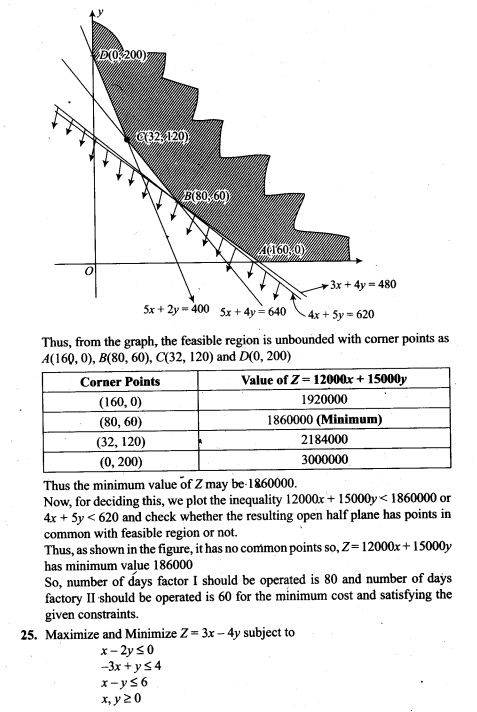
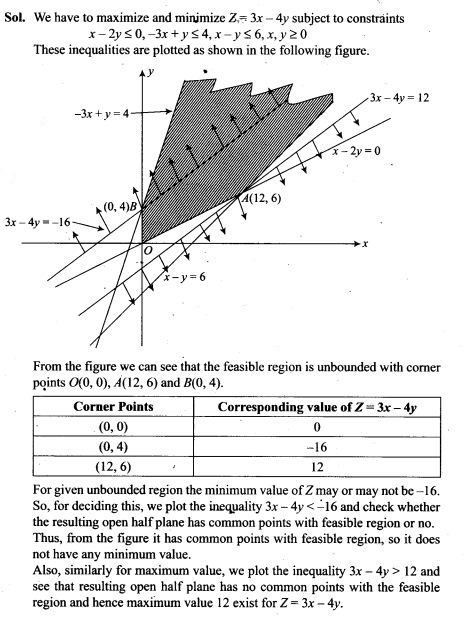
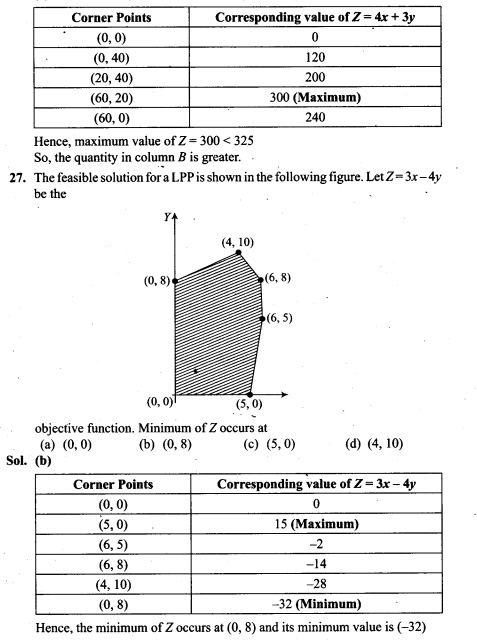
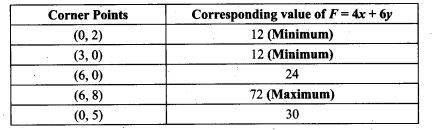
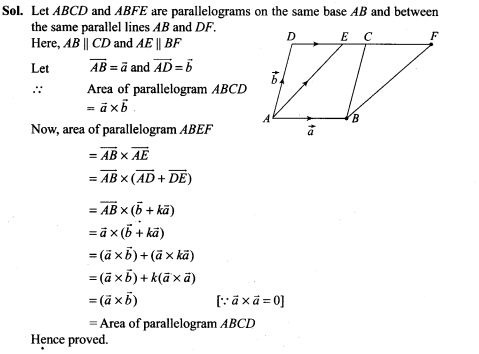
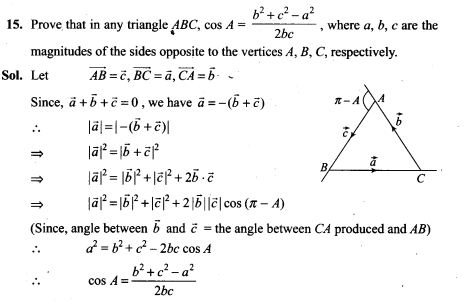
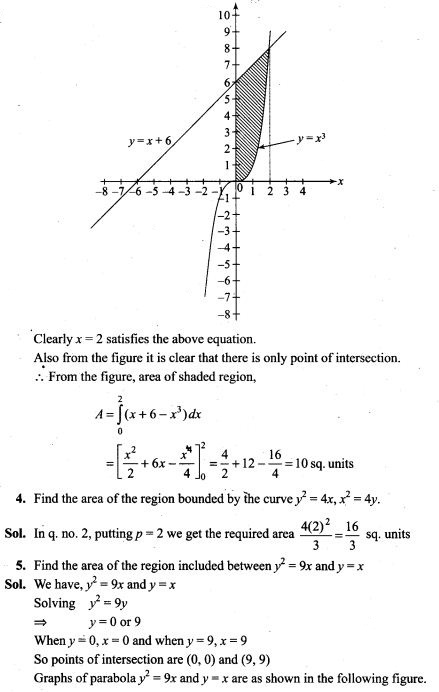
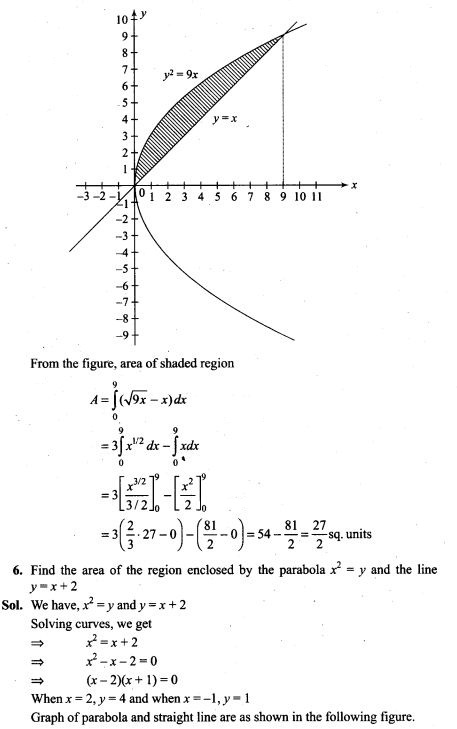
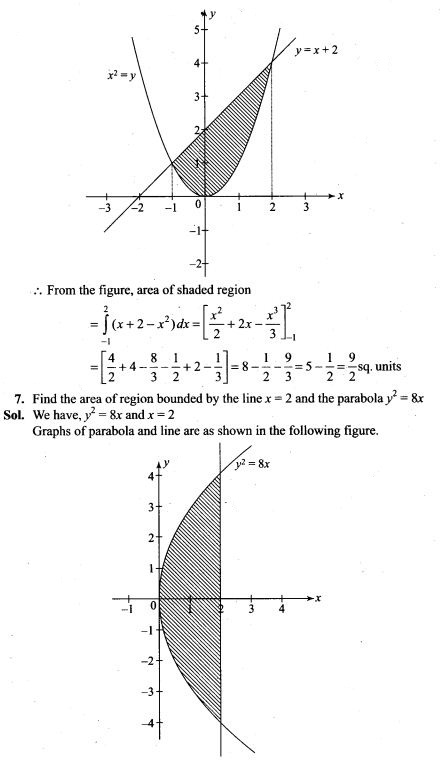
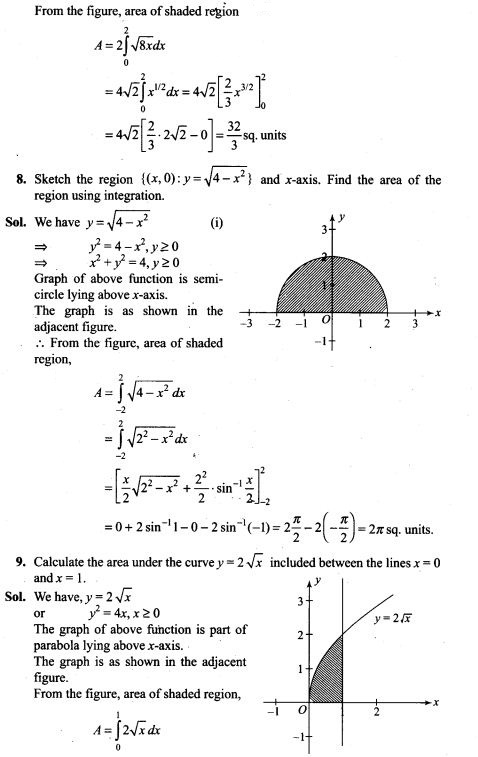
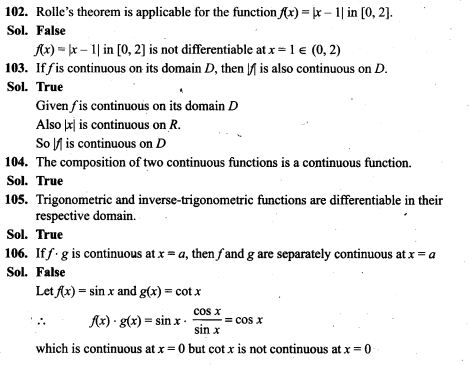
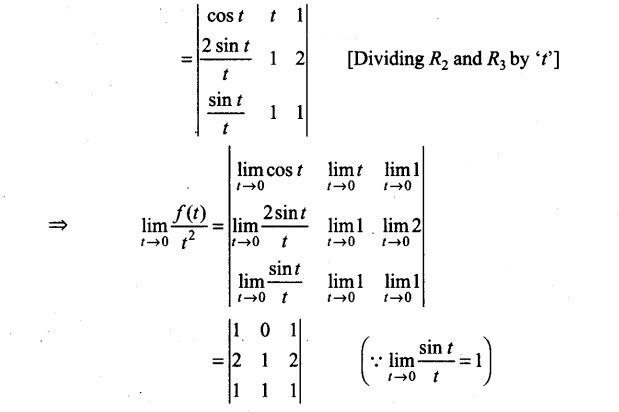
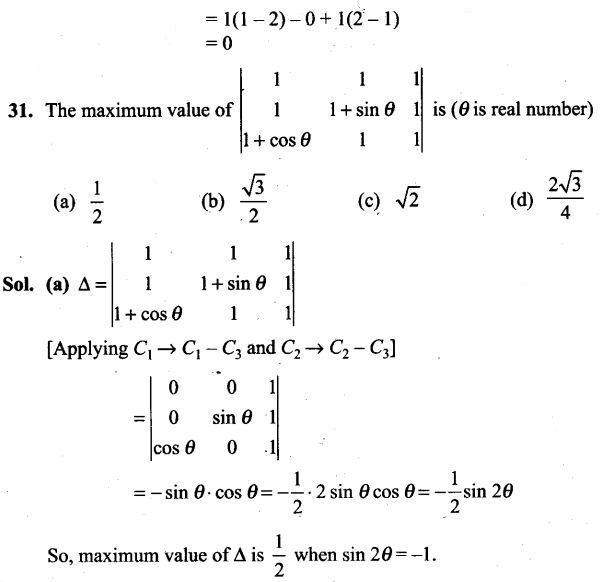
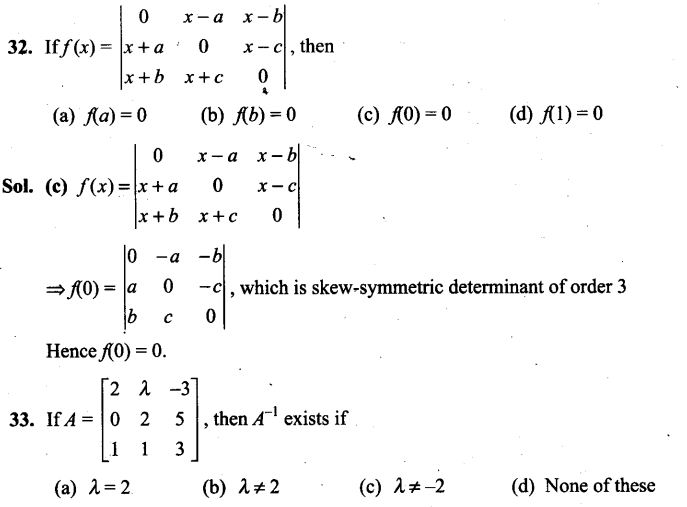
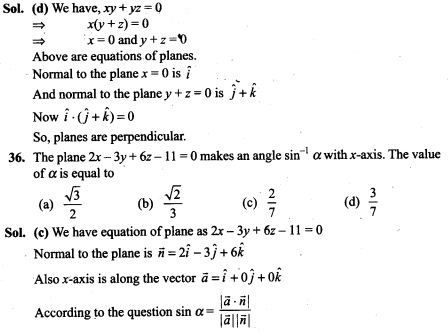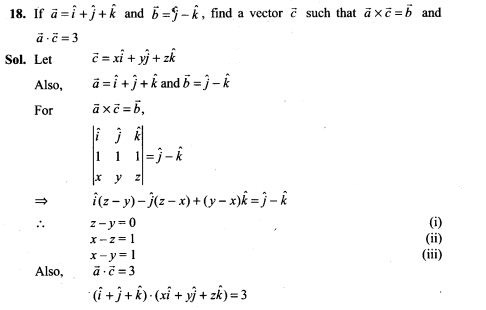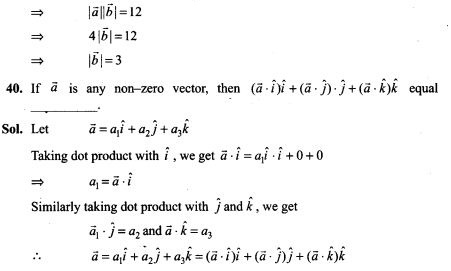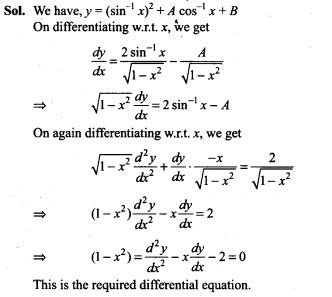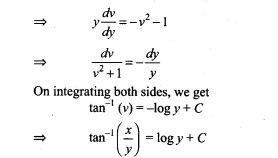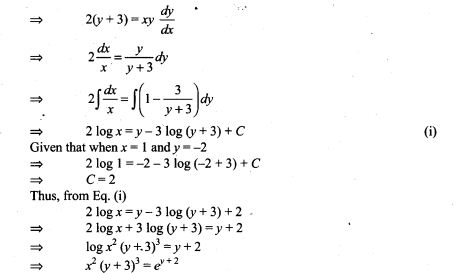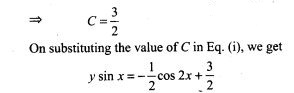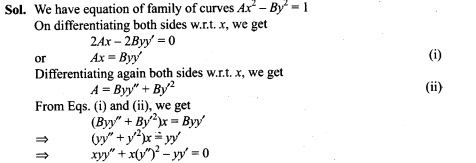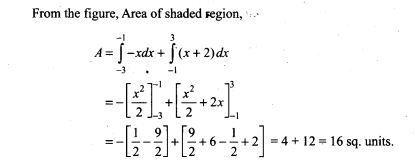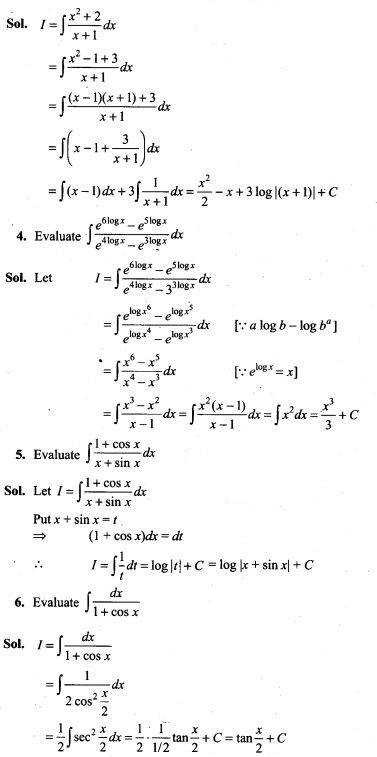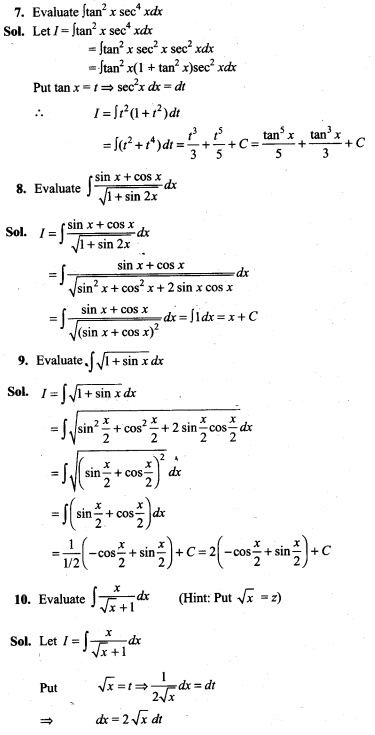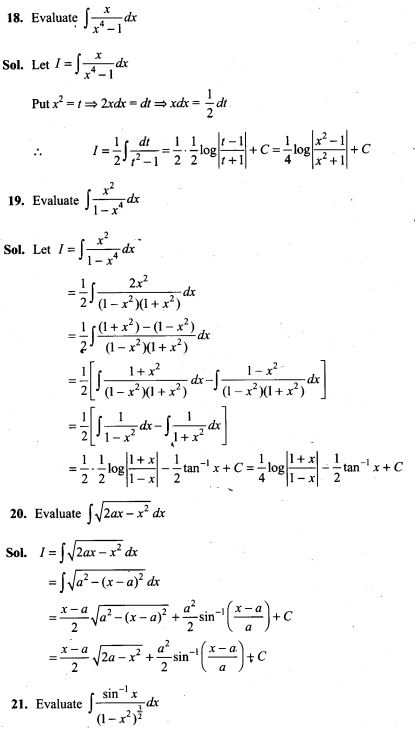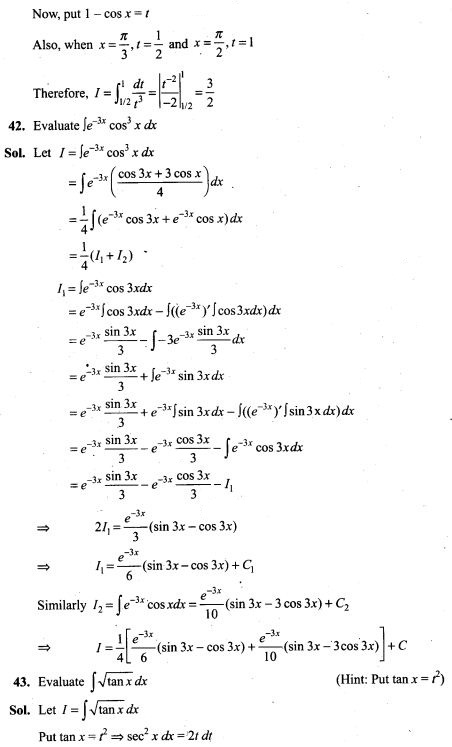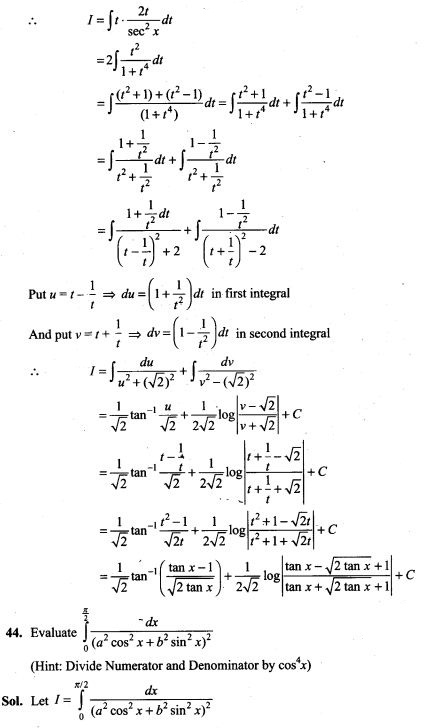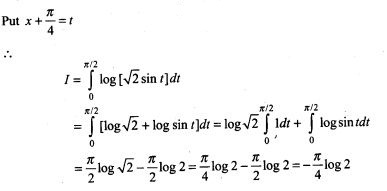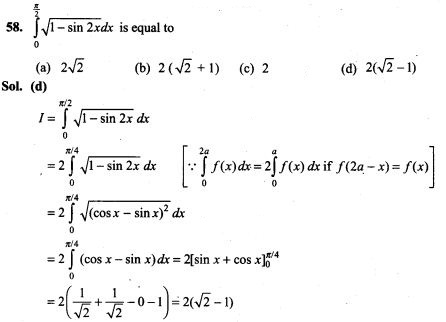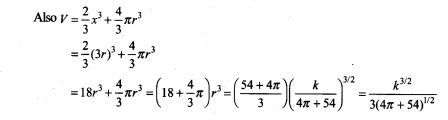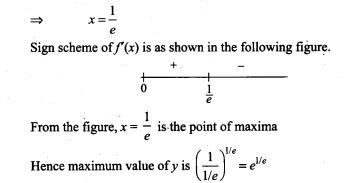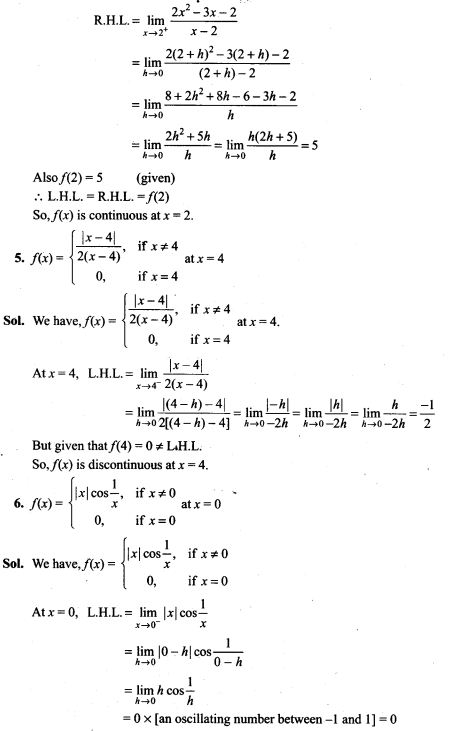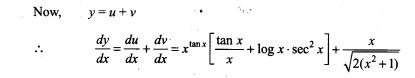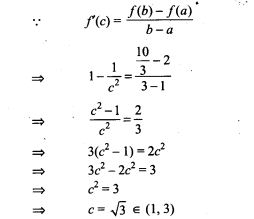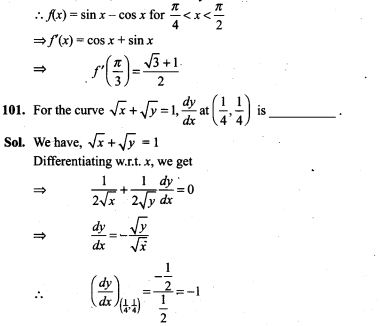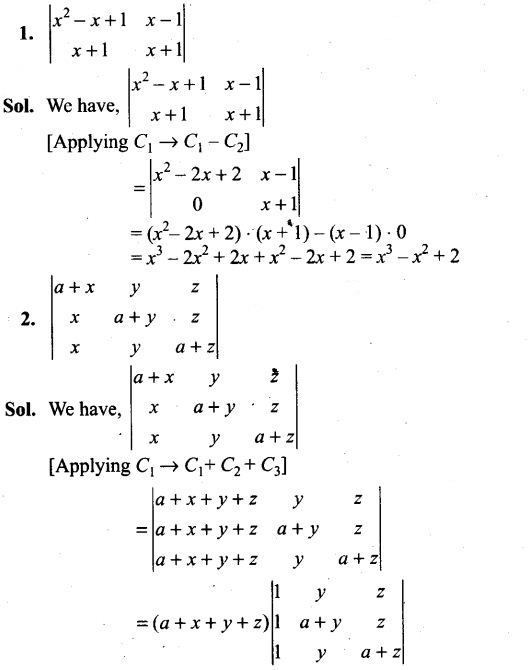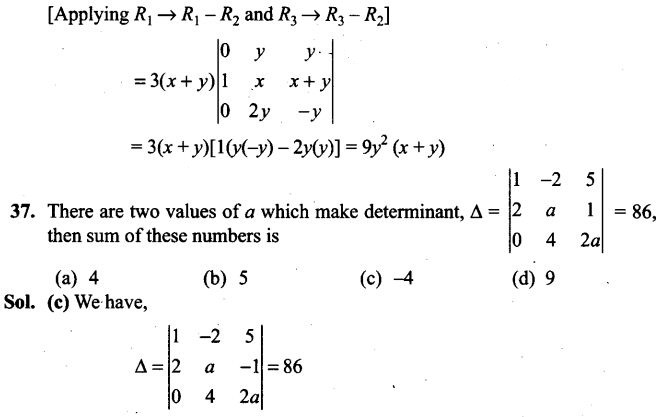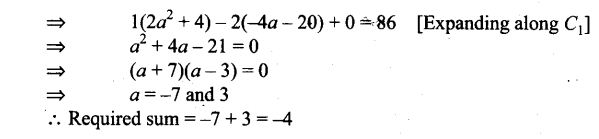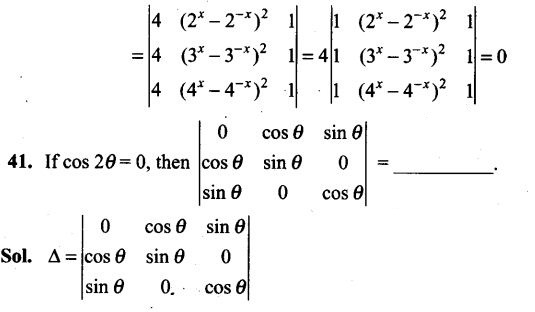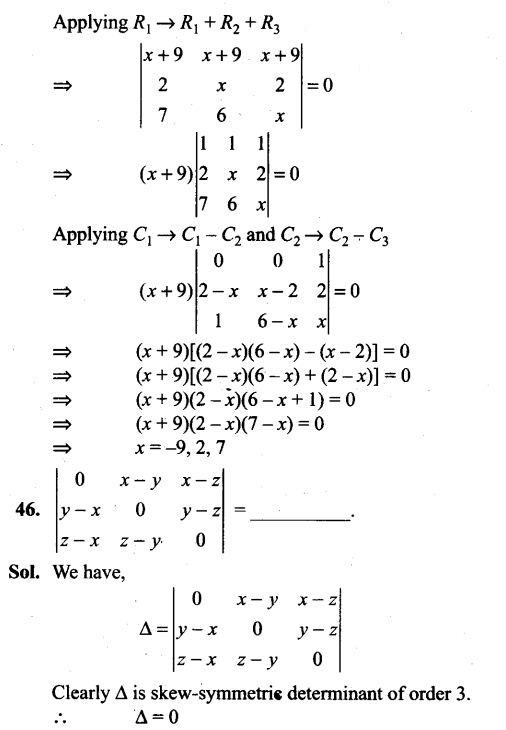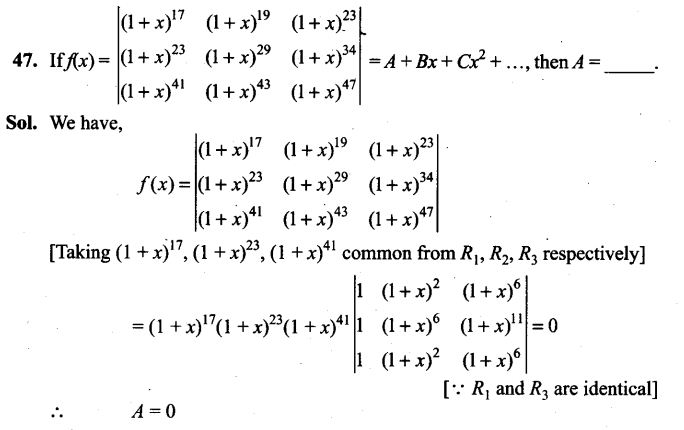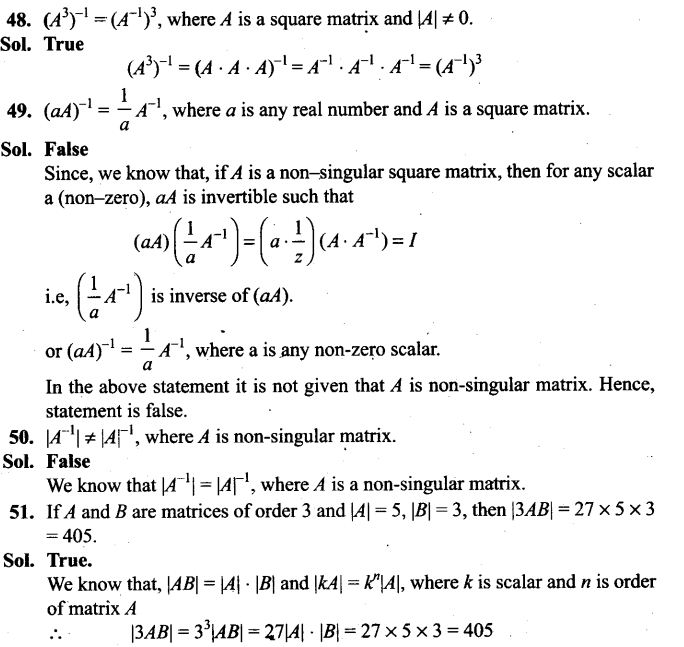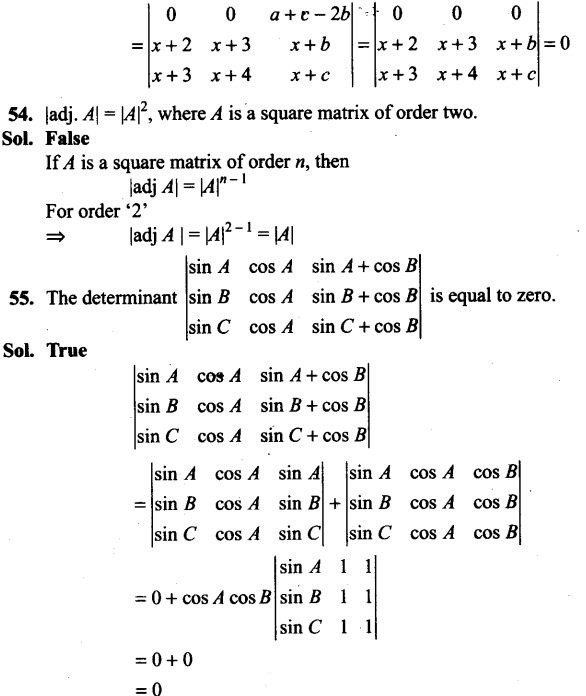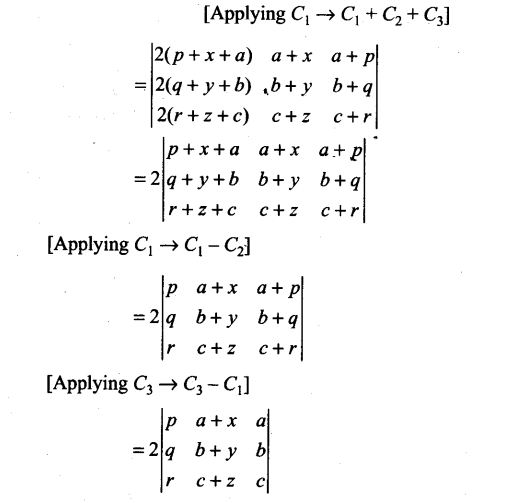NCERT Exemplar Problems Class 12 Mathematics Chapter 13 Probability
Short Answer Type Questions
1. For a loaded die, the probabilities of outcomes are given as under:
P(1) = P(2) = 0.2, P(3) = P(5) = P(6) = 0.1 and P(4) = 0.3.
The die is thrown two times. Let A and B be the events, ‘same number each time’, and ‘a total score is 10 or more’, respectively. Determine whether or not/l and B are independent.

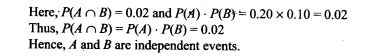
2. Refer to Exercise 1 above. If the die were fair, determine whether or not the events A and B are independent.
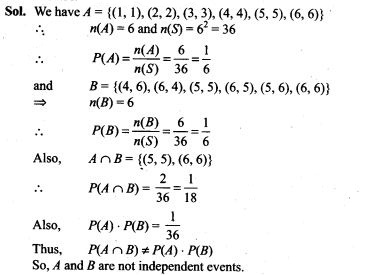

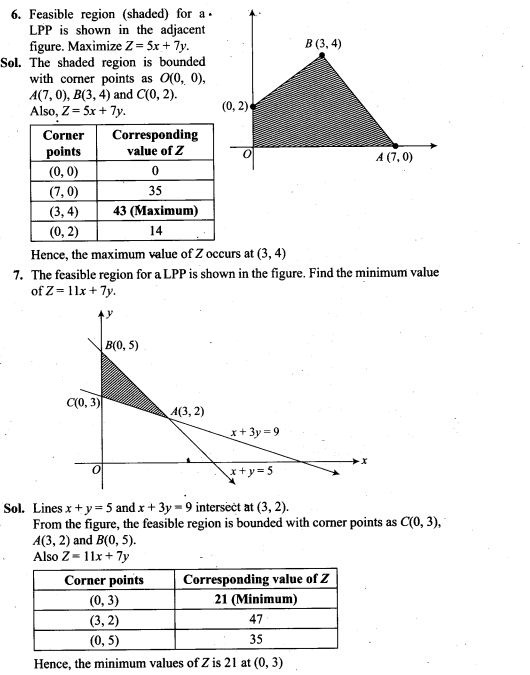
4. A bag contains 5 red marbles and 3 black marbles. Three marbles are drawn one by one without replacement. What is the probability that at least one of the three marbles drawn be black, if the first marble is red?

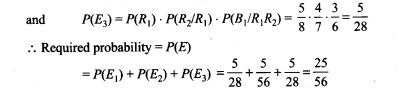
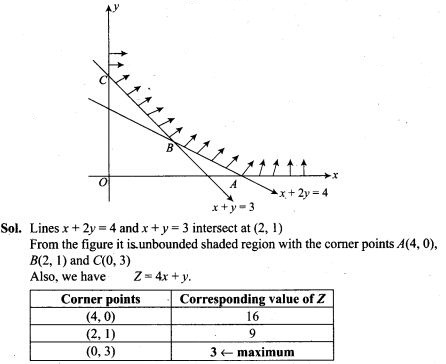
5. Two dice are thrown together and the total score is noted. The events E, F and G are ‘a total of 4’, ‘a total of 9 or more’, and ‘a total divisible by 5’, respectively. Calculate P(E), P(F) and P(G) and decide which pairs of events, if any, are independent.

6. Explain why the experiment of tossing a coin three times is said to have binomial distribution.
Sol. We know that, in a Bindmial distribution,
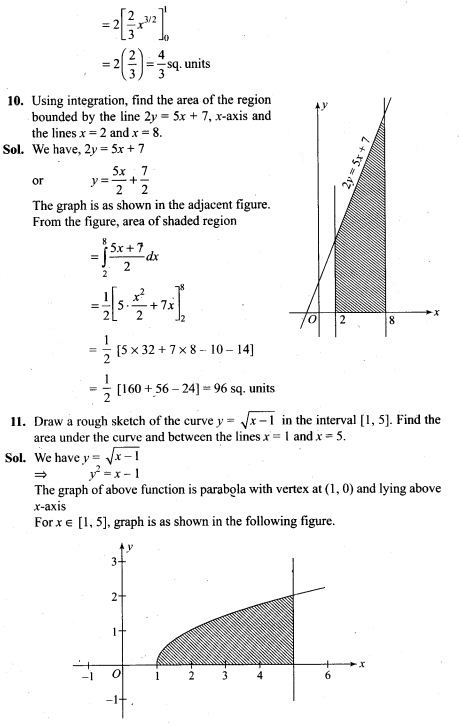
(i) There are 2 outcomes for each trial
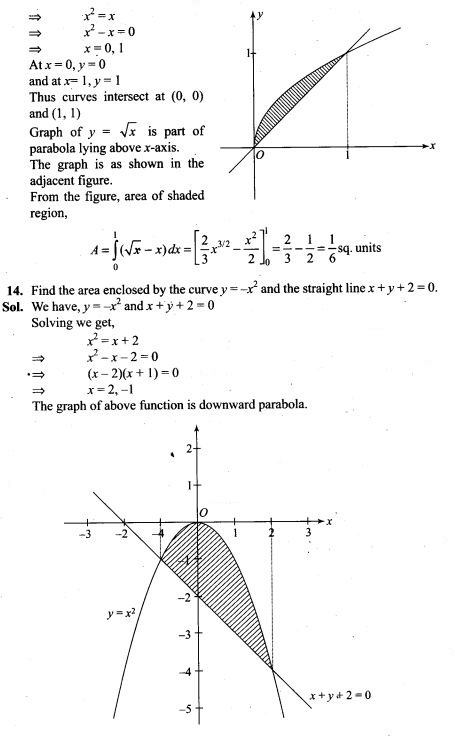
(ii) There is a fixed number of trials
(iii) The probability of success must be the same for all the trials.
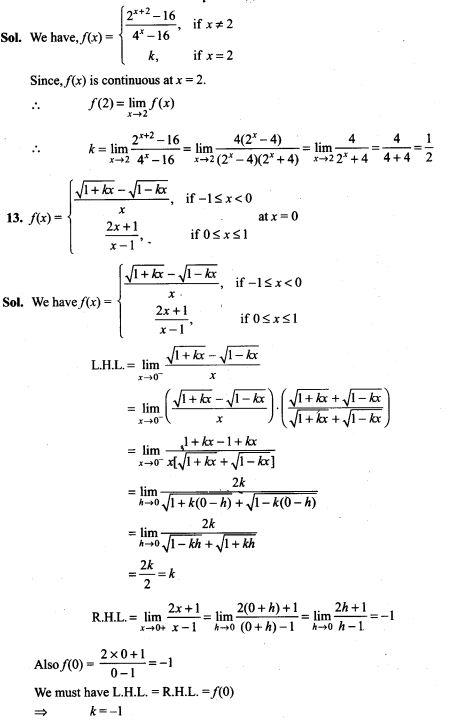
When coin is tossed, possible outcomes are Head and Tail.
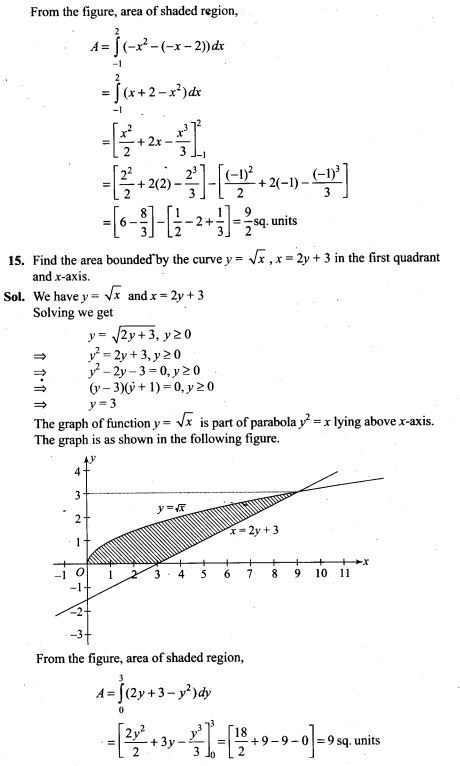
Since coin is tossed three times, we have fixed number of trials.
Also probability of Head and Tail in each trial is 1/2.
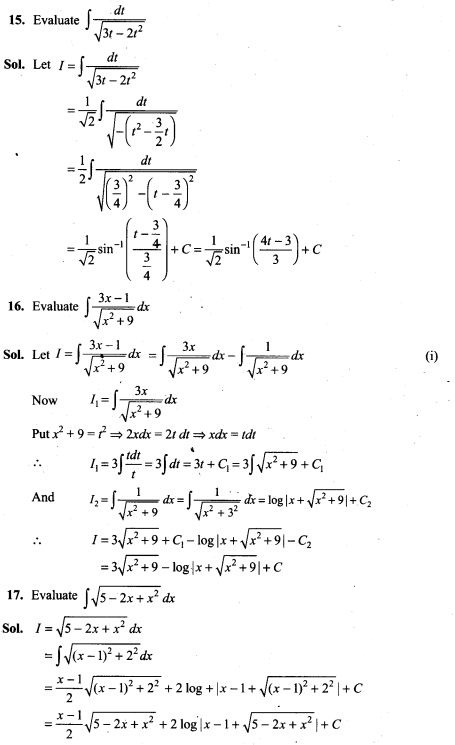
Thus given experiment is said to have binomial distribution.



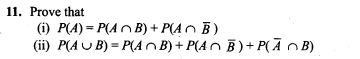
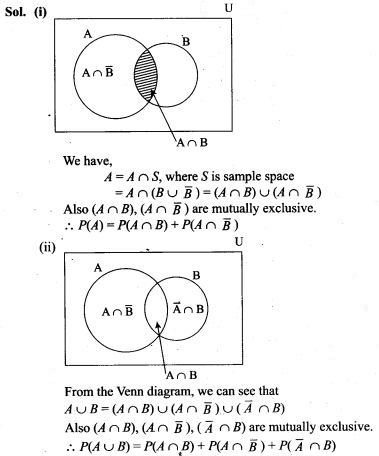
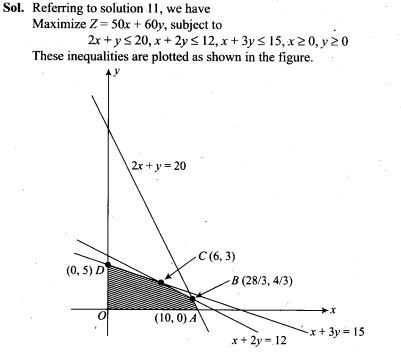
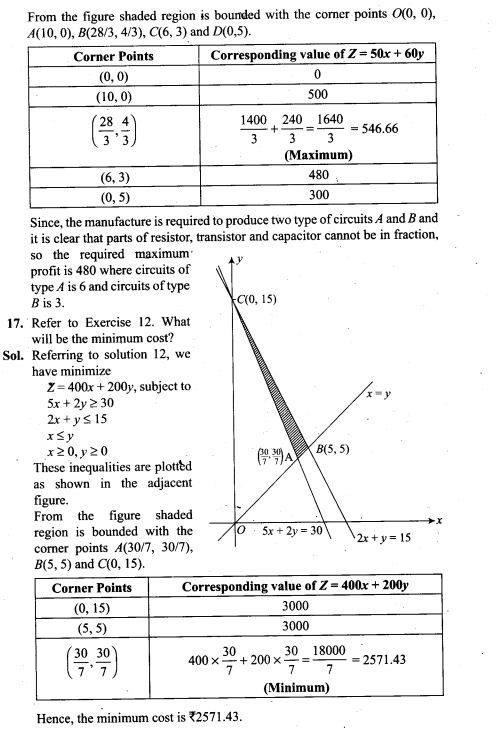
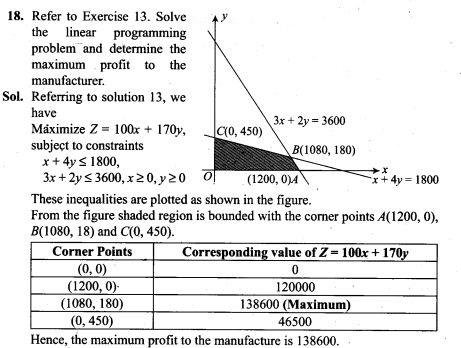
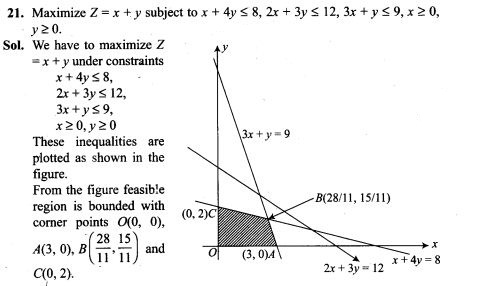
12. If X is the number of tails in three tosses of a coin, determine the standard deviation of X.

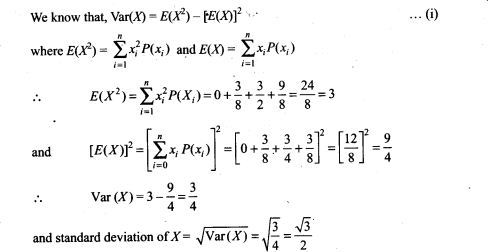
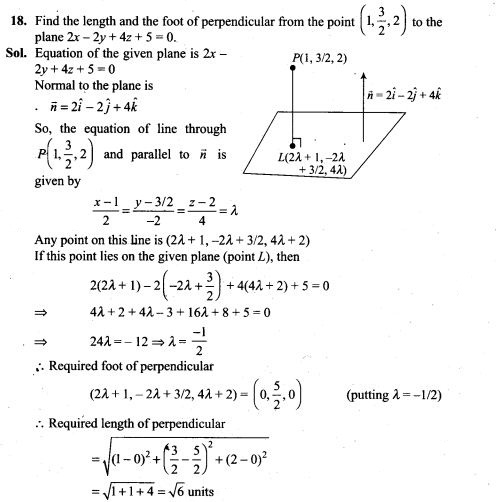
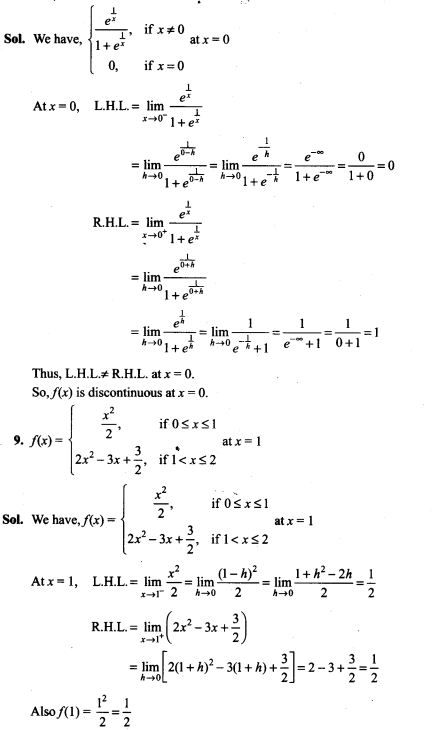
13. In a dice game, a player pays a stake of Rs 1 for each throw of a die. She receives Rs 5 if the die shows a 3, Rs 2 if the die shows a 1 or 6, and nothing otherwise. What is the player’s expected profit per throw over a long series of throws?

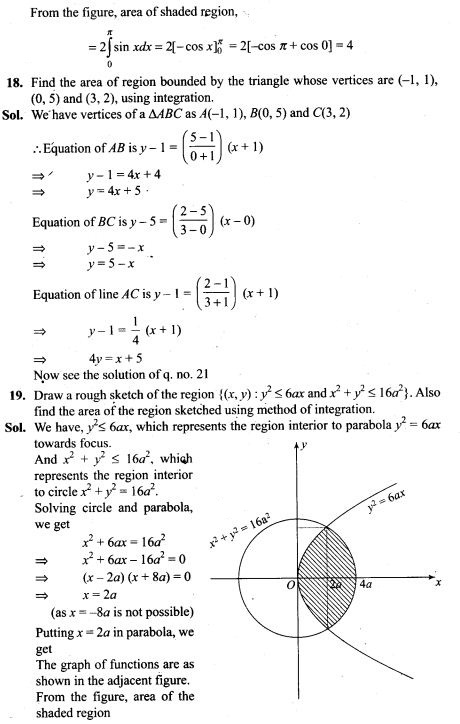
14. Three dice are thrown at the same time. Find the probability of getting three two’s, if it is known that the sum of the numbers on the dice was six.

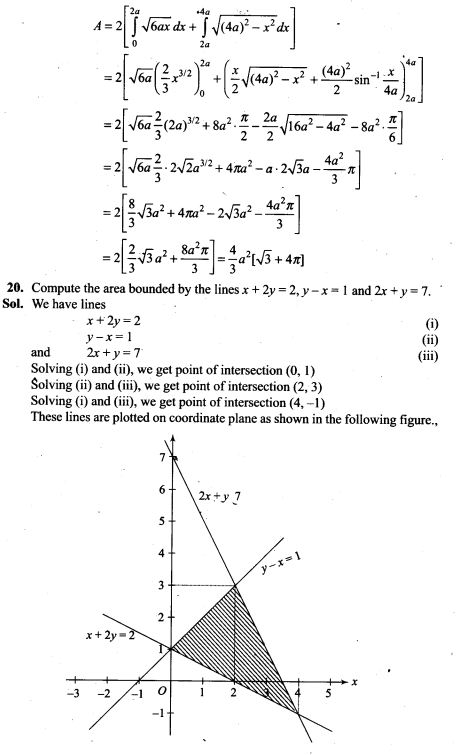
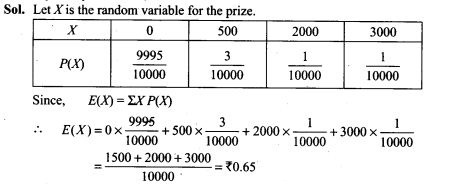
15. Suppose 10,000 tickets are sold in a lottery each for Rs 1. First prize is of Rs 3000 and the second prize is of Rs 2000. There are three third prizes of Rs.500 each. If you buy one ticket, what is your expectation?
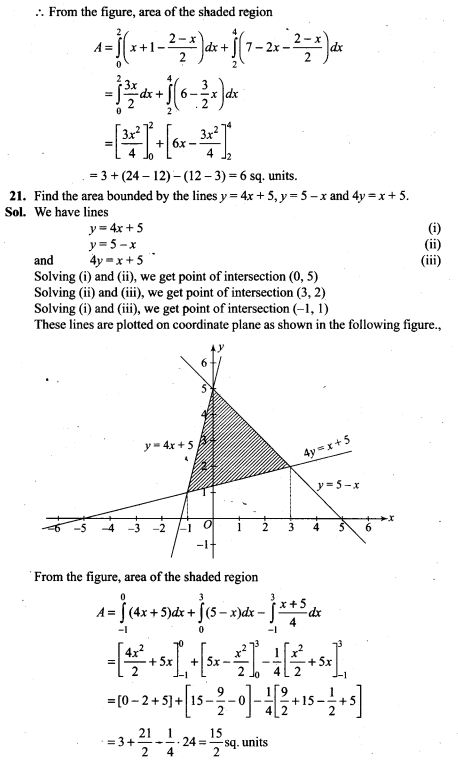
16. A bag contains 4 white and 5 black balls. Another bag contains 9 white and 7 black balls. A ball is transferred from the first bag to the second and then a ball is drawn at random from the second bag. Find the probability that the ball drawn is white.

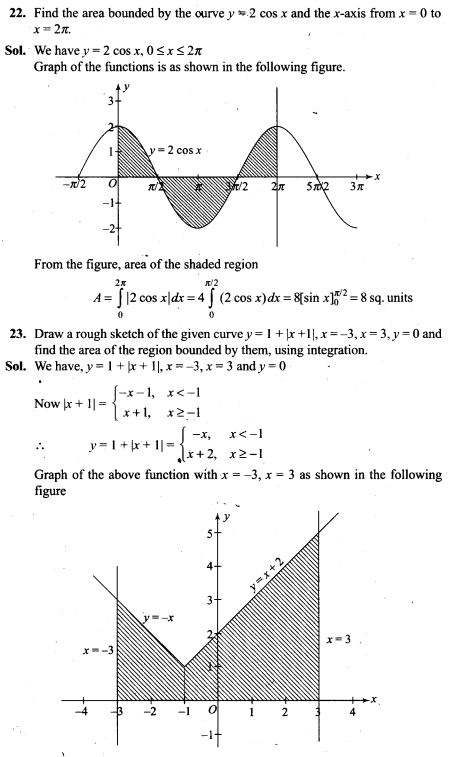
17. Bag I contains 3 black and 2 white balls, Bag II contains 2 black and 4 white balls. A bag and a ball is selected at random. Determine the probability of selecting a black ball.

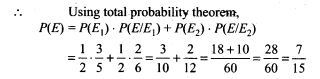
18. A box has 5 blue and 4 red balls. One ball is drawn at random and not replaced. Its colour is also not noted. Then another ball is drawn at random. What is the probability of second ball being blue?

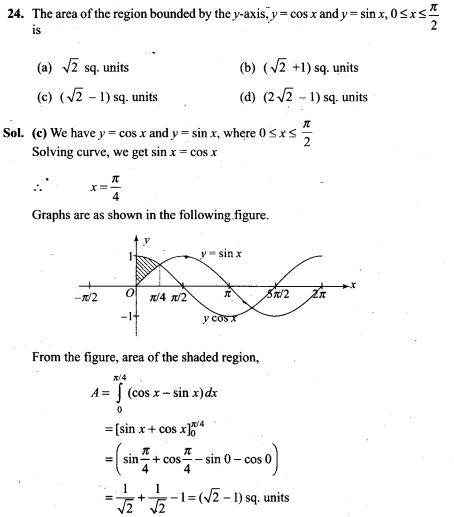
19. Four cards are successively drawn without replacement from a deck of 52 playing cards. What is the probability that all the four cards are kings?
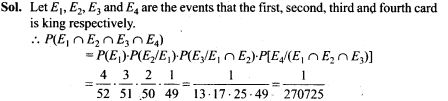
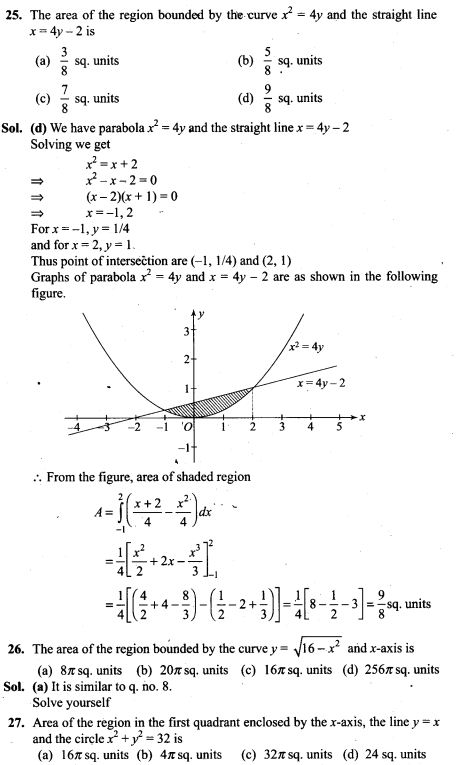
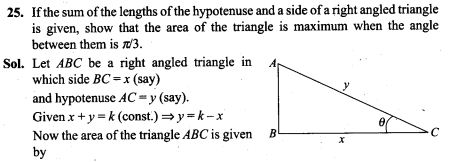
20. A die is thrown 5 times. Find the probability that an odd number will come up exactly three times.
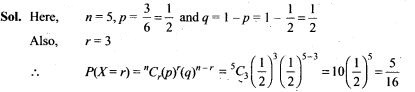
21. Ten coins are tossed. What is the probability of getting at least 8 heads?
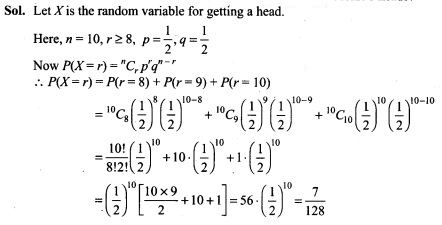
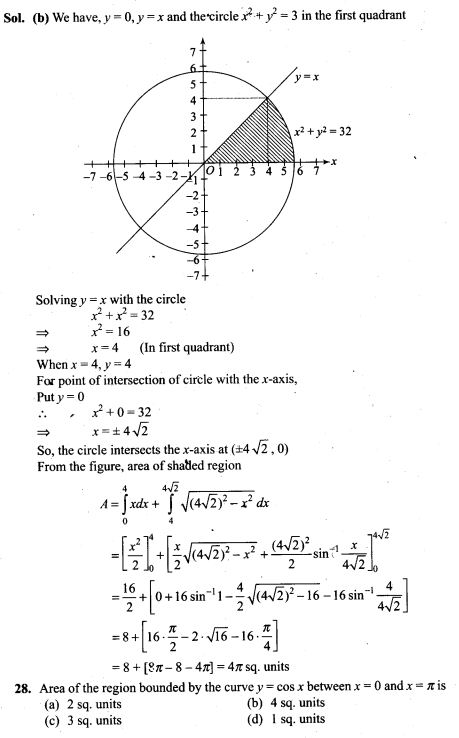
22. The probability of a man hitting a target is 0.25. He shoots 7 times. What is the probability of his hitting at least twice?
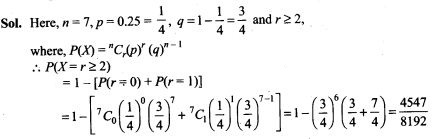
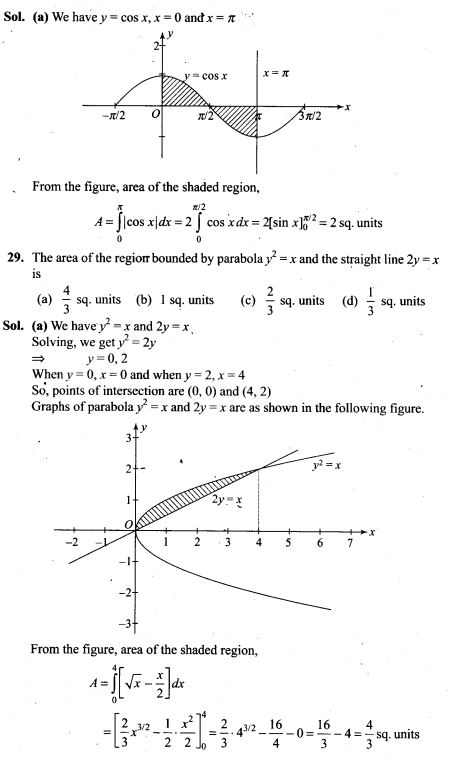
23. A lot of 100 watches is known to have 10 defective watches. If 8 watches are selected (one by one with replacement) at random, what is the probability that there will be at least one defective watch?





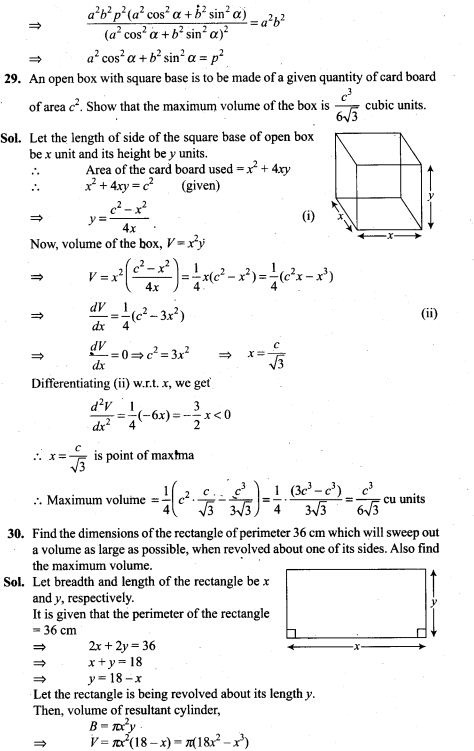
31. A factory produces bulbs. The probability that any one bulb is defective is 1/50 and they are packed in boxes of 10. From a single box, find the probability that
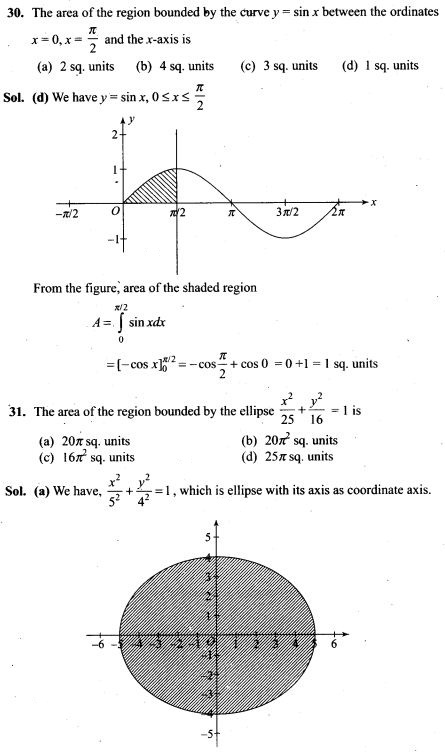
(i) none of the bulbs is defective
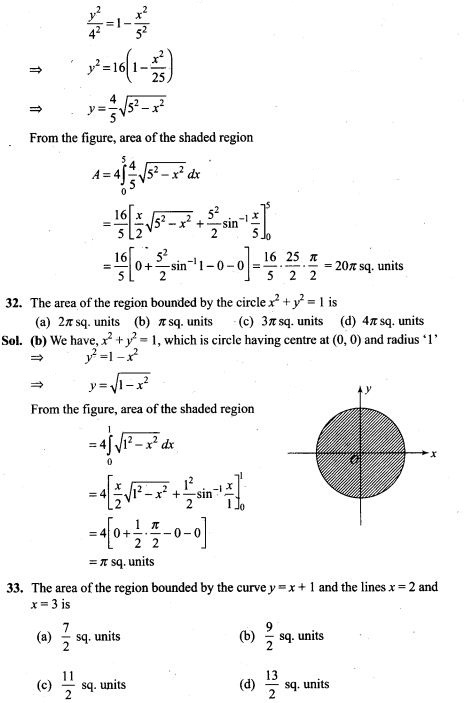
(ii) exactly two bulbs are defective
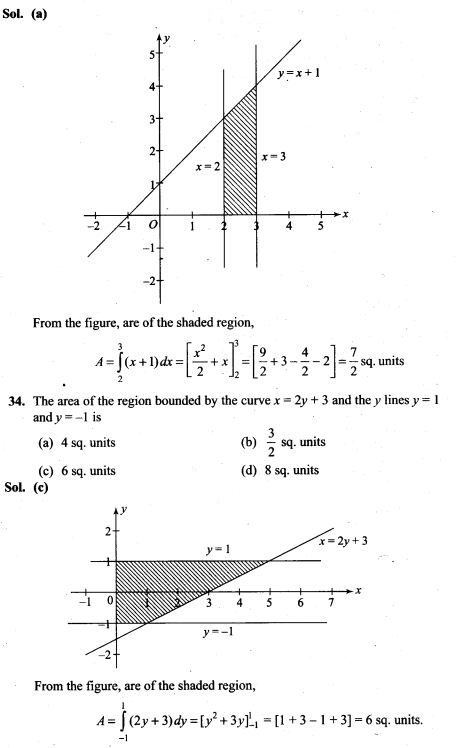
(iii) more than 8 bulbs work properly

32. Suppose you have two coins which appear identical in your pocket. You know that one is fair and one is 2-headed. If you take one out, toss it and get a head, what is the probability that it was a fair coin?
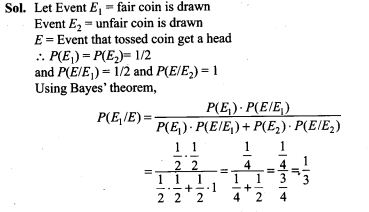
33. Suppose that 6% of the people with blood group O are left handed and 10% of those with other blood groups are left handed. 30% of the people have blood group O. If a left handed person is selected at . random, what is the probability that he/she will have blood group O?

35. Find the probability distribution of the maximum of the two scores obtained when a die is thrown twice . Determine also the mean of the distribution.

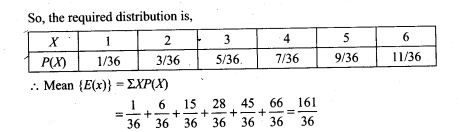
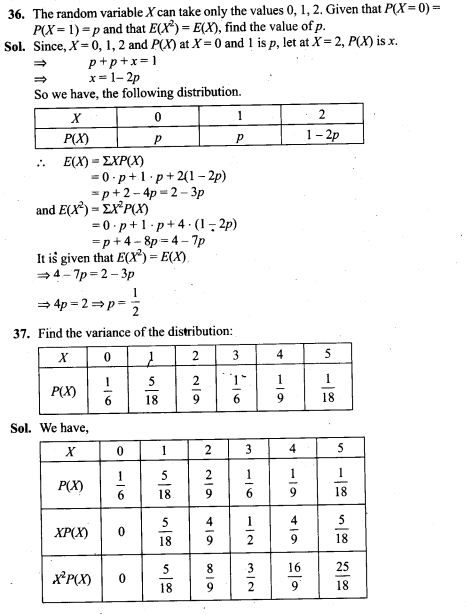
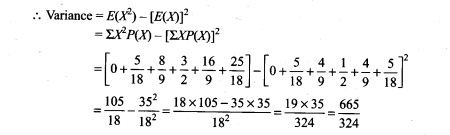
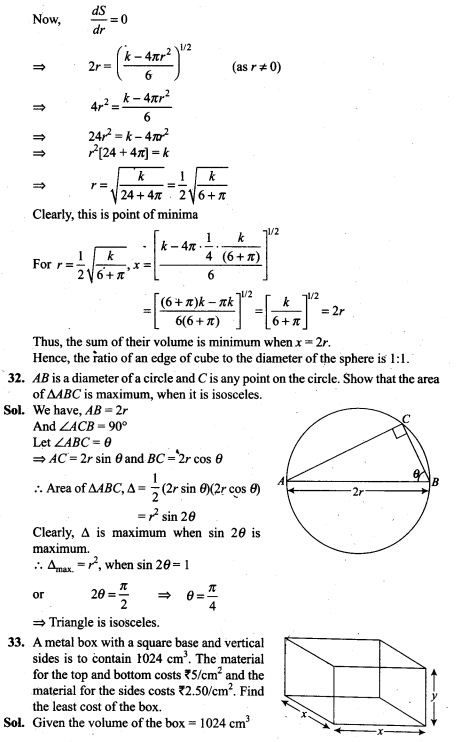
38. A and B throw a pair of dice alternately. A wins the game if he gets a total of 6 and B wins if she gets a total of 7. If A starts the game, find the probability of winning the game by A in third throw of the pair of dice.
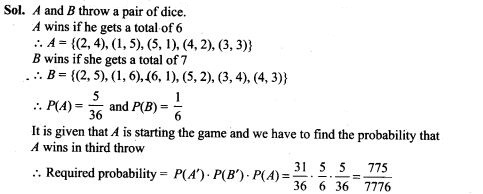

40. An um contains m white and n black balls. A ball is drawn at random and is put back into the um along with k additional balls of the same colour as that of the ball drawn. A ball is again drawn at random. Show that the probability of drawing a white ball now does not depend on k.

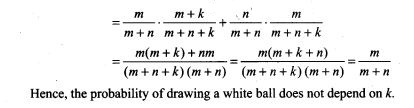
Long Answer Type Questions

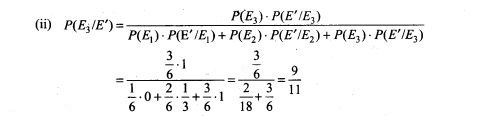
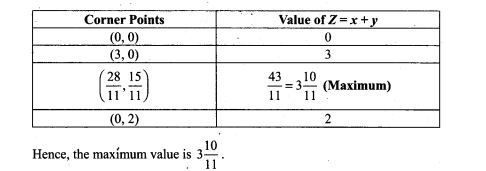
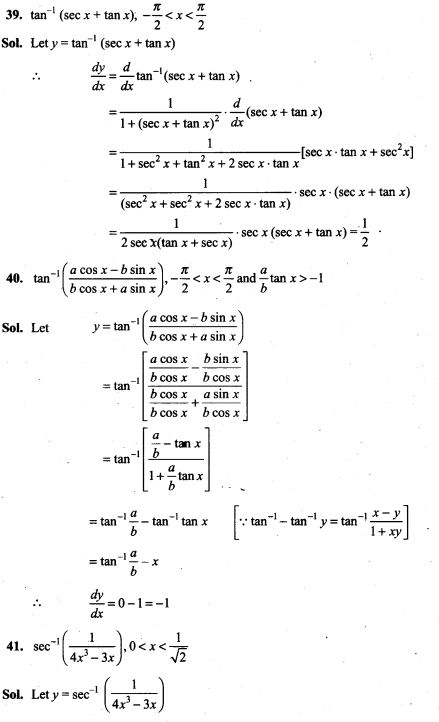
43. A shopkeeper sells three types of flower seeds A1,A2 and A3. They are sold as a mixture where the proportions are 4:4:2 respectively. The germination rates of the three types of seeds are 45%, 60% and 35%. Calculate the probability
(i) of a randomly chosen seed to germinate
(ii) that it will not germinate given that the seed is of type A3,
(iii) that it is of the type A2 given that a randomly chosen seed does not germinate.

44. A letter is known to have come either from TATA NAGAR or from CALCUTTA. On the envelope, just two consecutive letter TA are visible. What is the probability that the letter came from TATA NAGAR.
Sol. Let Ex be the event that letter is from TATA NAGAR and E2 be the event that letter is from CALCUTTA.

45. There are two bags, one of which contains 3 black and 4 white balls while the other contains 4 black and 3 white balls. A die is thrown. If it shows up 1 or 3, a ball is taken from the 1st bag; but it shows up any other number, a ball is chosen from the second bag. Find the probability of choosing a black ball.

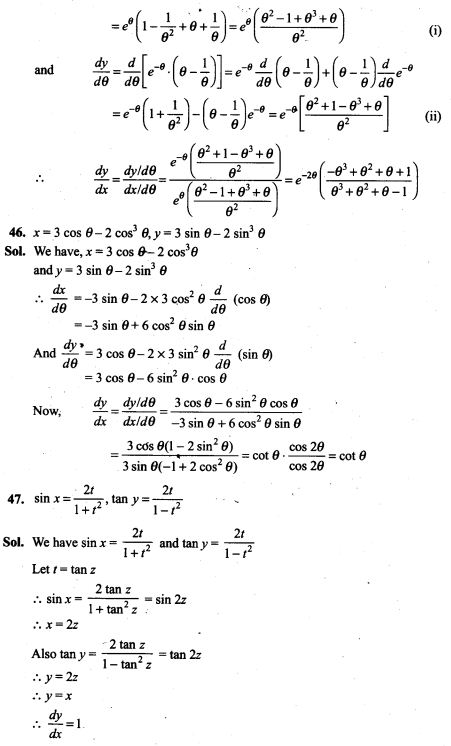
46. There are three urns containing 2 white and 3 black balls, 3 white and 2 black balls, and 4 white and 1 black balls, respectively. There is an equal probability of each urn being chosen. A ball is drawn at random from the chosen urn and it is found to be white. Find the probability that the ball drawn was from the second urn.
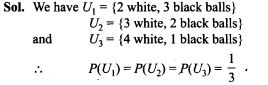

47. By examining the chest X ray, the probability that TB is detected when a person is actually suffering is 0.99. The probability of ah healthy person diagnosed to have TB is 0.001. In a certain city, 1 in 1000 people suffers from TB. A person is selected at random and is diagnosed to have TB. What is the probability that he actually has TB?
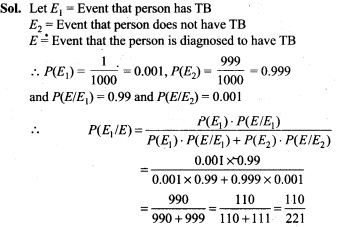
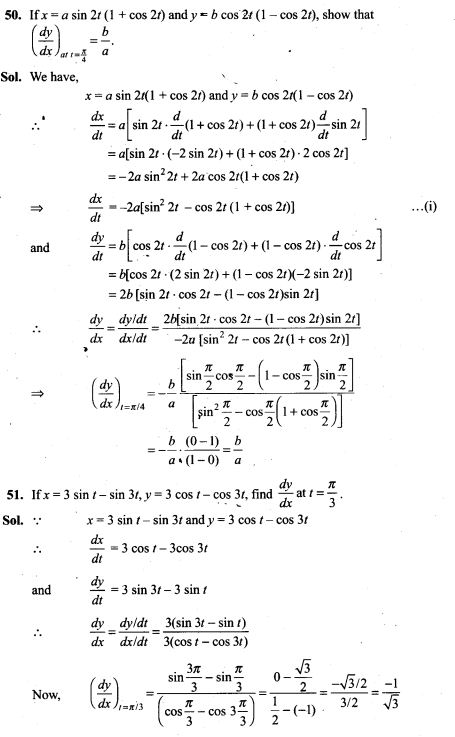
48. An item is manufactured by three machines A, B and C. Out of the total number of items manufactured during a specified period, 50% are manufactured on A, 30% on B and 20% on C. 2% of the items produced on A and 2% of items produced on B are defective, and 3% of these produced on C are defective. All the items are stored at one go down. One item is drawn at random and is found to be defective. What is the probability that it was manufactured on machine A?
Sol. Let E1, E2, E3 be the event that item is manufactured on A,B and C respectively. Let E be the event that an item is defective.
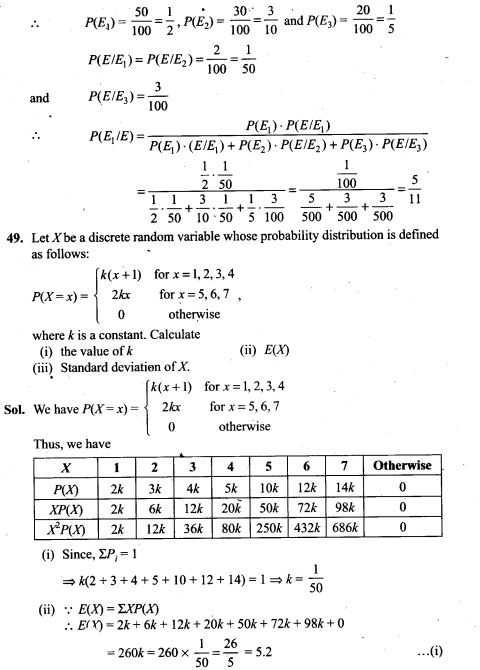
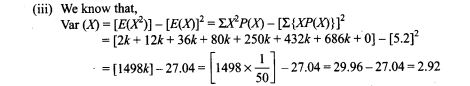
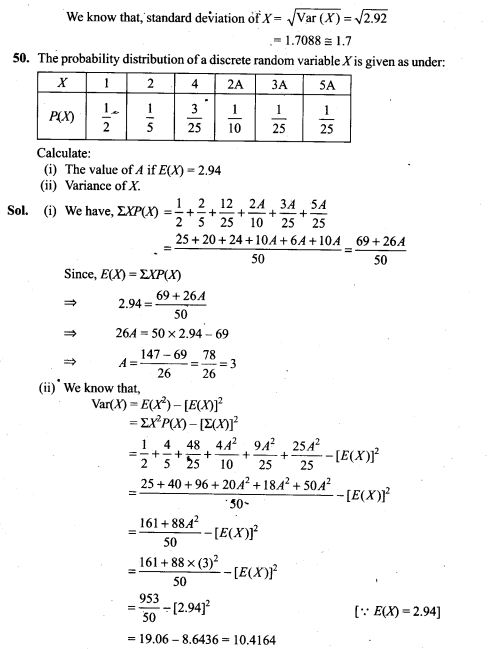

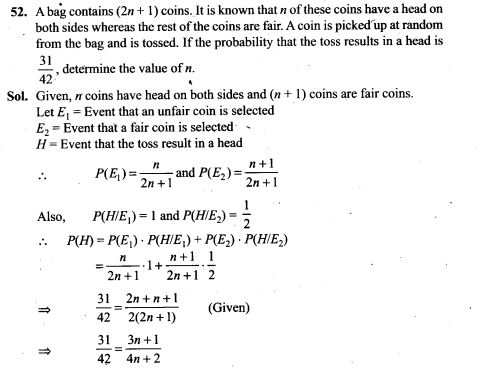
=> 124n + 62 = 126n + 42
=> 2n = 20=>n=10
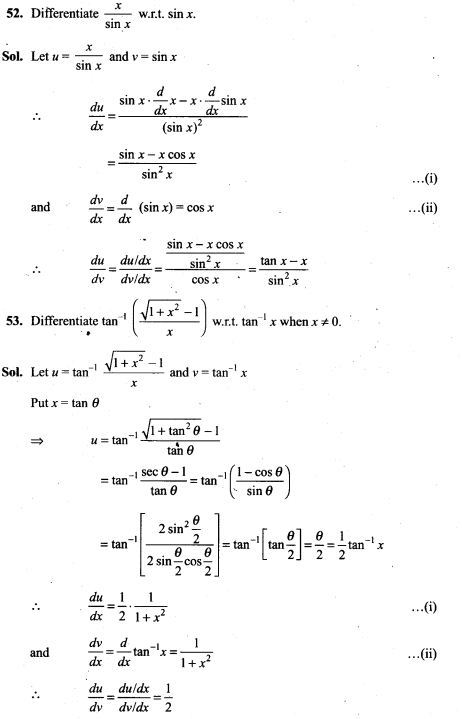
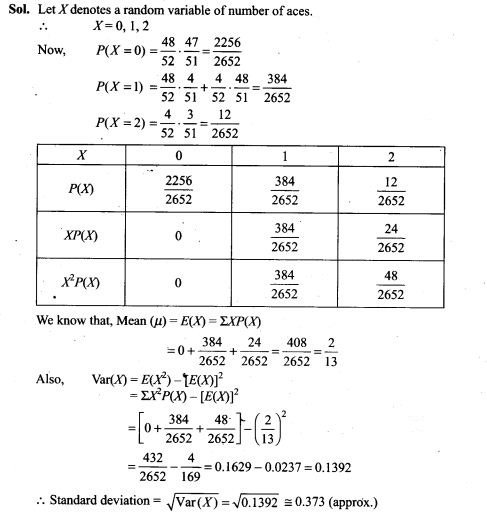
53. Two cards are drawn successively without replacement from a well shuffled deck of cards. Find the mean and standard variation of the random variable X where X is the number of aces.
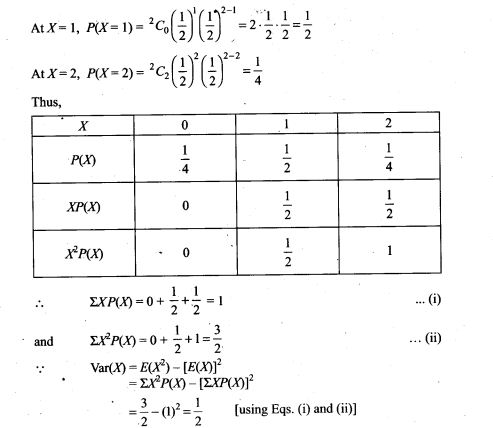
54. A die is tossed twice. A ‘success’ is getting an even number on a toss. Find the variance of the number of successes.
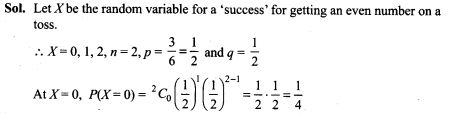
55. There are 5 cards numbered 1 to 5, one number on one card. Two cards are drawn at random without replacement. Let X denote the sum of the numbers on two cards drawn. Find the mean and variance of X.


Objective Type Questions
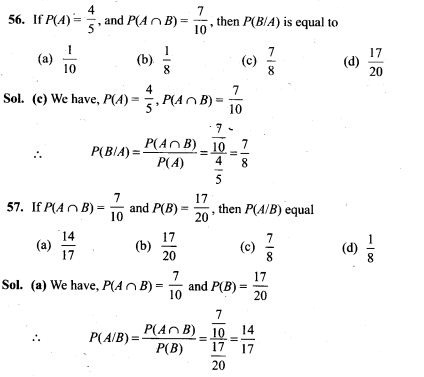




70. If two events are independent, then
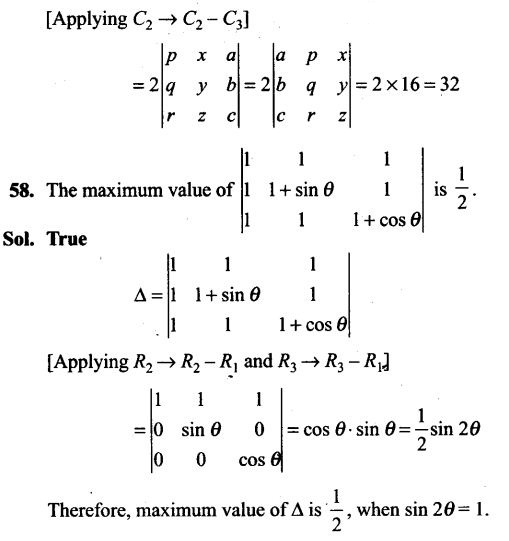
(a) they must be mutually exclusive
(b) the sum of their probabilities must be equal to 1
(c) (A) and (B) both are correct
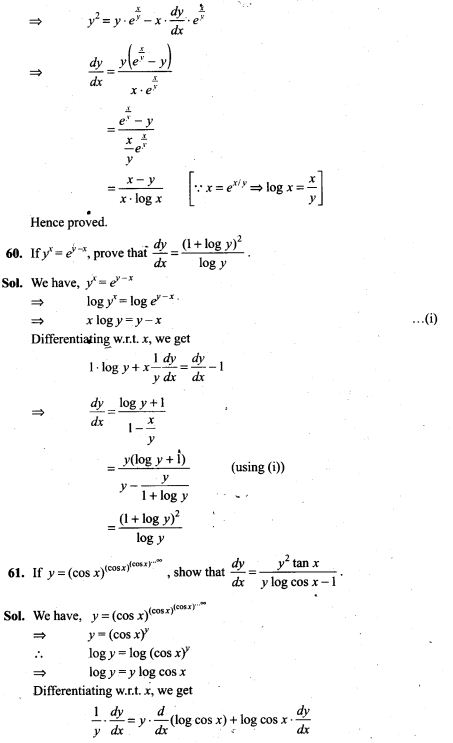
(d) None of the above is correct
Sol. (d) If two events A and B are independent, then we know that
![]()
If A and B are independent, knowledge that A occurred does not change the probabilities that B may have occurred. Whereas if A and B are disjoint, knowledge that A occurred completely changes the probabilities that B may have occurred by collapsing it to 0.
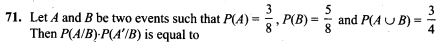



77. Assume that in a family, each child is equally likely to be a boy or a girl. A family with three children is chosen at random. The probability that the eldest child is a girl given that the family has at least one girl is






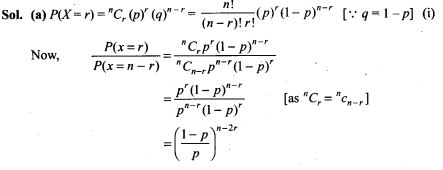


True/False Type Questions


Fill in the Blanks Type Questions