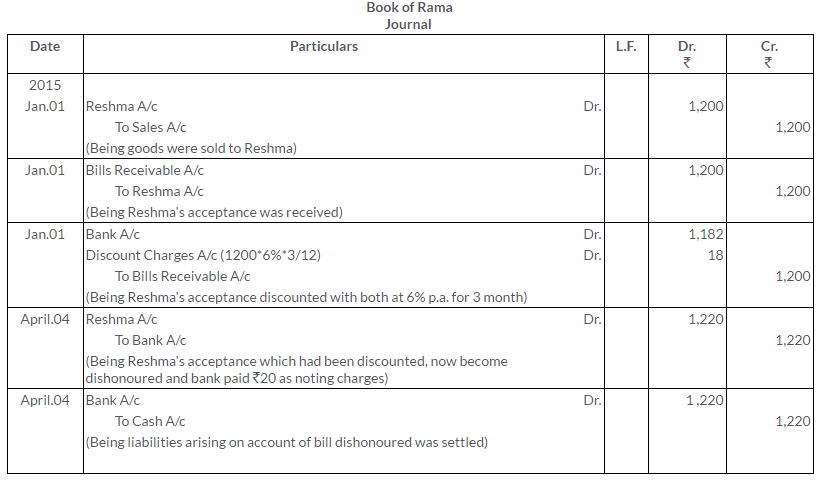
Question 20.
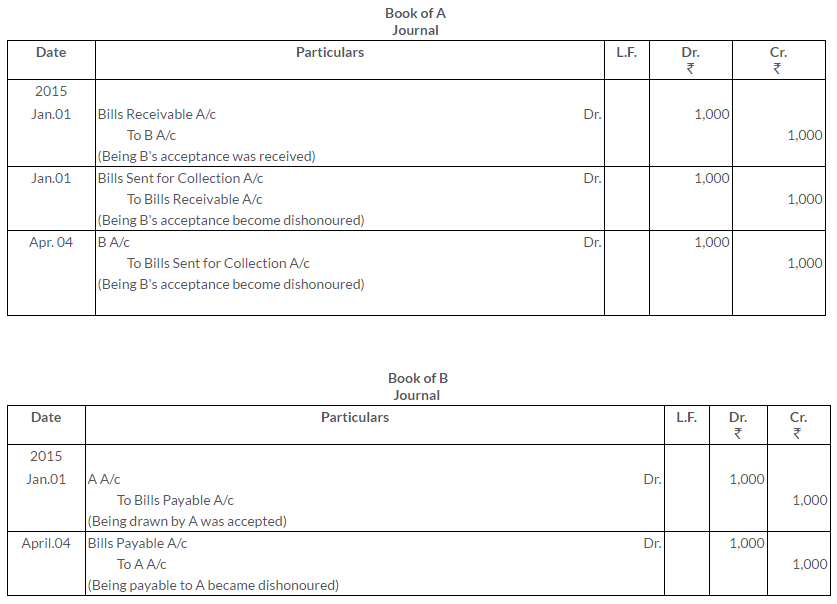
On 1st January, 2015, A draws a bill on B for Rs.1,000 payable after 3 months. Immediately after its acceptance, A sends the bill to his bank for collection. On the due date, the bill was dishonoured. Record the transactions in the Journals of A and B.
Solution:
Question 21.
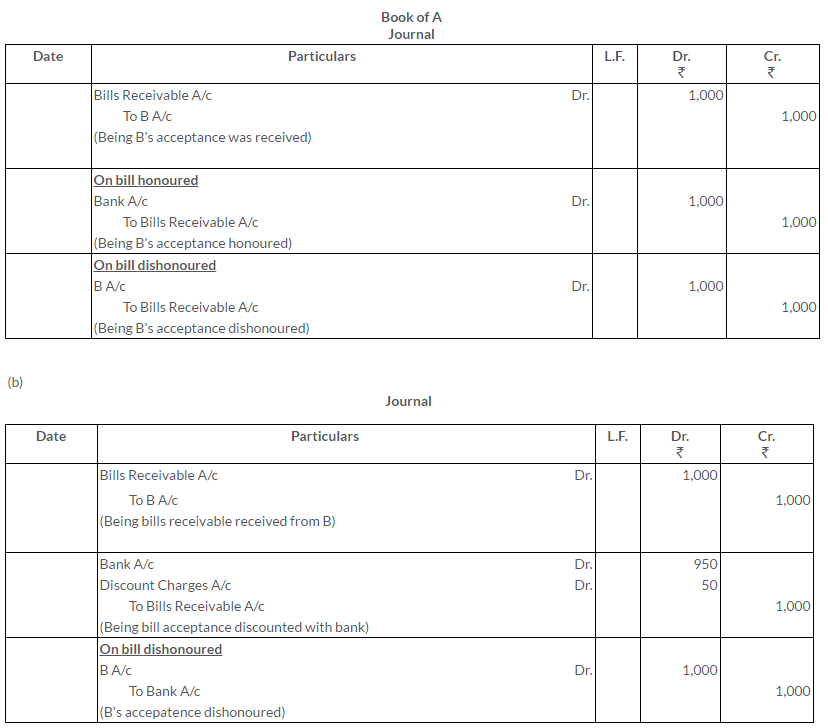
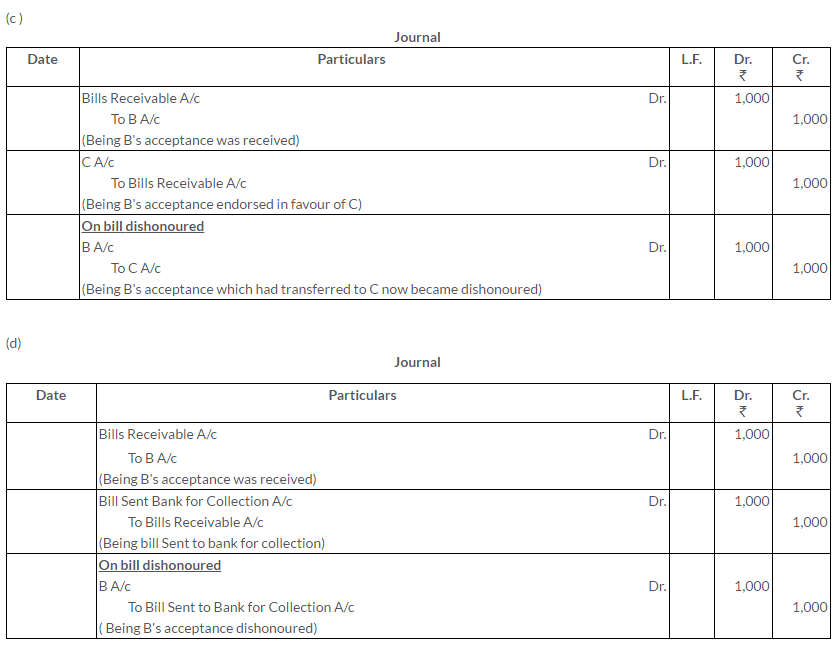
A bill for Rs.21,000 is drawn by A on B and accepted by the latter payable at the New Bank of India. Show what entries should be passed in the books of A under each of the following circumstances:
i. If A retained the bill till the due date and then realised it on maturity.
ii. If A discounted it with his bankers for Rs.950.
iii. If A endorsed it to his creditor C in full settlement of his debt.
iv. If A sent it to his bankers for collection.
Also, give the necessary entries in each of the cases if the bill is dishonoured.
Solution:
Question 22.
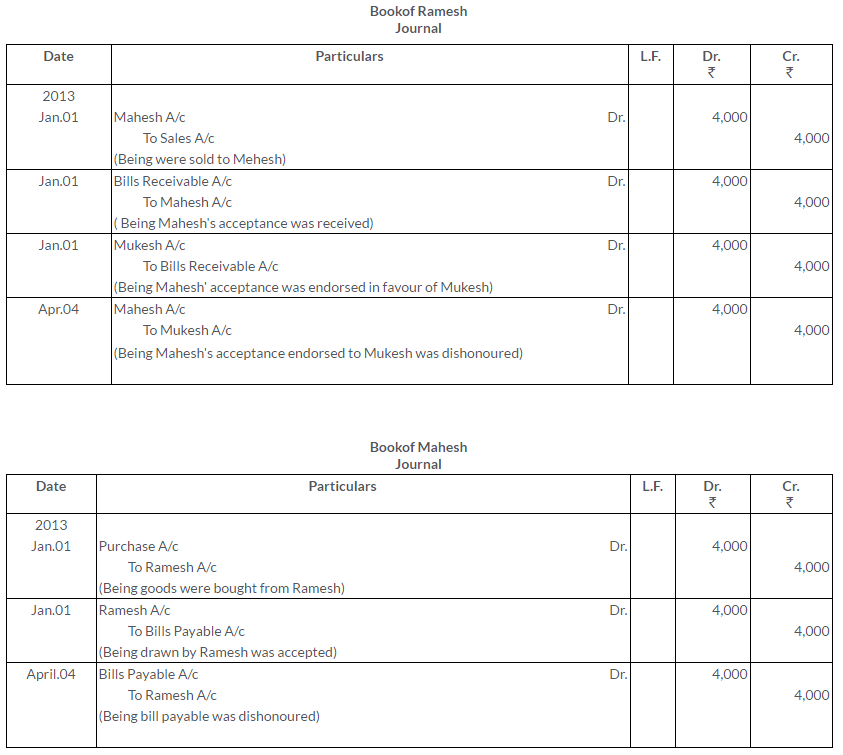
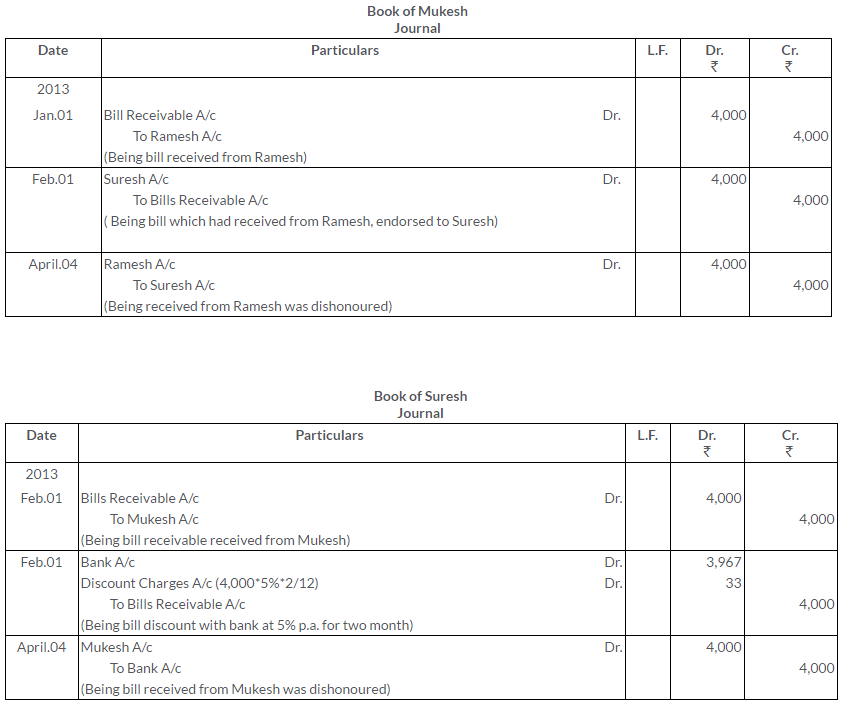
On 1st January, 2013 for goods sold, Ramesh drew a Bill of Exchange Mahesh for Rs.4,000, for a period of 3 months. Mahesh accepts it and returns to Ramesh. Ramesh then endorses it to Mukesh who in turn endorses it to Suresh on 1st February. 2013. The bill is then discounted by Suresh on the same date with his banker at 5% p.a. On the due date the bill is dishonoured. Pass the necessary Journal entries in the books of all the four parties.
Solution:
Question 23.
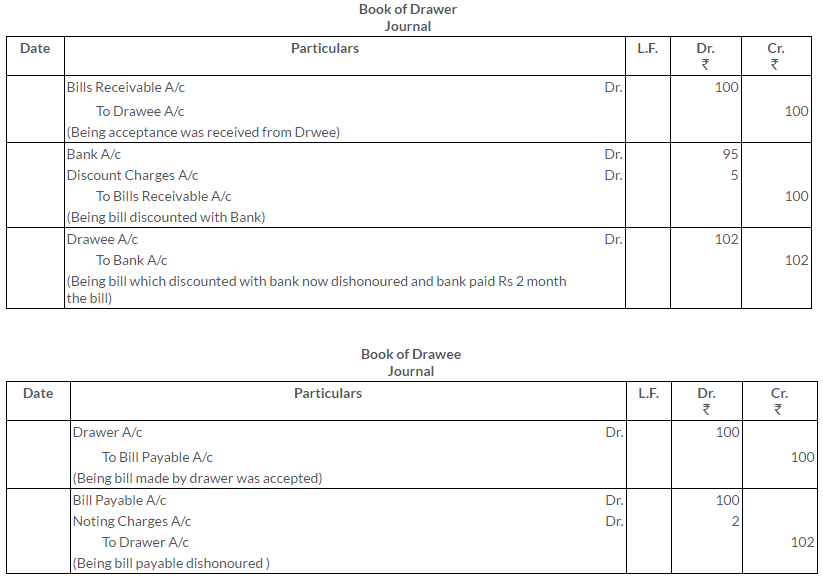
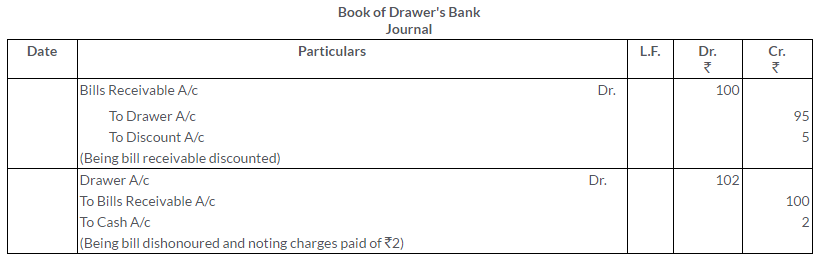
A Bill Receivable for Rs.100, which has been discounted at Rs.95, is dishonoured and the bank paid Rs.2 as noting charges.
Give the Journal entries to record the above in the books of
i. the Drawer
ii. the Drawee
iii. the Bank
Solution:
Question 24.
A purchases goods worth Rs.6,200 from B and gives him his acceptance for Rs.6,000 in full satisfaction. B purchases goods worth Rs. 10,000 from C and endorses the bill to him, paying the balance by cheque. On maturity the bill is dishonoured, noting charges amounted to Rs.100. Give the Journal entries in the books of A, B and C.
Solution:


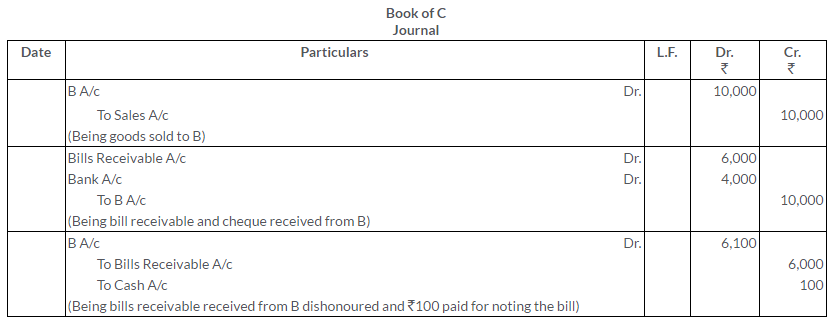
Question 25.
A draws a bill of Rs.500 on B. on getting B’s acceptance, he endorse it to C and C to D. On maturity the bill is dishonoured, nothing charges amounted to Rs.10.
Give the Journal entries in the books of all the parties to record the above transactions.
Solution:
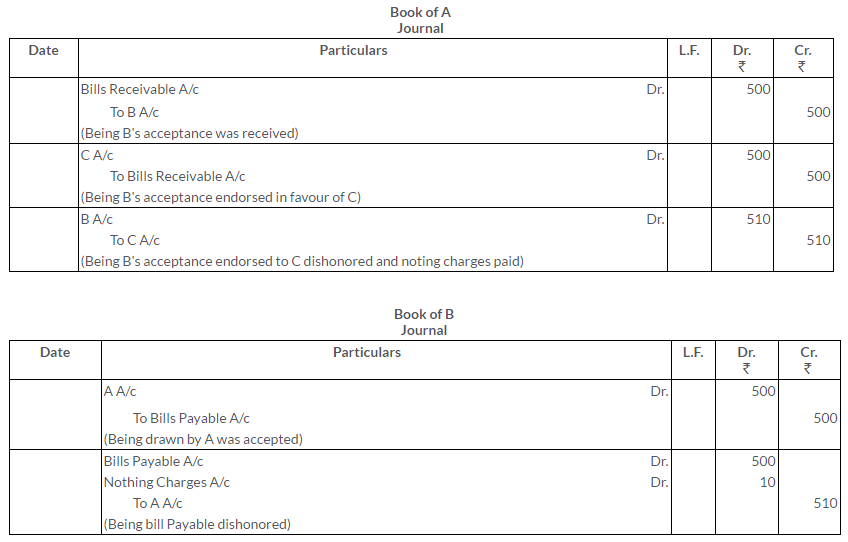
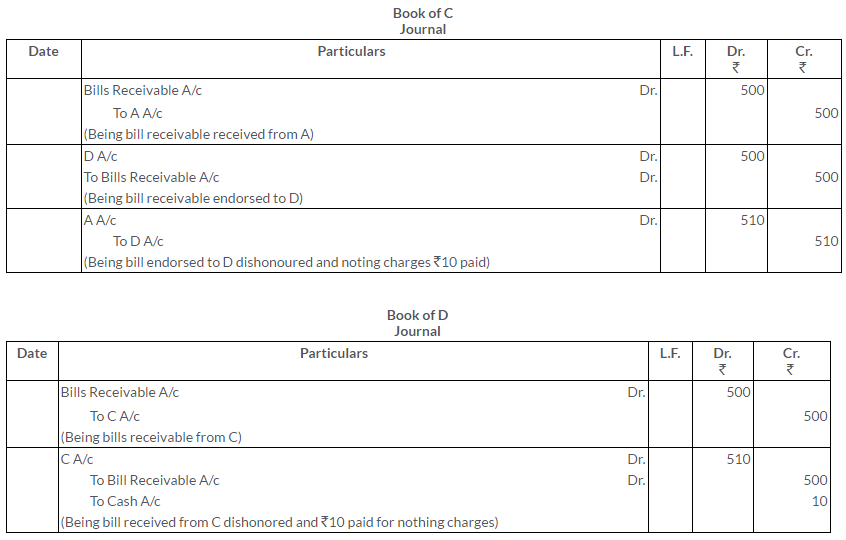
Question 26.
On 1st January 2013, X received from Y three Bills of Exchange for Rs.6,000; Rs.8,000 and Rs.10,000 for 6 months, 4 months and 3 months respectively. On 3rd January the first was discounted by X with his bankers at a discount of 5% p.a. On 1st February the 3rd bill was endorsed in favor of a creditor Z. The second bill was retained till the due dates all the three bills were dishonored.
Show the necessary Journal entries in the books of X and Y.
Solution:
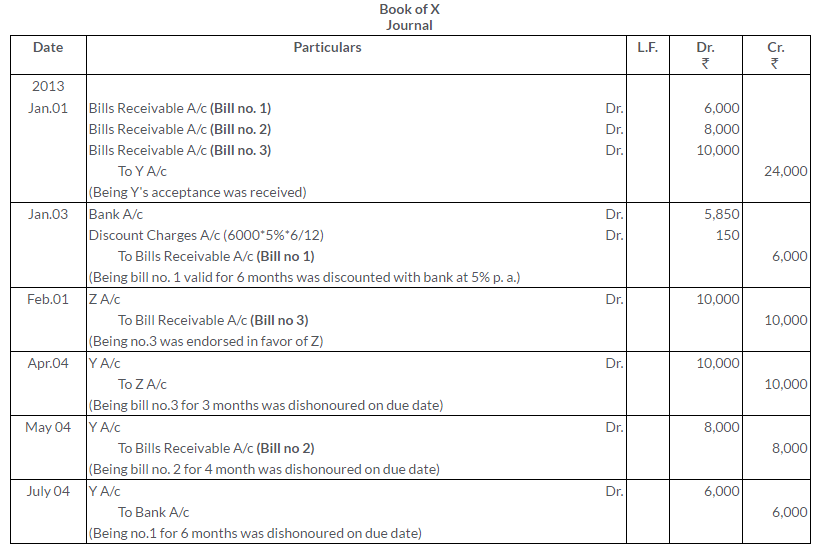
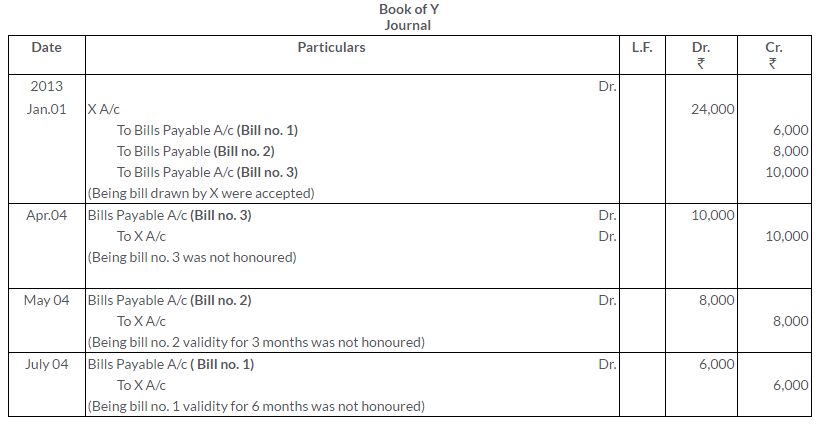
Question 27.
On 1st January, 2013, Mr. X sold goods to Mr. Y for Rs.4,500 on credit and drew 3 bills on him: first bill for Rs.1,000 for 1 month, second bill for Rs.1,500 for 2 months and third bill Rs. 2,000 for 3 months. Mr. Y accepted and returned all the bills to Mr. X.
The first bill was retained by Mr. X till the date of maturity. Second bill was endorsed his creditor Mr. Z on 3rd January, 2013 and third bill was sent to bank for collection on 4th January, 2013. On maturity all the bills were dishonoured and noting charges amounted to Rs.10, Rs.15 and Rs.20 respectively.
Solution:
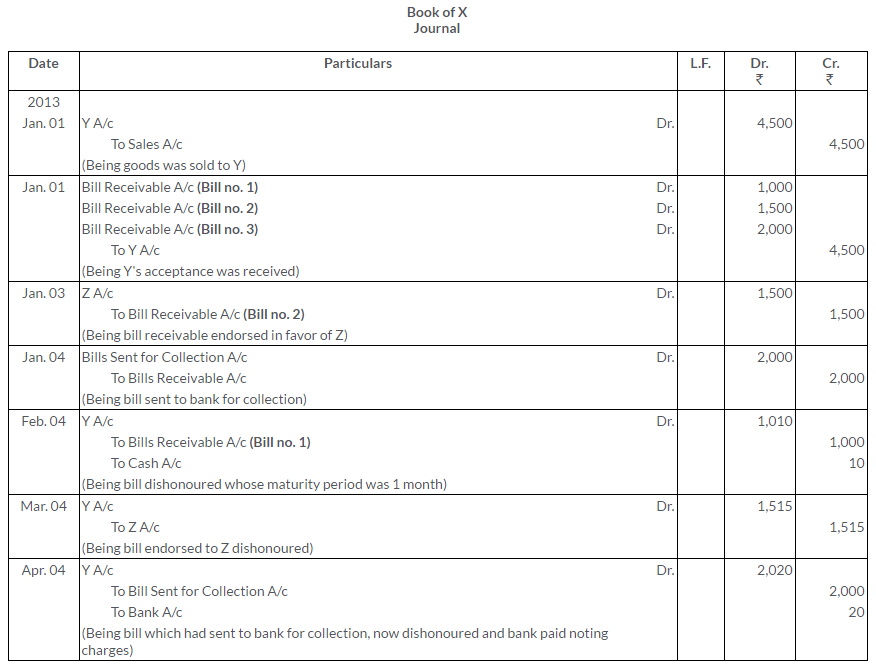

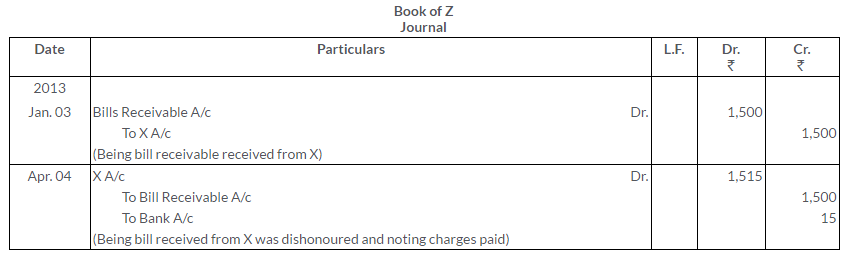
Question 28.
Ram owes Rs.2,000 to Mohan on 1st January, 2013. On this date, he accepted a draft for amount for 3 months. Mohan got the bill discounted at his bank @ 6% p.a. On the due the bill was dishonoured, noting charges Rs.20. Ram agreed to pay Rs.520 immediately accept another bill for the remaining amount for 3 months together with interest at 9% p.a.
This bill was met on the due date. Give the Journal entries in the books of both the parties.
Solution:

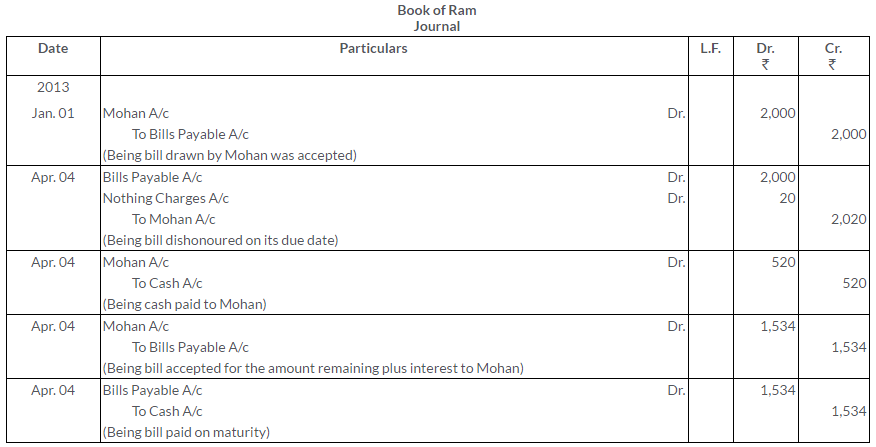
Question 29.
On 15th June, 2013, X sold to Y goods to the value of Rs.1,500 drawing upon the latter bills, one for Rs.1,000 payable 2 months after date and other for Rs.500 payable 3 month after date. X discounted the first bill with his bankers at 6% p.a. and endorsed the second bill in favor of this creditor Z. The first bill was met on maturity but the second dishonoured. Z paid Rs.5 as noting charges. On 1st October, Y cleared his account paying Rs.510 which included Rs.5 as interest.
Record the necessary Journal entries in the books of both X and Y.
Solution:
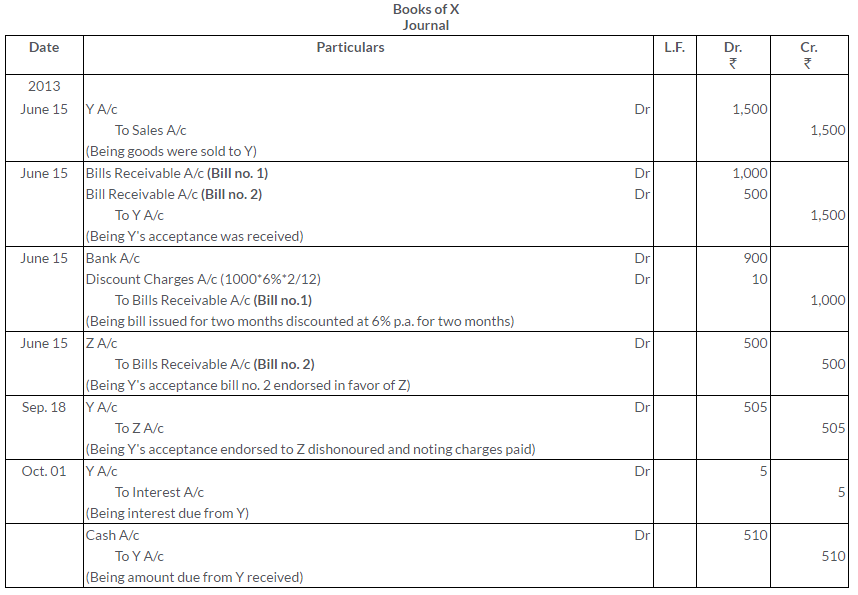
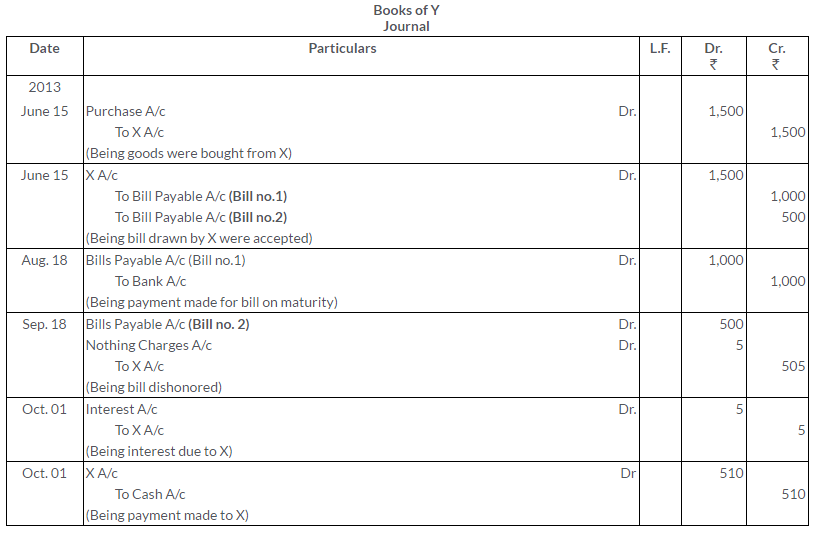
Question 30.
X draws a bill on Y for Rs.2,000 on 1st January, 2013. Y accepts the same and returns it to X. The bill was drawn by X in full settlement of a debt owing by Y amounted to Rs.2,050. X discounts the bill on the same date with the Central Bank of India for Rs.1,980. At maturity the bill was duly met by Y. Give the entries in the books of X and Y.
Suppose the bill is dishonoured, what entries will be passed?
Solution:

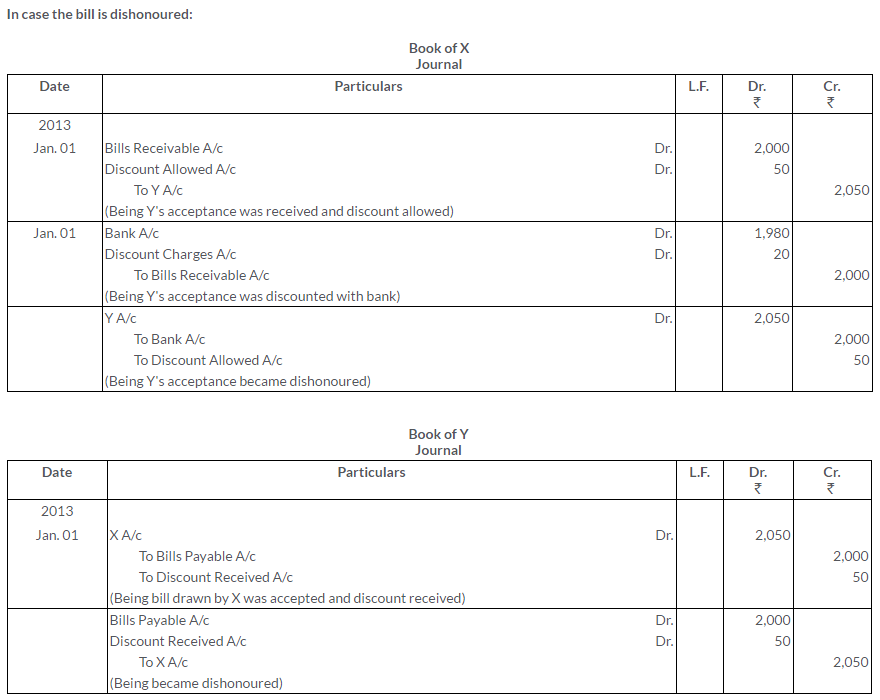
Question 31.
On 1st June, 2013, A sold goods to B for Rs.250. B gave to A his acceptance payable 1 month after date. Before maturity B requests A to renew it, which A does adding Rs.10 to the new bill for interest. Make the necessary Journal entries to record these transactions in the books of both A and B.
Solution:
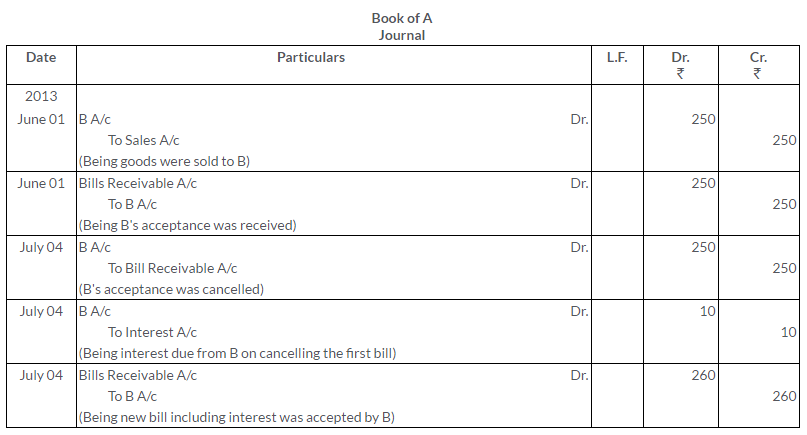
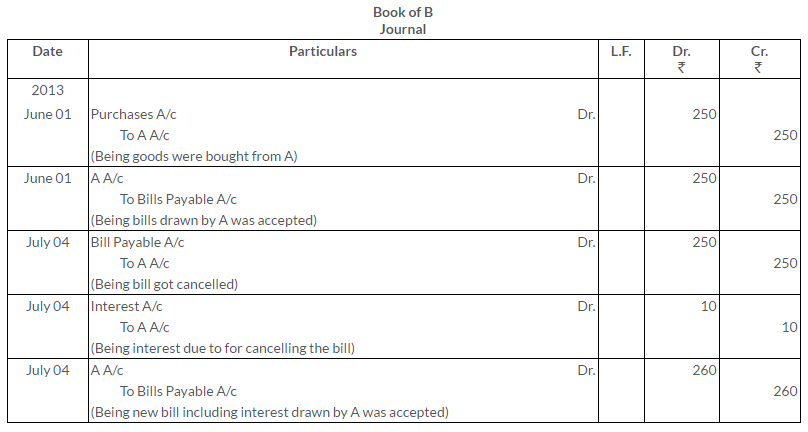
Question 32.
A sold goods to B on 1st September, 2013 for Rs.16,000. B immediately accepted a 3 months bill. On the due date, B requested that the bill be renewed for a further period of 2 months. A agreed provided interest at 9% p.a. was paid immediately in cash. To this B was agreeable. The second bill was met on the due date. Give the Journal entries in the books of A.
Solution:


Question 33.
On 1st May, 2013, Merchant and Co. sold goods to A.B and Co. valued at Rs.500 and drew upon them a bill at 3 months for the amount. A.B and Co. accepted the draft on presentation. When the bill was about to mature. A.B and Co. expressed their inability to meet it, and offered to pay Merchant and Co. Rs.200 in cash and to accept a fresh bill for the balance plus interest at 6% p.a. for 3 months. Merchant and Co. agreed to the proposal and bill was renewed. On maturity, the bill was duly met. Make the entries in the books of both the parties to record the above transactions.
Solution:
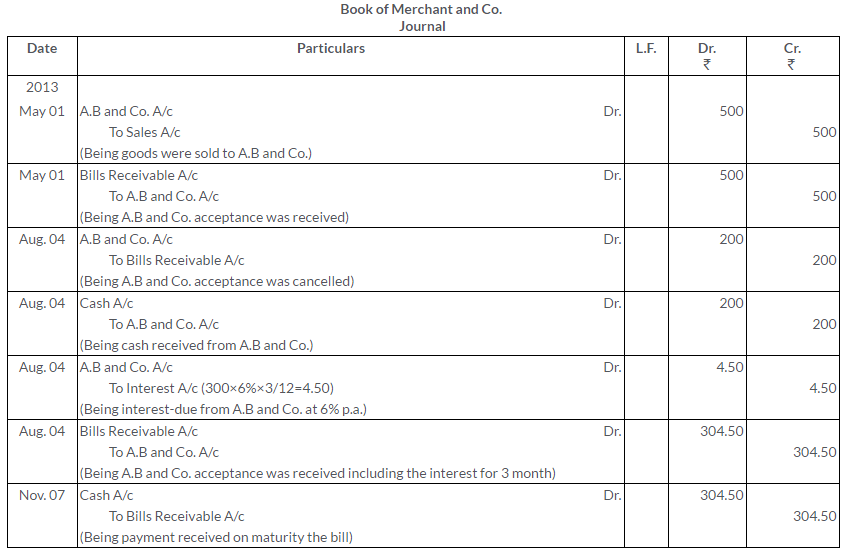

Question 34.
A owed B Rs.400. A accepted a Bill of Exchange at 3 months date for this amount which B discounted for Rs.380.
Give the necessary Journal entries in the books of A and B if this bill is:
(a) dishonoured on the due date; (b) met at maturity and (c) retired under rebate at 6% p.a. 2 months before its maturity.
Solution:
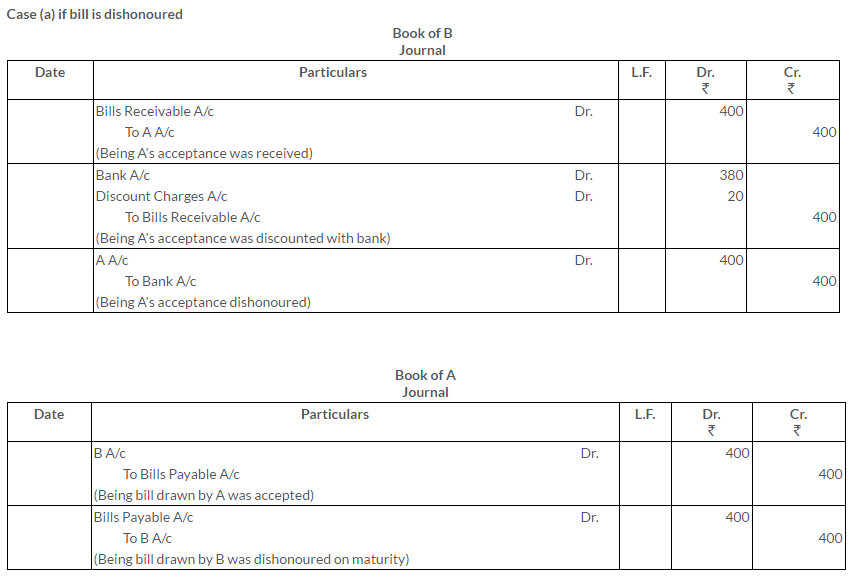


Question 35.
Amar sells goods to Bhola for Rs.10,000 and draws upon him a bill for the amount payable 3 months after date. The bill is accepted by Bhola. Amar discounts the bill with his bankers at a discount of Rs.150 inclusive of all charges. Bhola fails to meet this bill on maturity. Amar pays off his banker and his expenses amounting to Rs.100. Bhola gives a fresh bill, 2 months’ date to Amar for Rs.10,250, which he met at maturity.
Show the necessary Journal entries in Amar’s books.
Solution:

Question 36.
Amar purchased goods worth Rs.1,000 from Bimal on 1st January, 2013 and accepted a bill for 1 month drawn by Bimal for the same. Being unable to meet the bill on the due date, Amar requested Bimal to accept cash Rs.250 and draw a new bill for 2 months for the balance amount plus interest of Rs.10. Bimal accepted this proposal and drew on Amar another bill. The bill was duly met on the due date. Pass the Journal entries in the books of both the parties.
Solution:
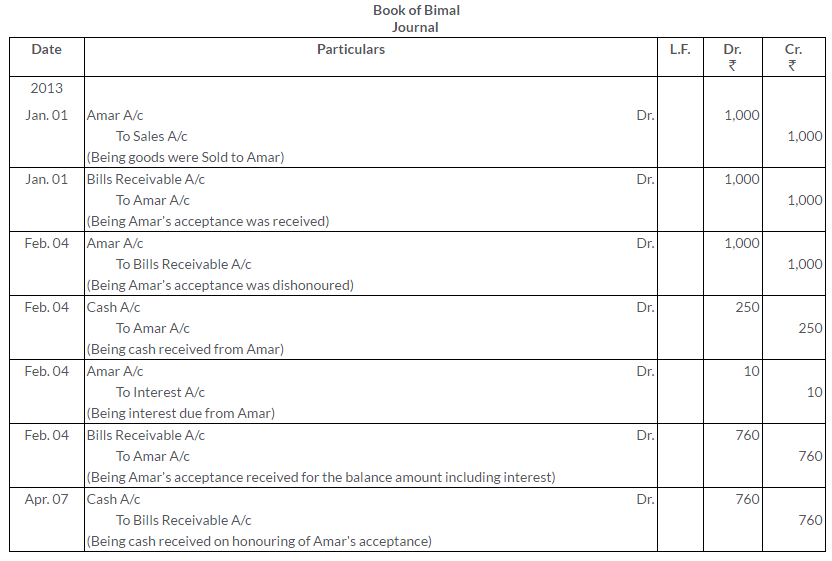
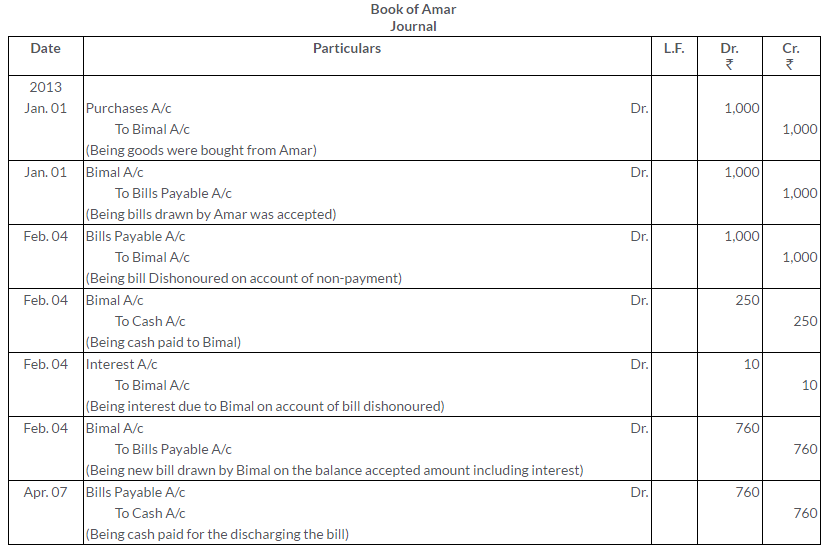
Question 37.
‘B’, being unable to meet his acceptance for Rs.2,000 due on 15th June, approaches the Drawer `A’ (who is in possession of the bill) on 30th June, with the request to receive Rs. 800 in cash and draw on him for the balance plus Rs. 15 for interest at 3 months date and cancel the old Bill for 2000.”A’ agrees to this. Pass the entries in the books of ‘A’ and ‘B’.
Solution:
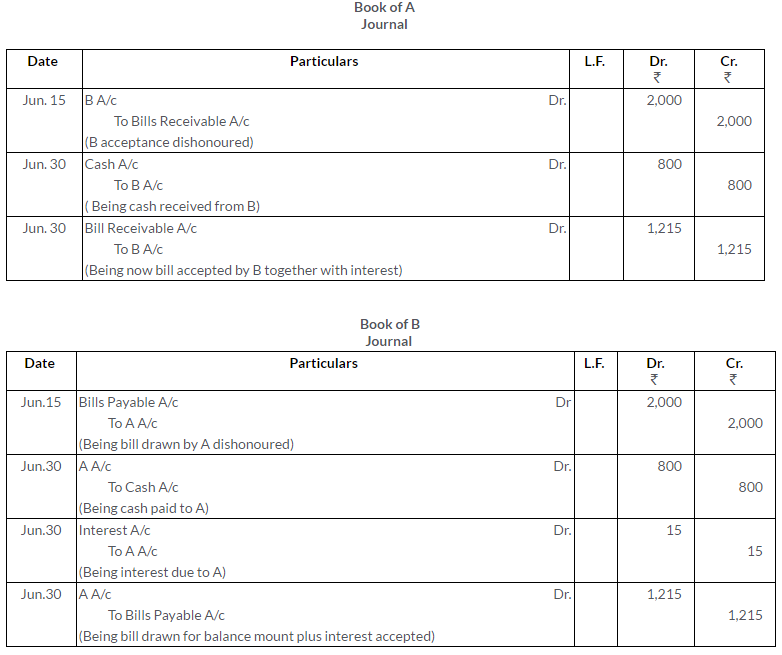
Question 38.
Give the Journal entries for the following:
a. B’s acceptance to us for Rs.1,000 due this day, renewed at his request for 3 months with interest @ 6% p.a.
b. Our bill to C. Chandra for Rs.5,000 renewed for 2 months with interest @ 6% p.a.
c. B’s acceptance of Rs.3,000 is discharged on his paying us cash 1,000 and accepting a fresh bill for the balance with interest Rs.100.
Solution:
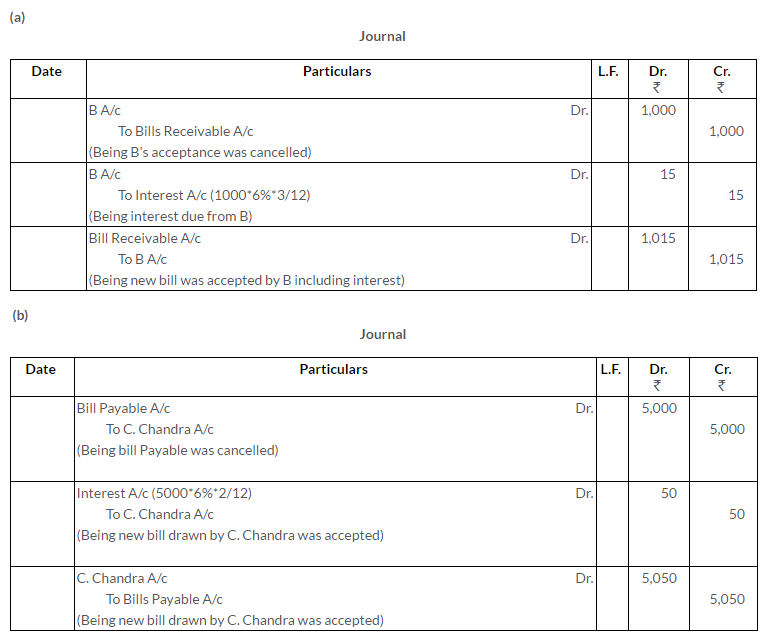

Question 39.
Leena sold goods to Meena on 1st March, 2009 for Rs.68,000 and drew two Bills of Exchange of the equal amount upon Meena payable after three months. Leena immediately discounted the first bill with her bank at 12% p.a. The bill was dishonoured by Meena and Bank paid Rs.55 as noting charges. The second bill was retired on 4th May, 2009 under a rebate of 6% p.a. with mutual agreement.
Journalize the above in the books of Leena and Meena.
(KVS 2010)
Solution:
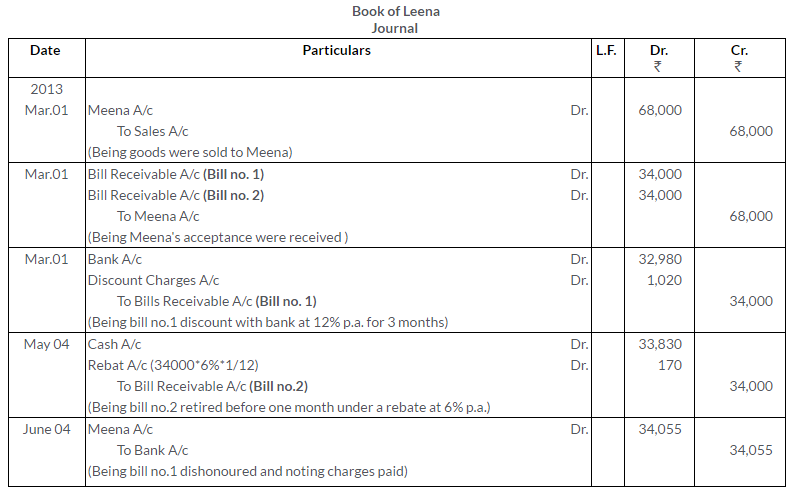

Question 40.
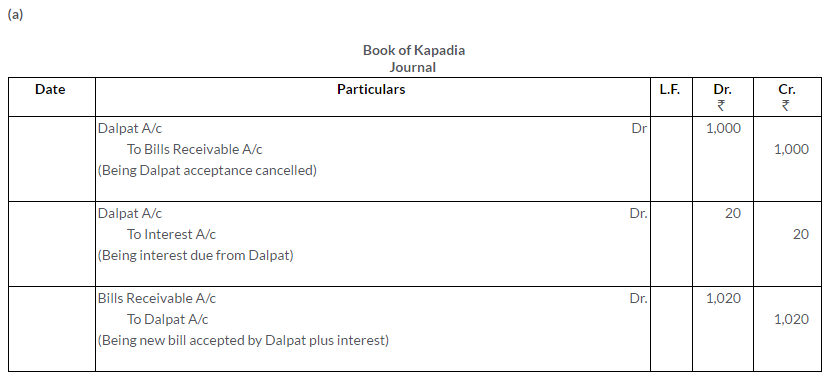
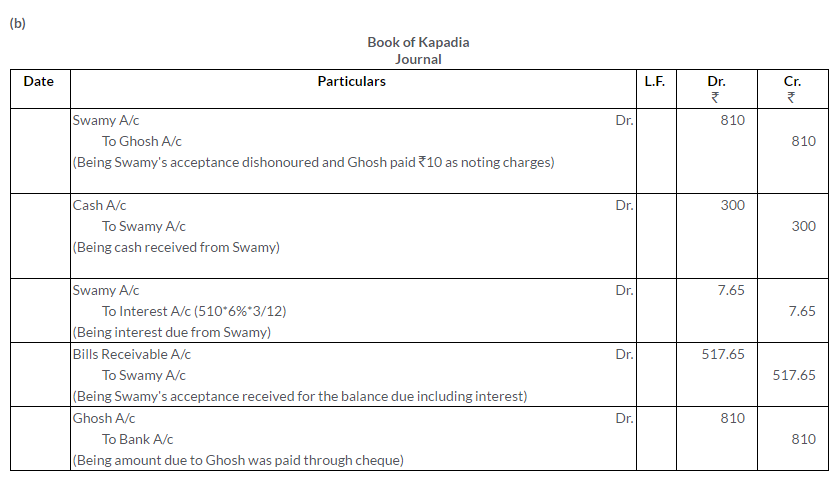
How will you record the following transactions in the books of Kapadia?
a. A bill received from Dalpat for Rs.1,000 has to be renewed; Dalpat agrees to pay Rs.20 as interest.
b. Swamy’s bill for Rs.800 endorsed in favour of Ghosh dishonoured. Ghosh pays Rs.10 as noting charges. Swamy pays Rs.300 immediately and agrees to accept a new bill for 3 months for the balance together with interest at 6% p.a. Ghosh’s Account is settled by cheque.
Solution:
Question 41.
Y purchased goods for Rs.6,000 on 1st June, 2011 from X and on the same date accepted a bill payable after three months. 3 days later, X endorsed the bill to Z. On maturity, the bill was dishonoured for non-payment and Z had to pay Rs.50 as noting charges. Two days after the dishonour of bill, Y paid Rs.2,000 to X and requested him to draw a second bill of the balance plus Rs.90 for the amount of interest, payable after two months. X accepted the proposal and draws the bill on Y, which was accepted by Y and was duly met on maturity.
Pass Journal entries for the above transactions in the books of X.
(MSE Chandigarh 2013)
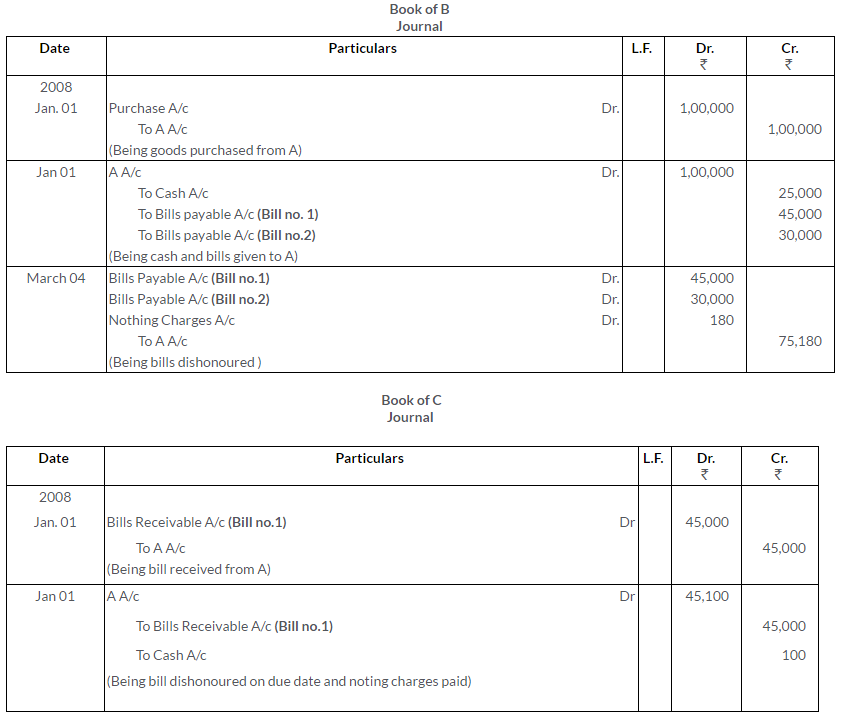
Solution:
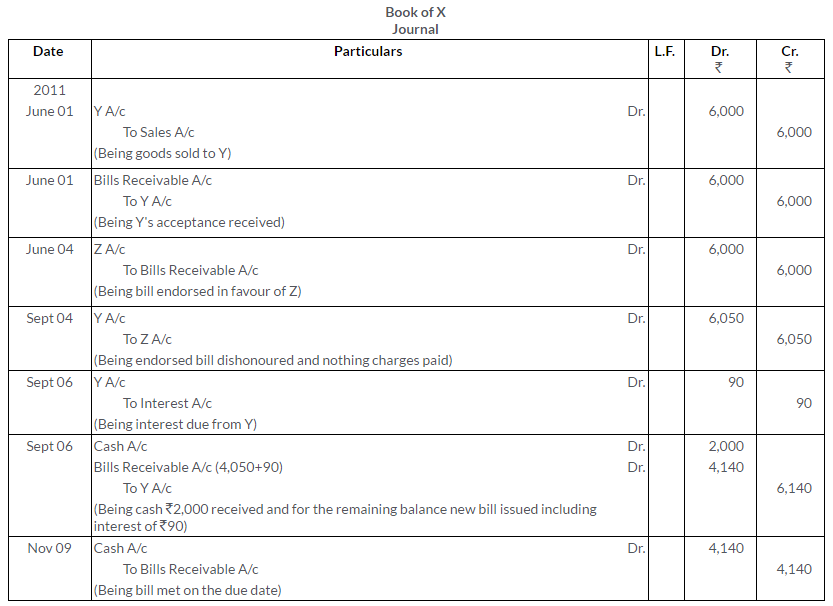
Question 42.
On 1st January, 2008, A sold goods to B for C Rs.1,00,000 received Rs.25,000 in cash and drew two bills, first Rs.45,000 and second for Rs.30,000 of two months each. Both bills duly accepted by B. First bill was endorsed to C in settlement of his account of Rs.45,000 and second bill was discounted from the bank at the rate of 12% p.a. On the due date of these bills, both bills were dishonoured. C has paid Rs. 100 and bank has paid Rs.80 as noting charges.
Pass Journal entries in the books of A, B and C.
(MSE Chandigarh.)
Solution:
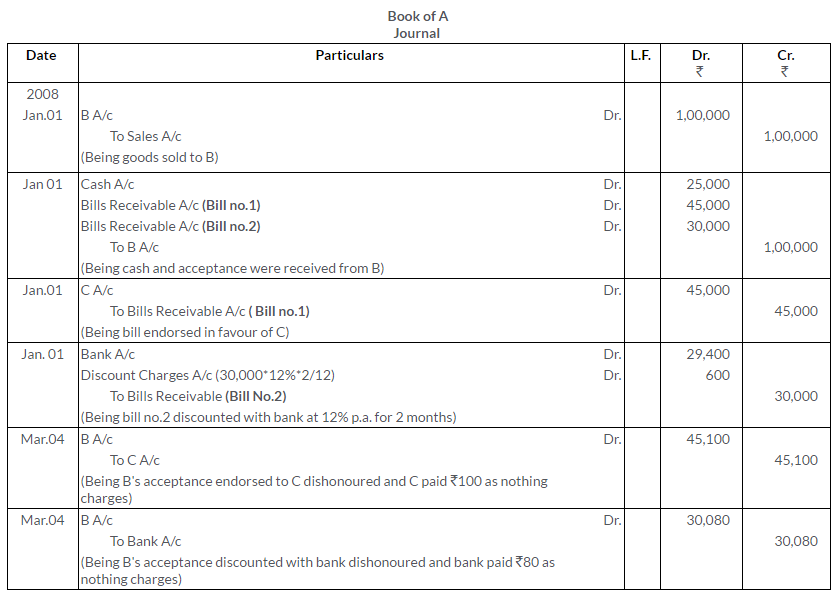
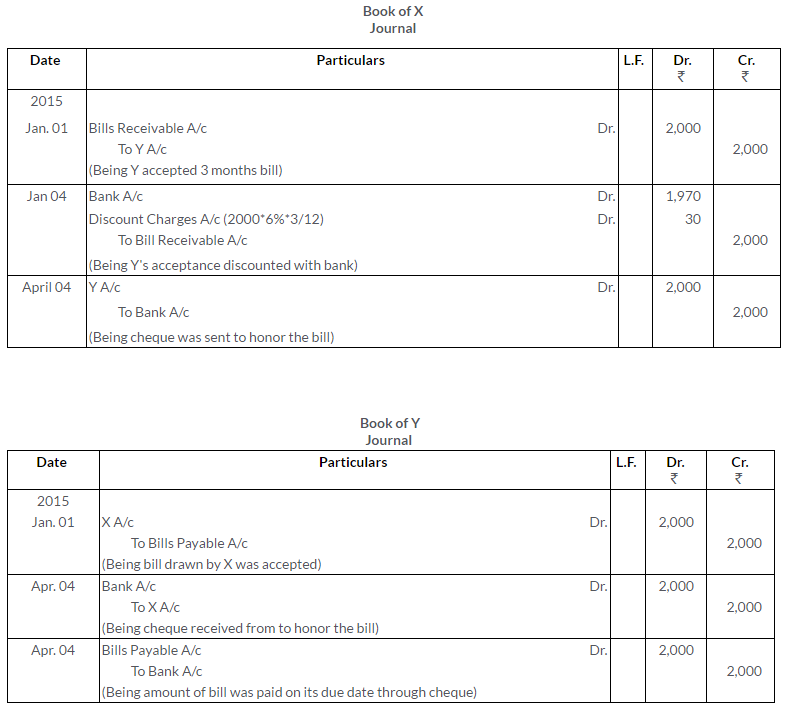
Question 43.
On 1st January, 2015, Y accepted a three months bill for Rs.2,000 drawn on him by X for the latter’s benefit. X discounted the bill on 4th January @ 6% p.a. and on the due date sent a cheque for Rs.2,000 in order to enable him to honor the bill. Y duly honoured his acceptance.
Pass the Journal entries in the books of X and Y.
Solution:
Question 44.
On 1st January, 2015, B accepted a three months bill for Rs.20,000 drawn on him by A for latter’s benefit. A discounted the bill on 4th January @ 20% p.a. and on the due date sent B a cheque for Rs.20,000 in order to enable him to honour the bill. B duly honored his acceptance. Pass the Journal entries in the books of A and B.
Solution:

Question 45.
For the mutual accommodation of P and Q, P draws a bill on Q for Rs.1,500. Q accepts the bill and returns it to P. P discounts the same with his bankers and receives Rs.1,464. The proceeds are shared between P and Q in proportion to 2/3rd and 1/3rd respectively. On the due date P remits his proportion to Q who meets the bill.
Pass the Journal entries in the books of P and Q to record the above transactions.
Solution:

Question 46.
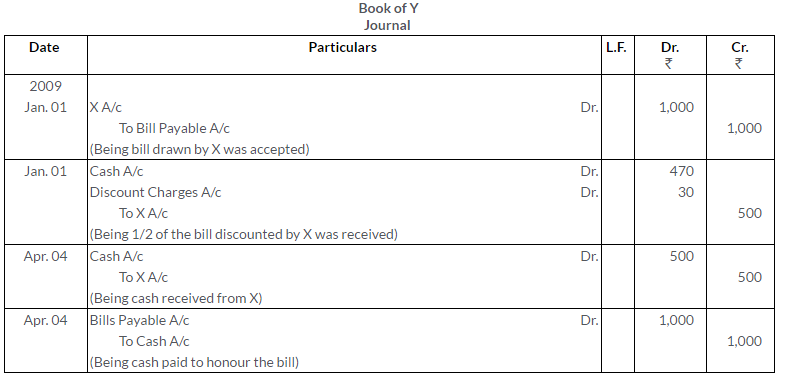
X, for the temporary and mutual accommodation of himself and Y, draws upon the latter a Bill of Exchange at 3 months for Rs.1,000. On 1st January, 2009, X discounts the bill at 6% and hands half the proceeds to Y. On the due date, X remits the amount due to Y who meets the bill. Pass the Journal entries in the books of both the parties.
Solution: