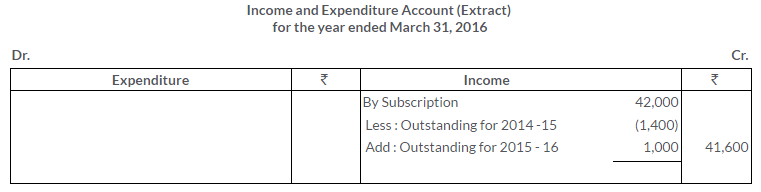
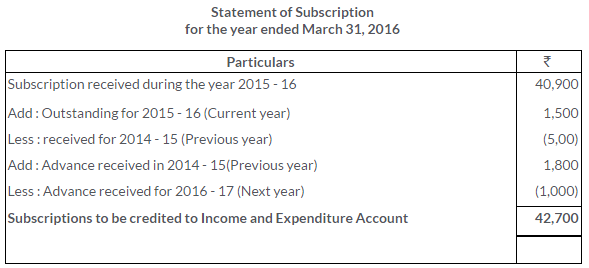
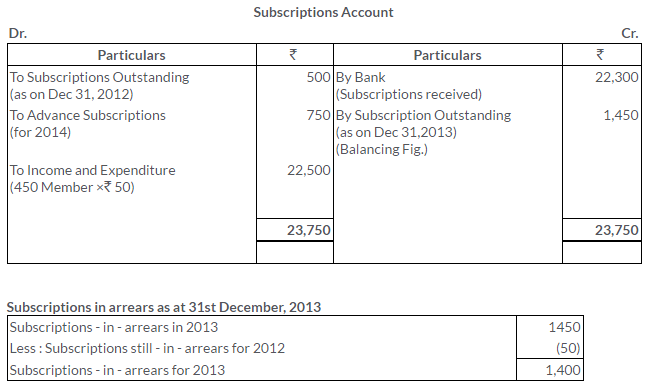
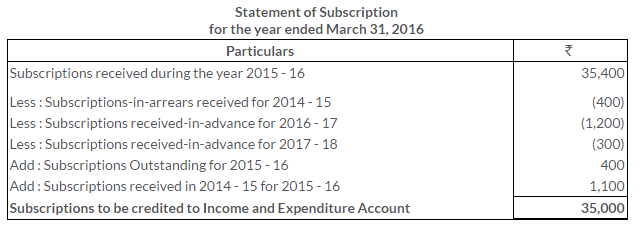
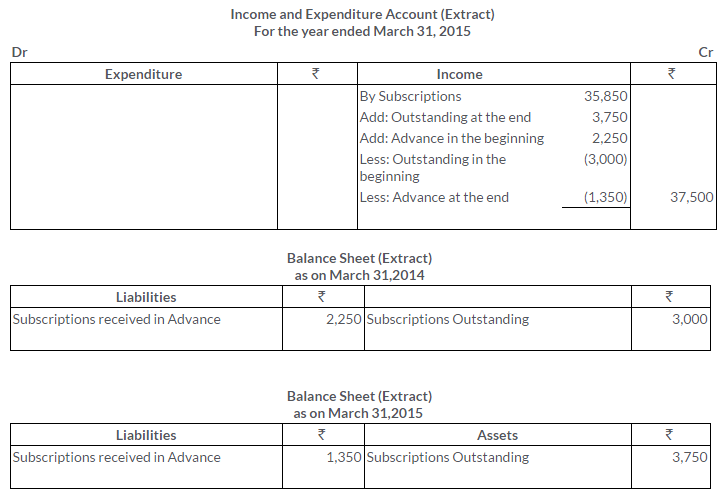
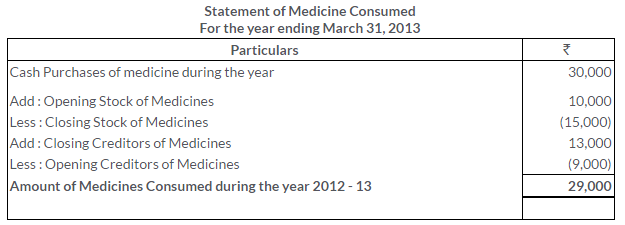
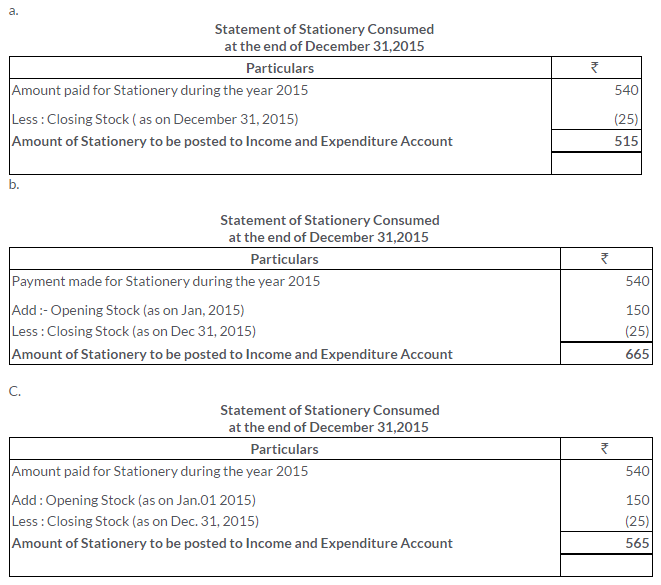
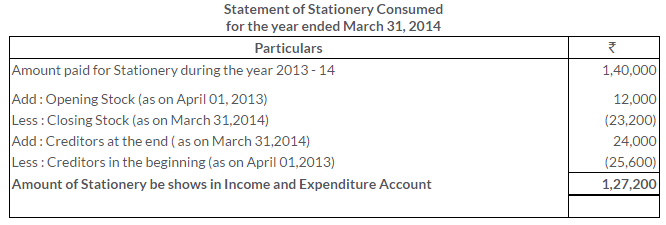
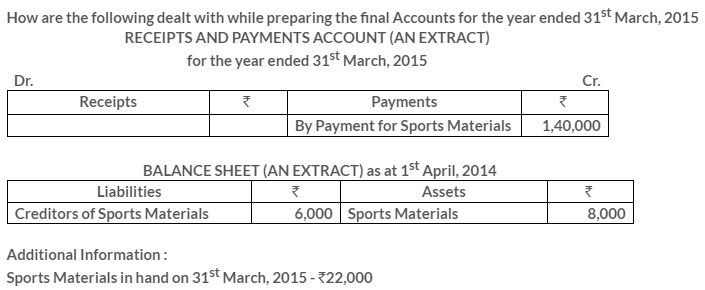
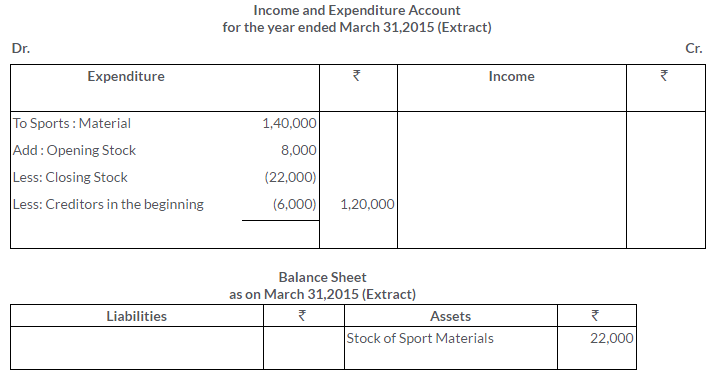
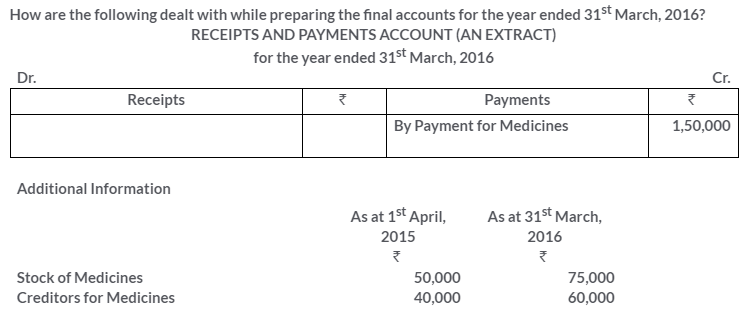
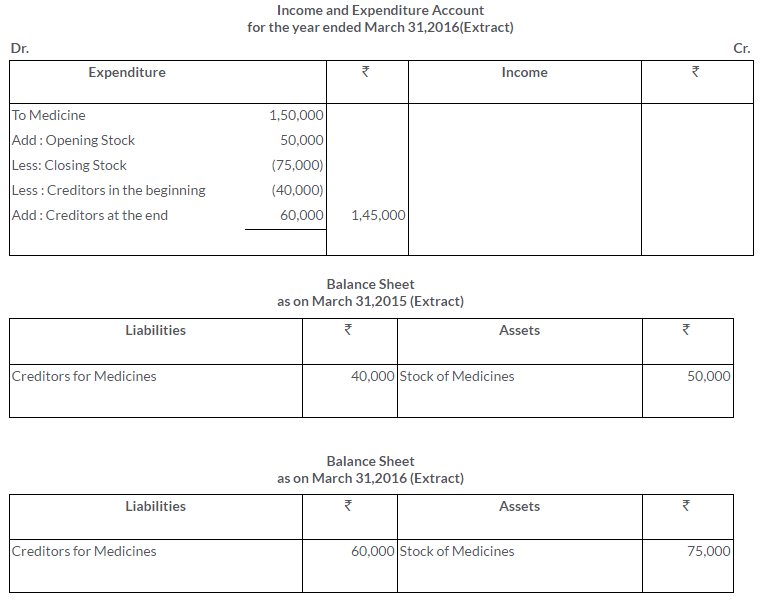
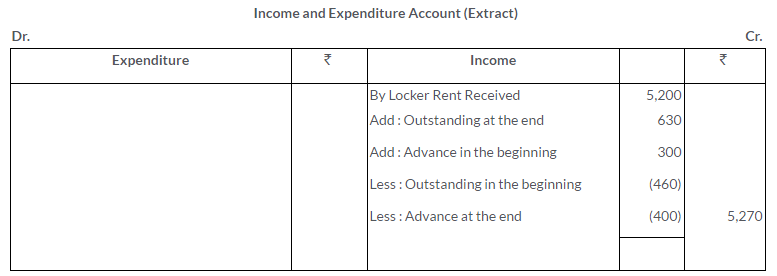
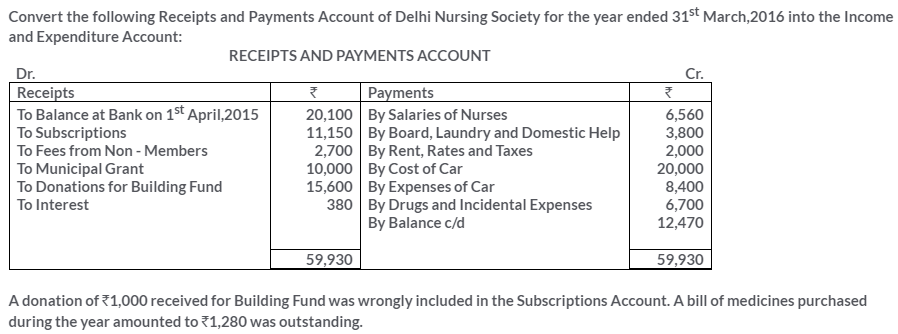
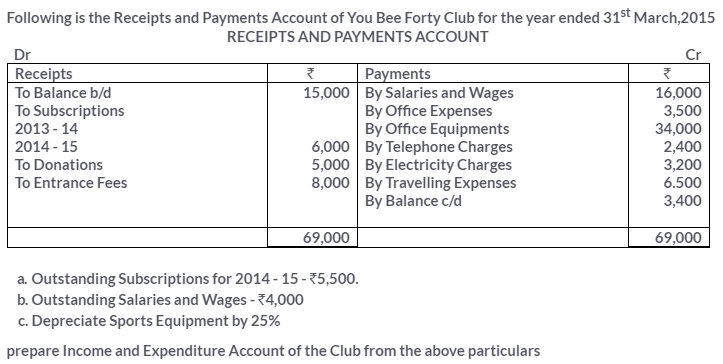
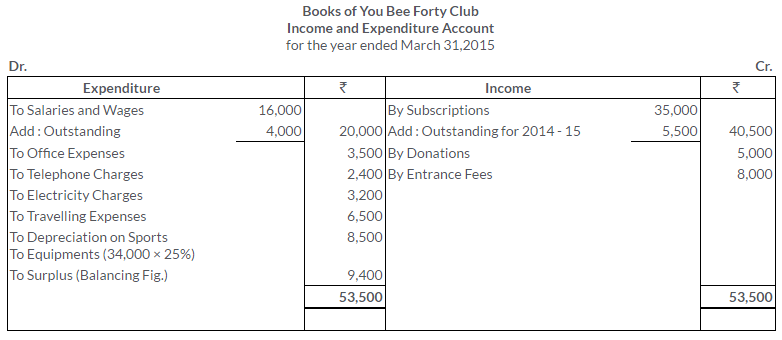
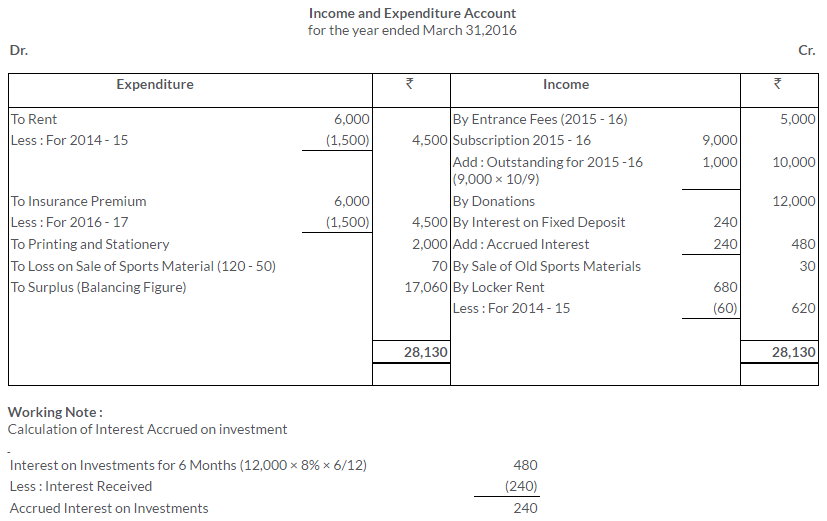
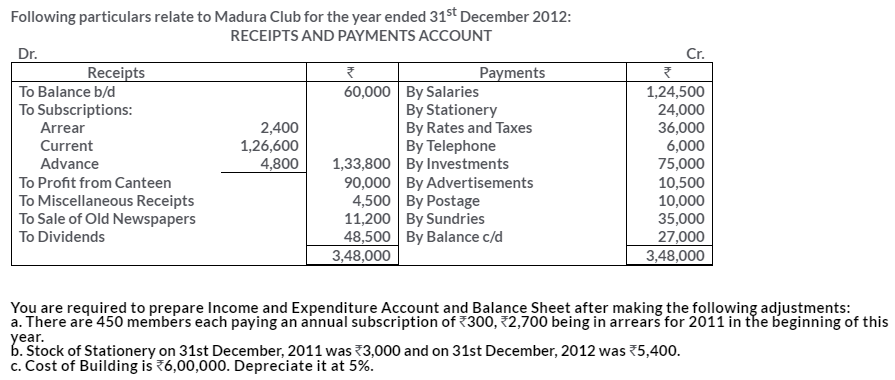
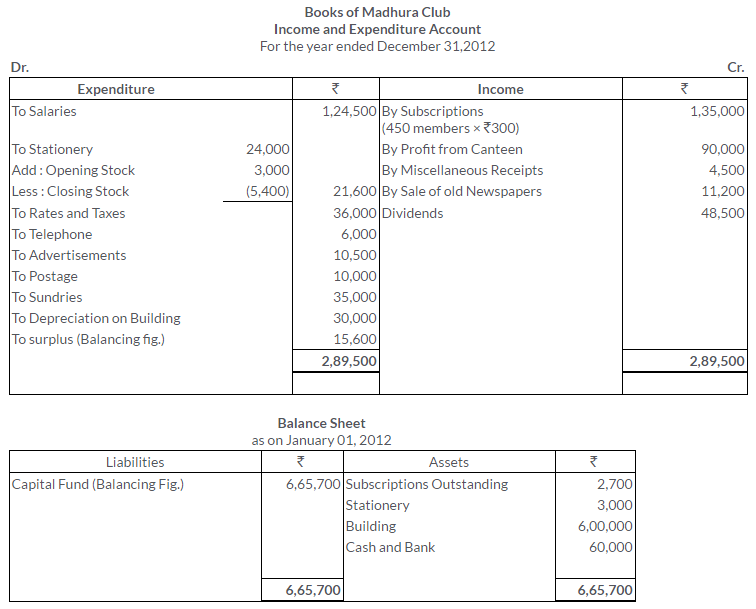
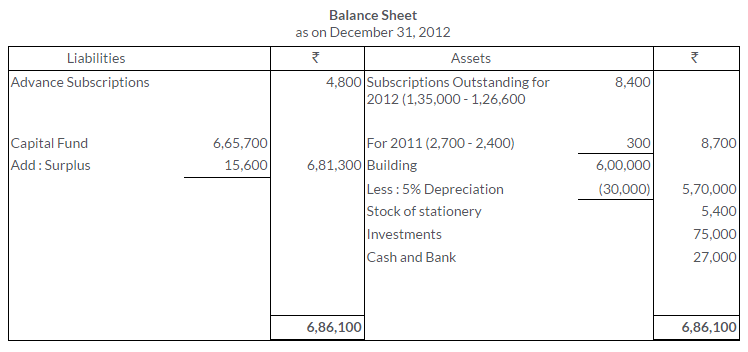
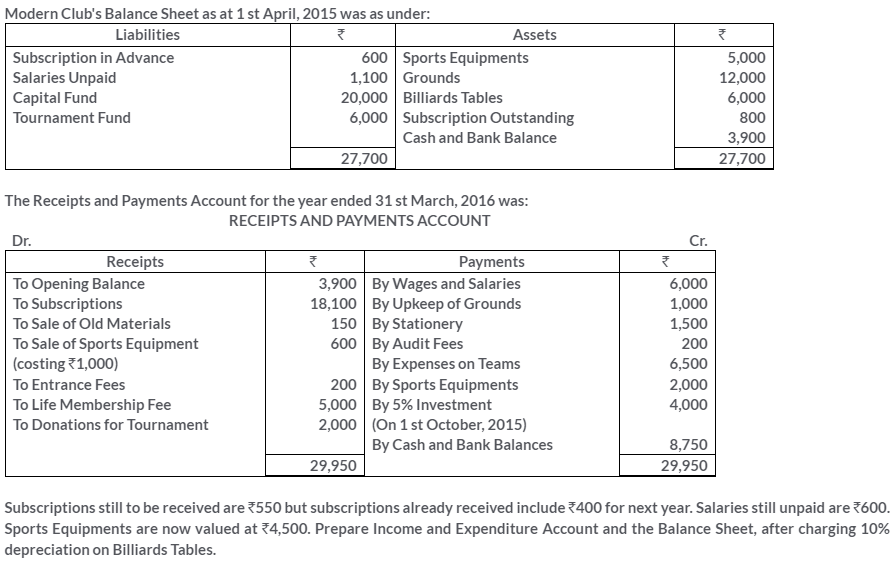
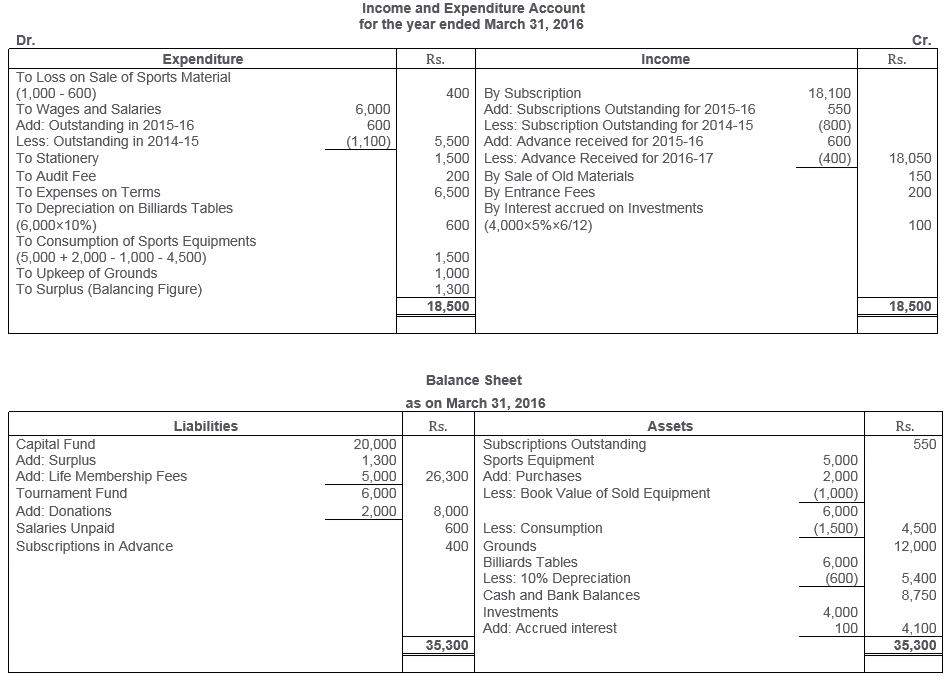
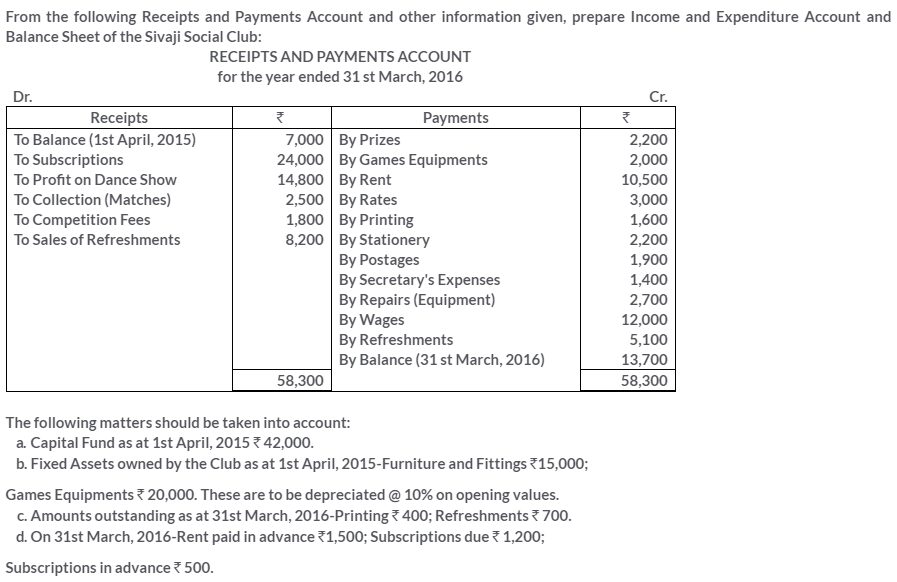
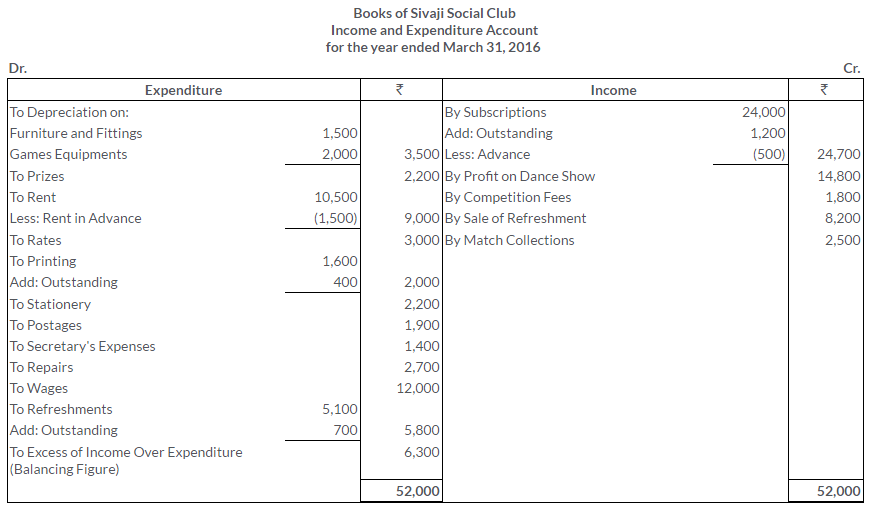
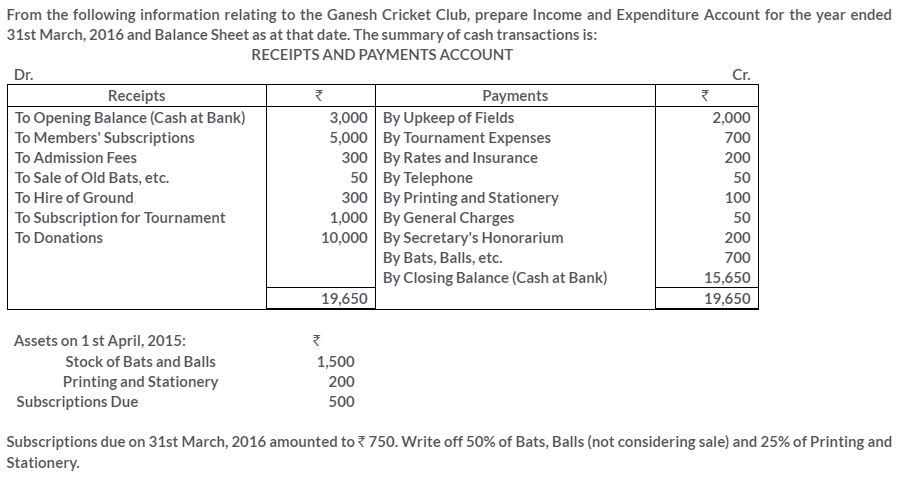
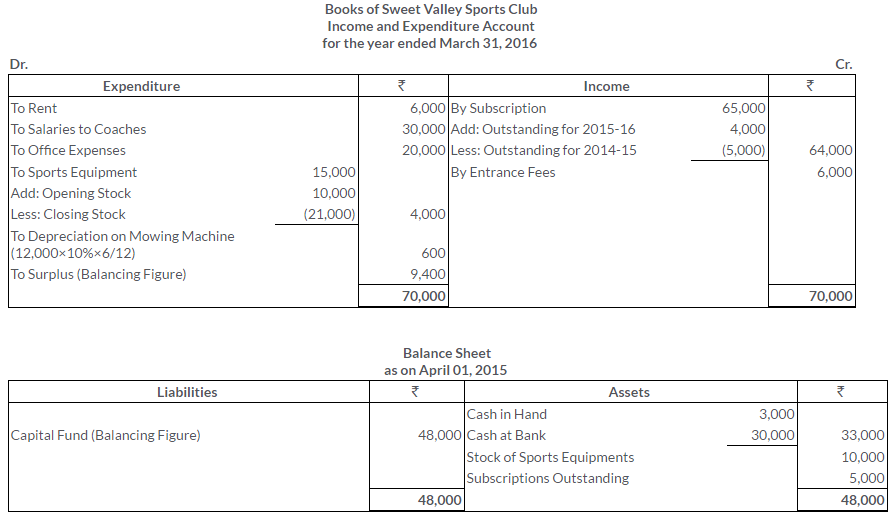
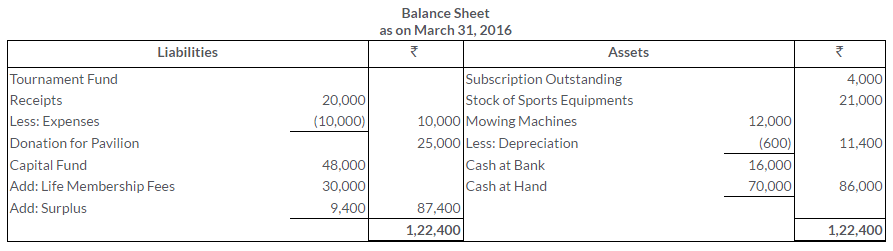
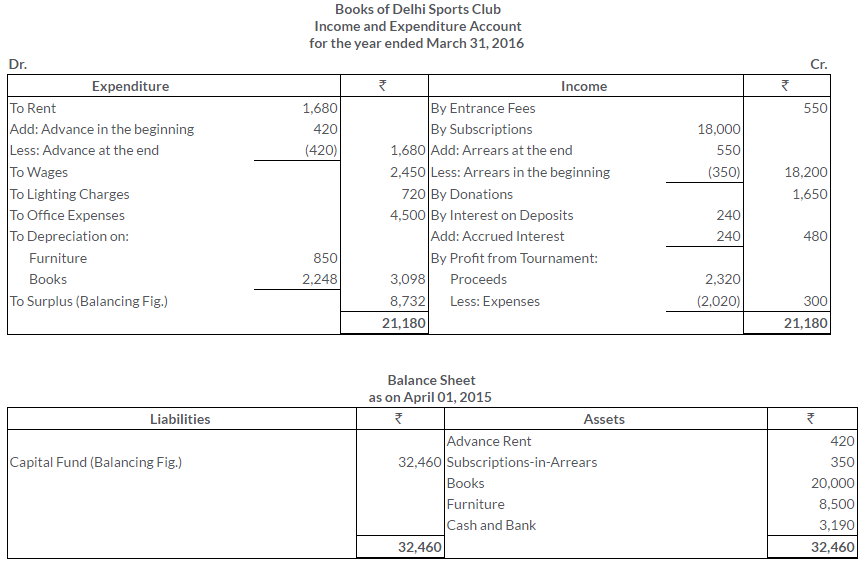
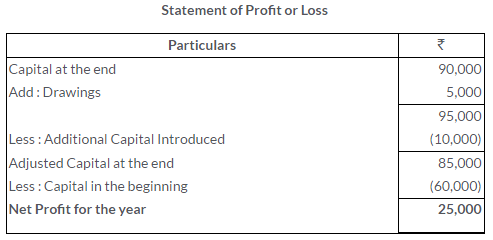
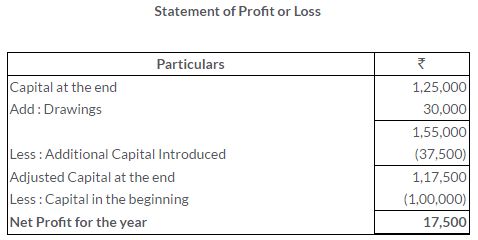
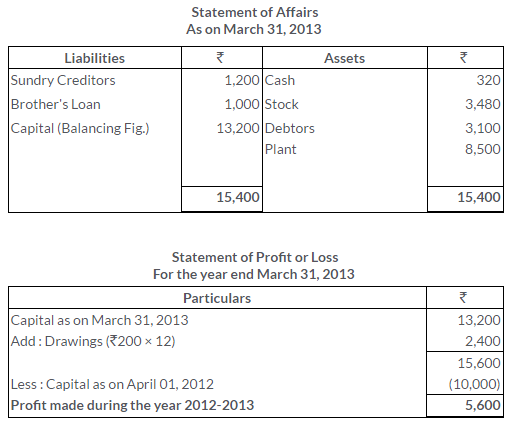
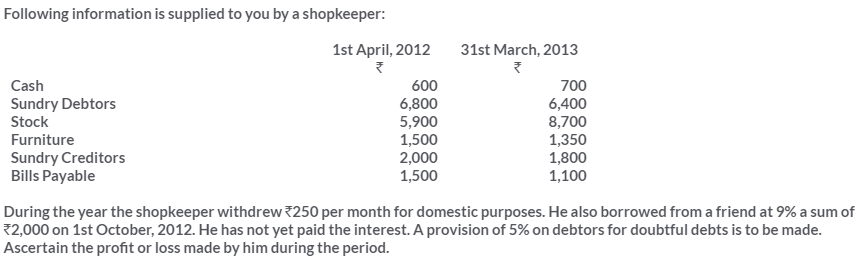
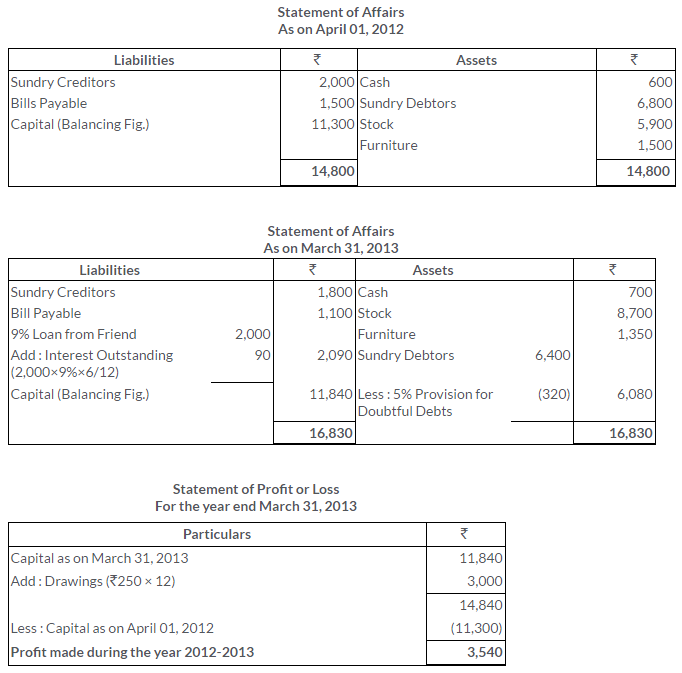
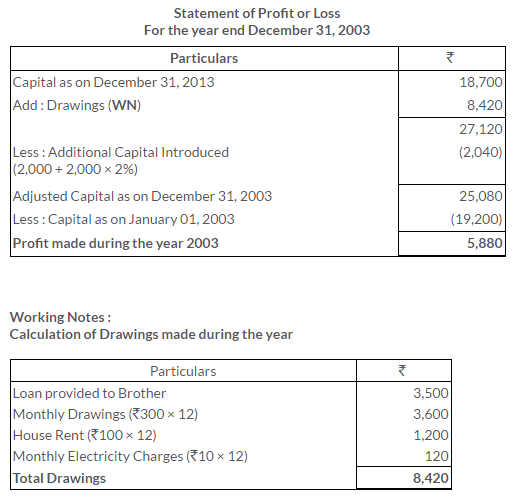
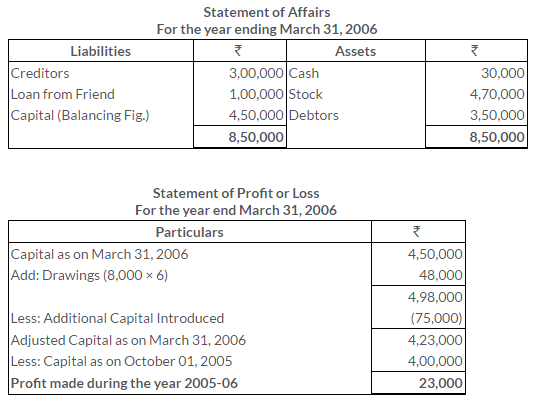
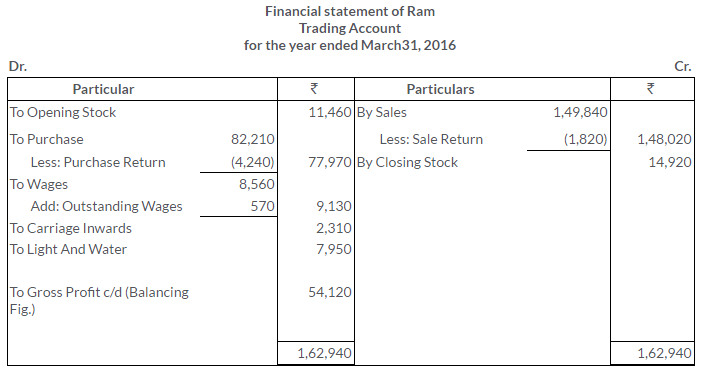
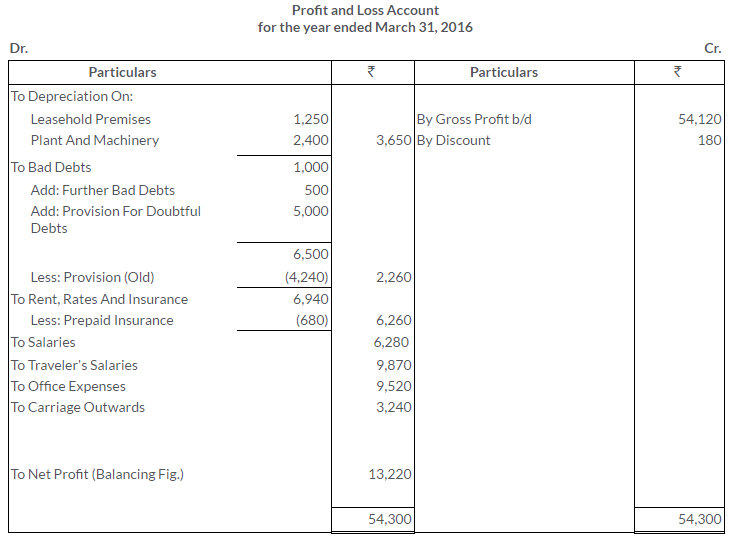
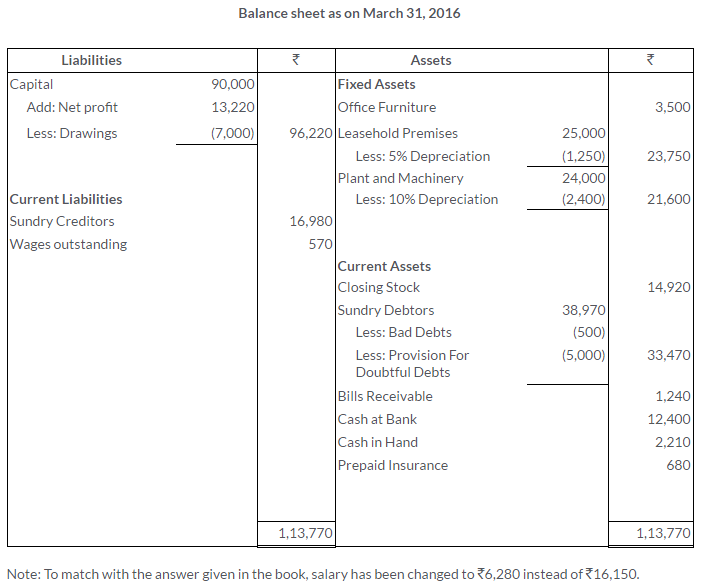
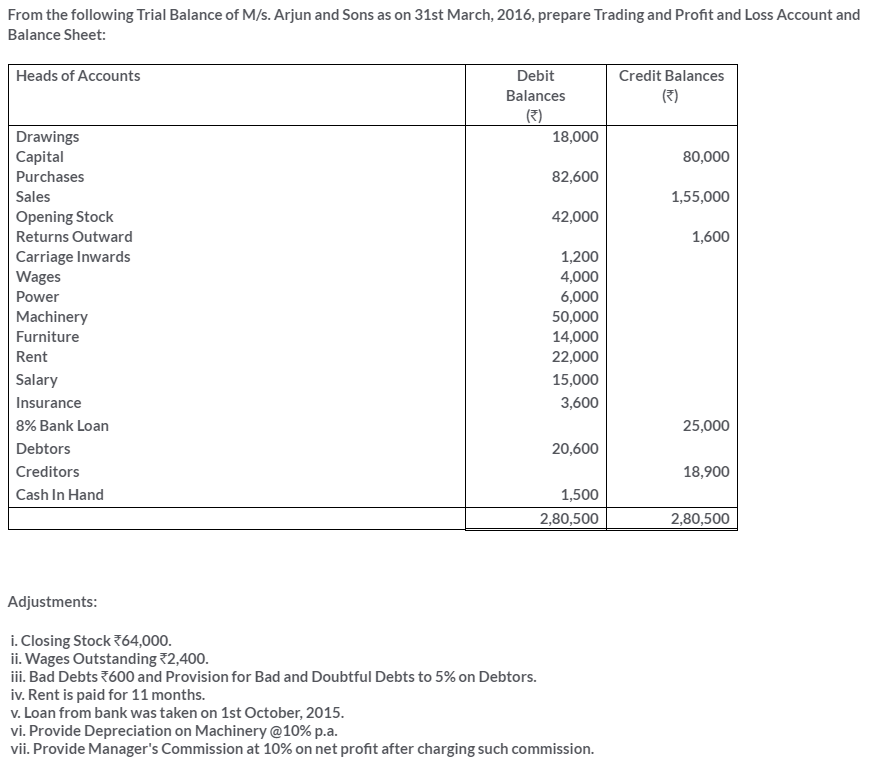
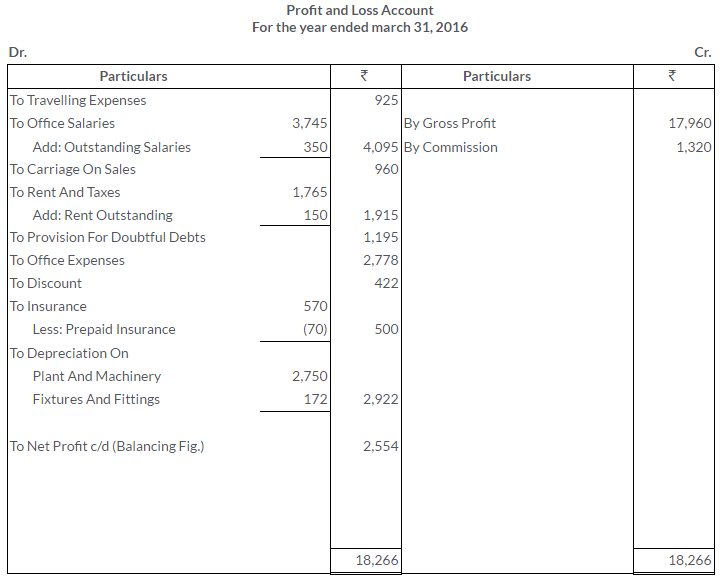
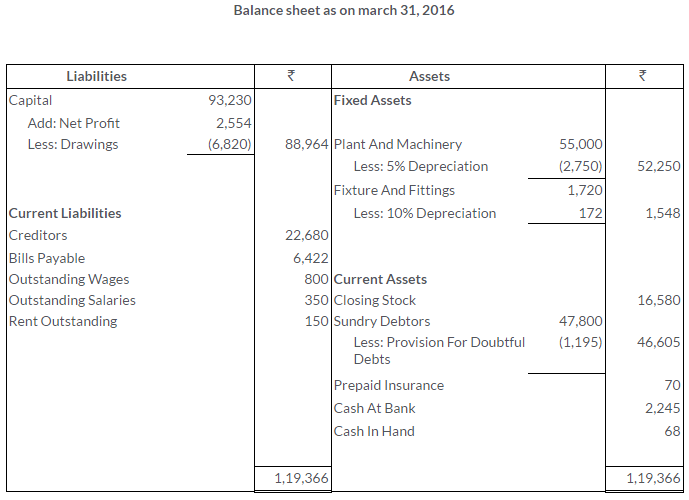
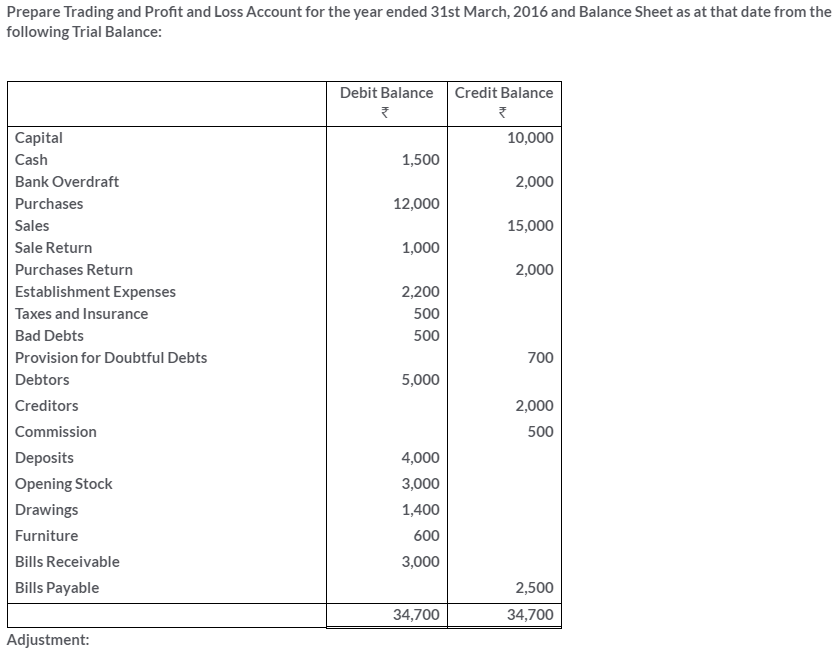
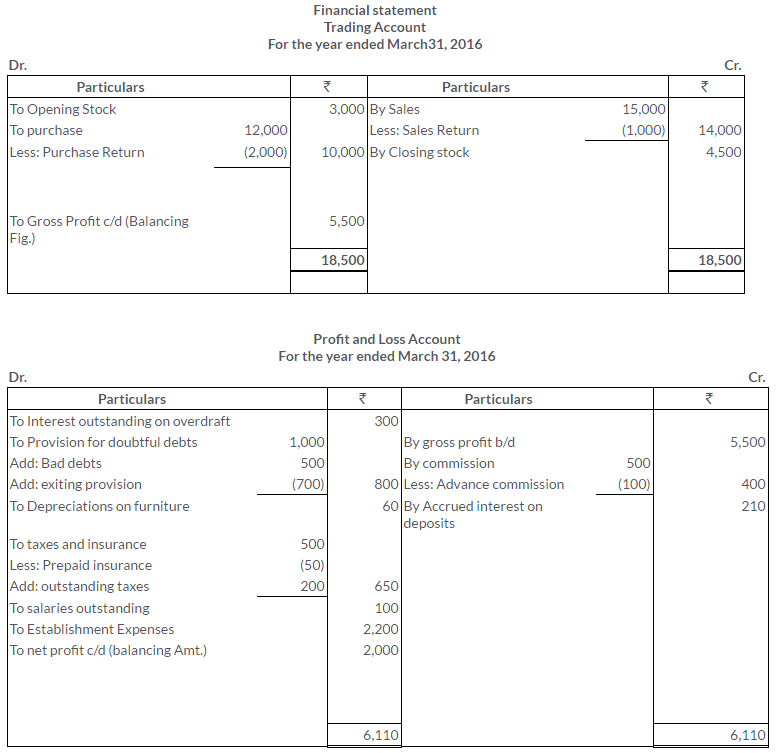
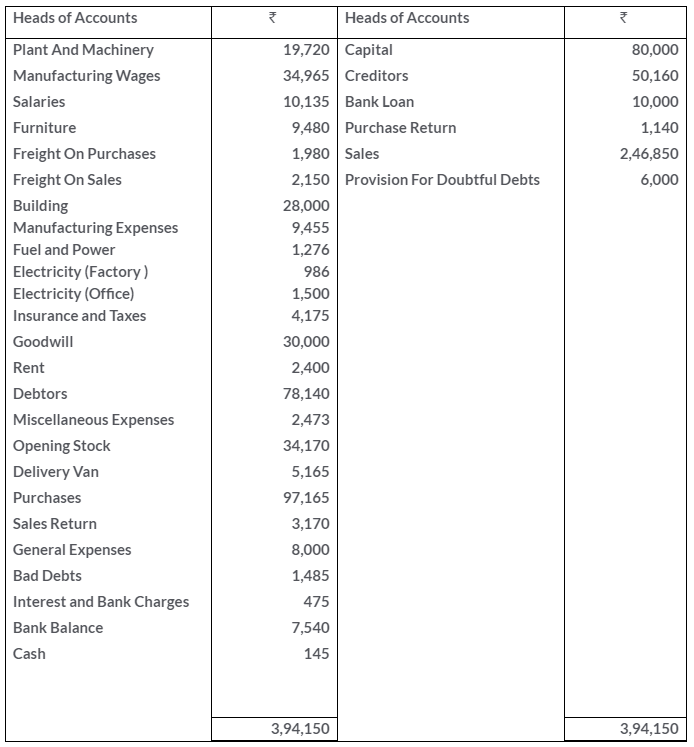
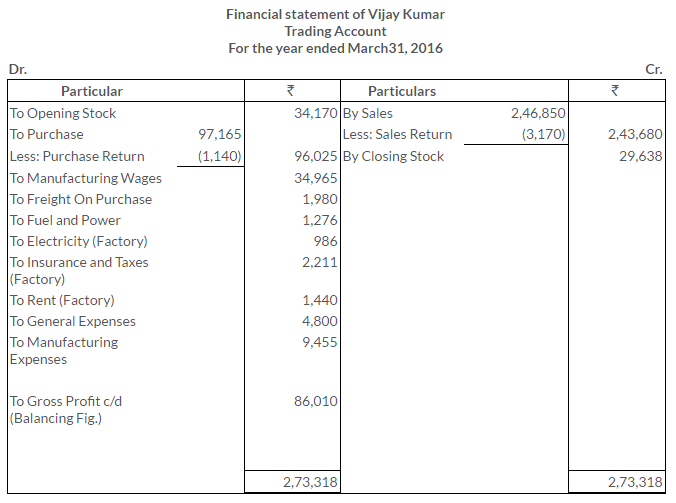
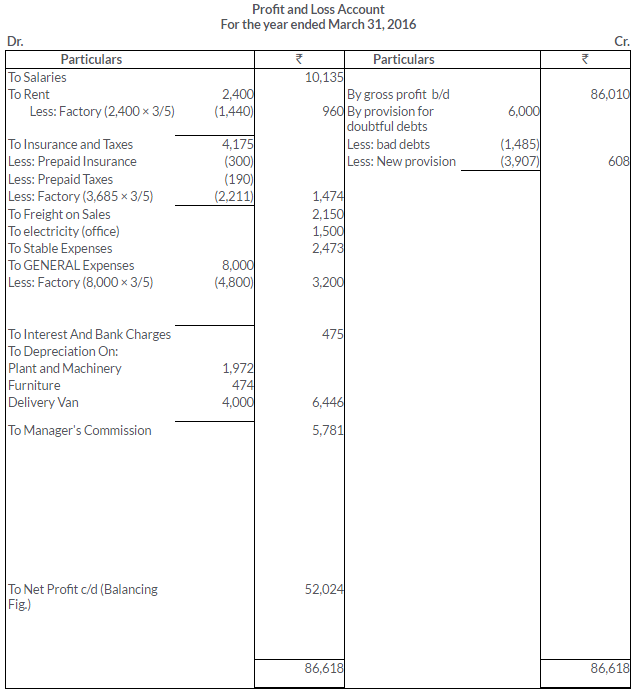
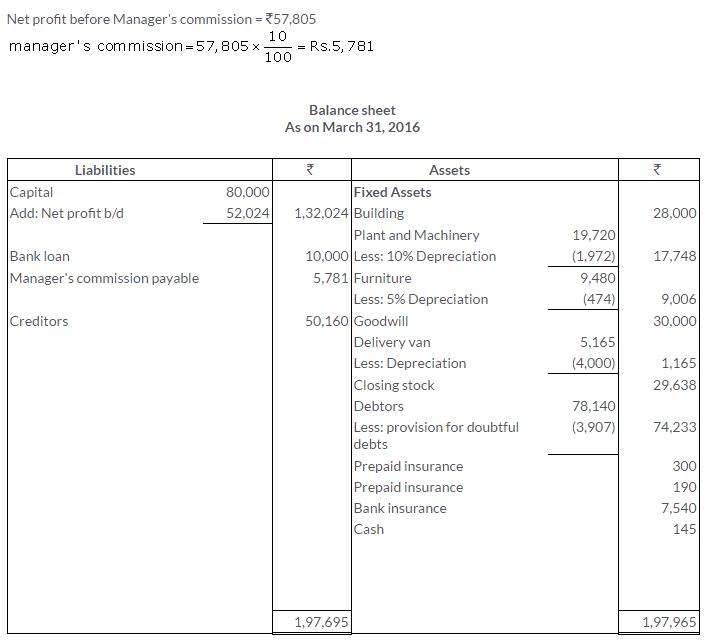
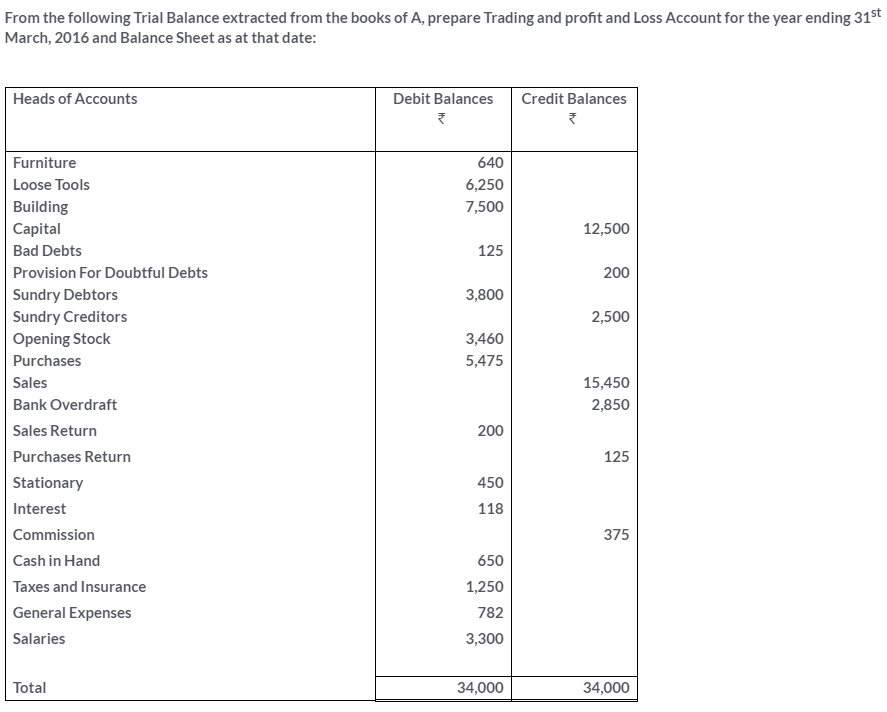
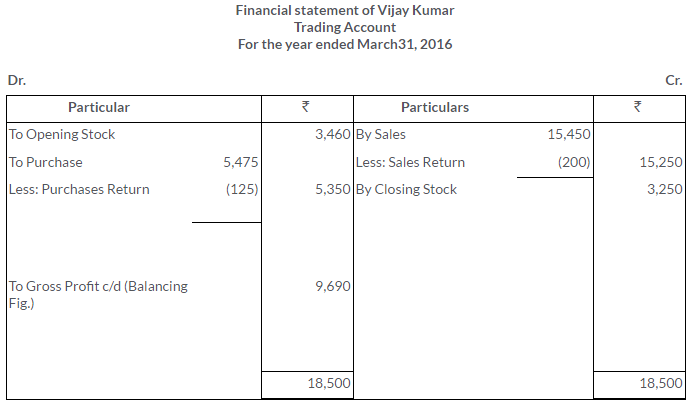
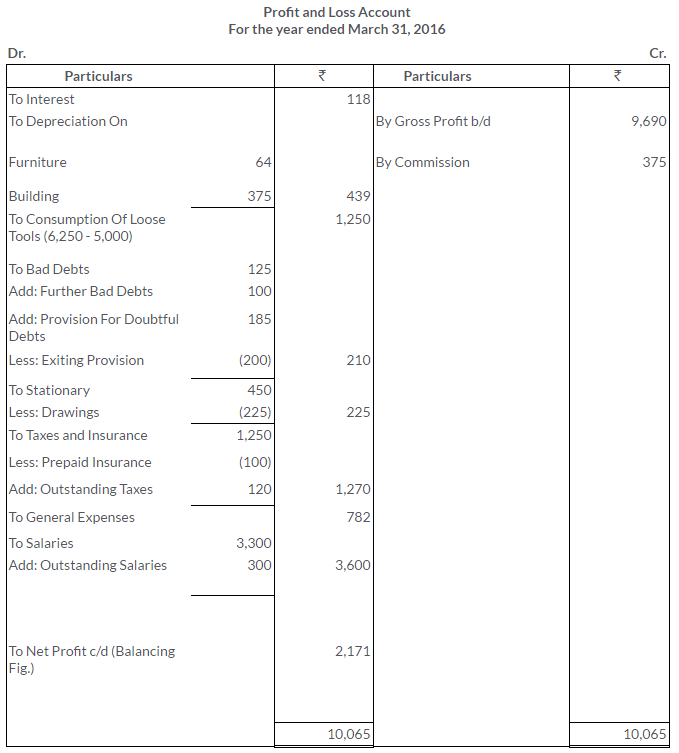
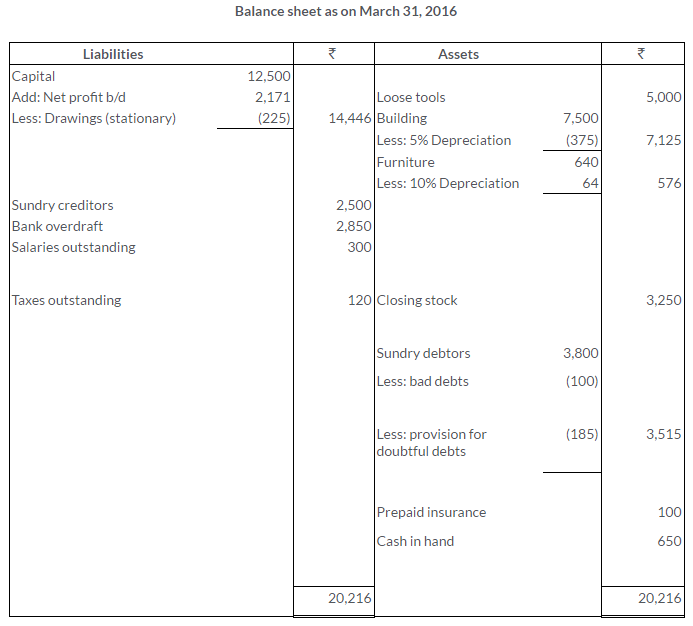
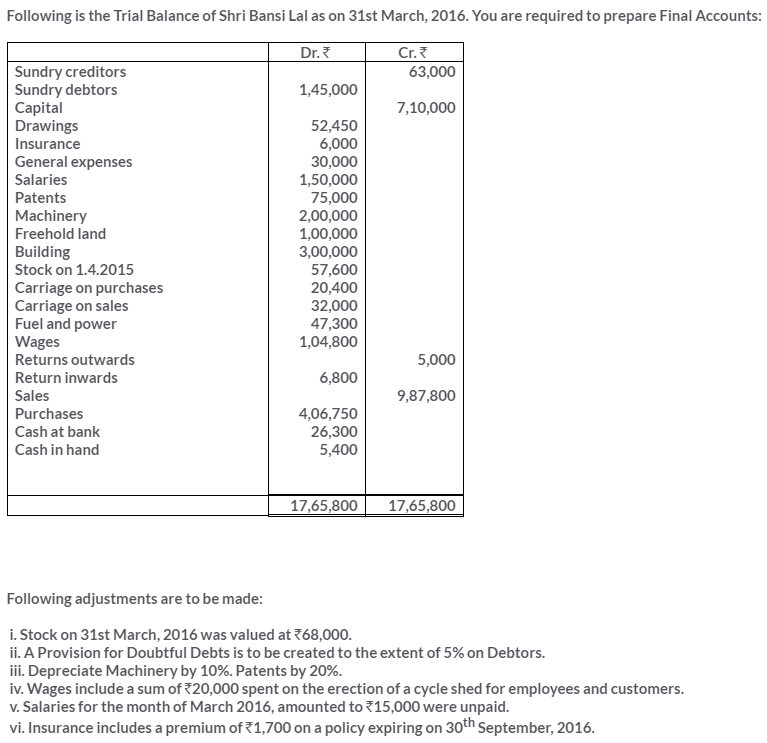
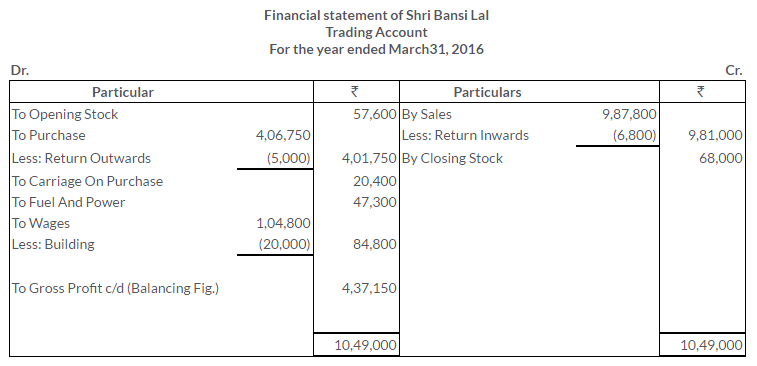
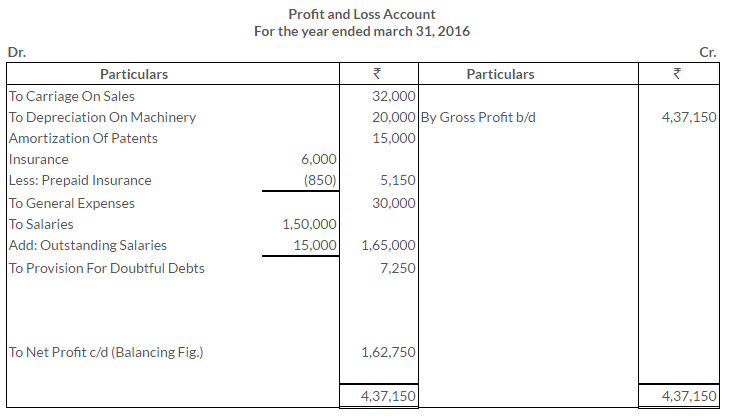
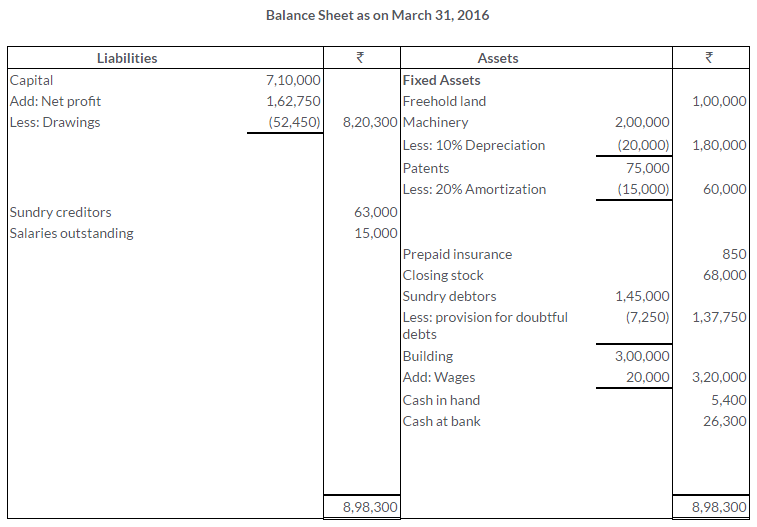
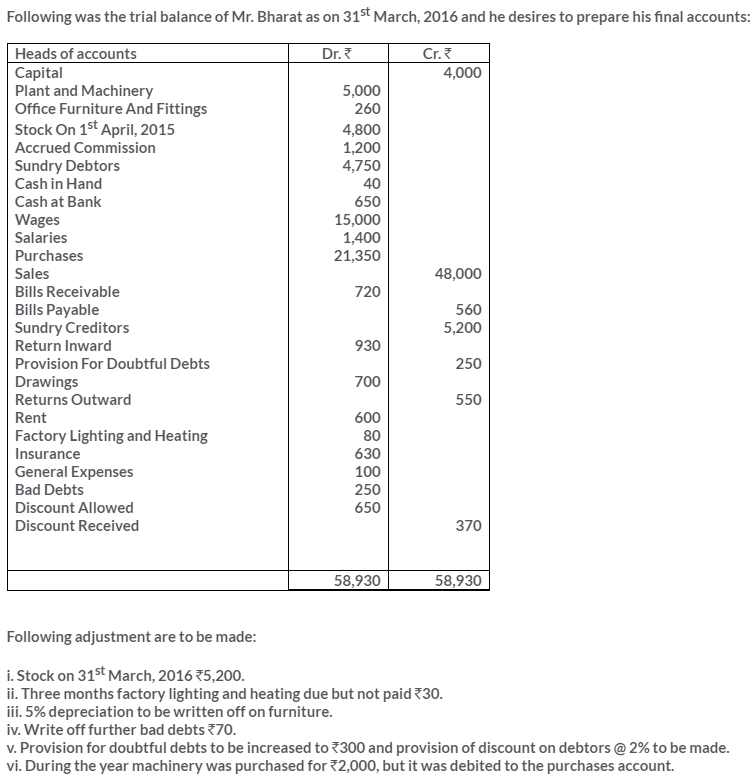
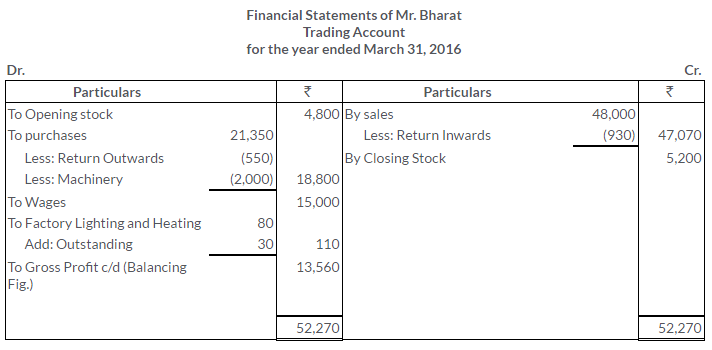
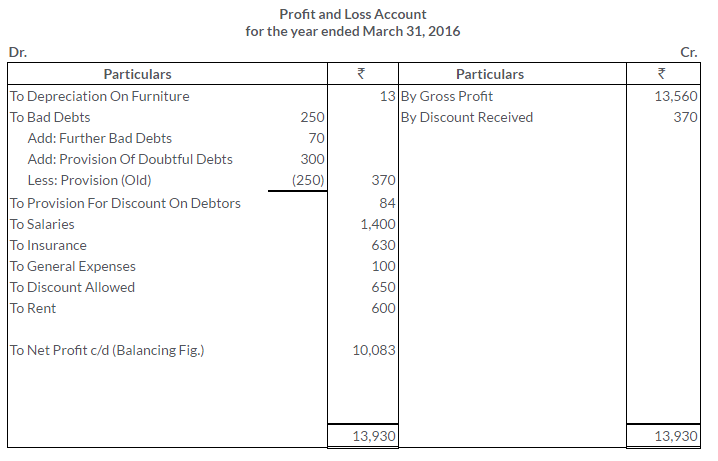
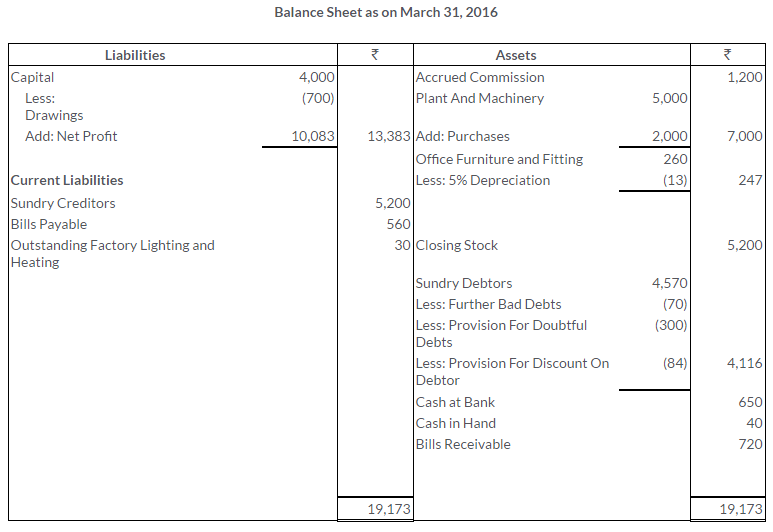
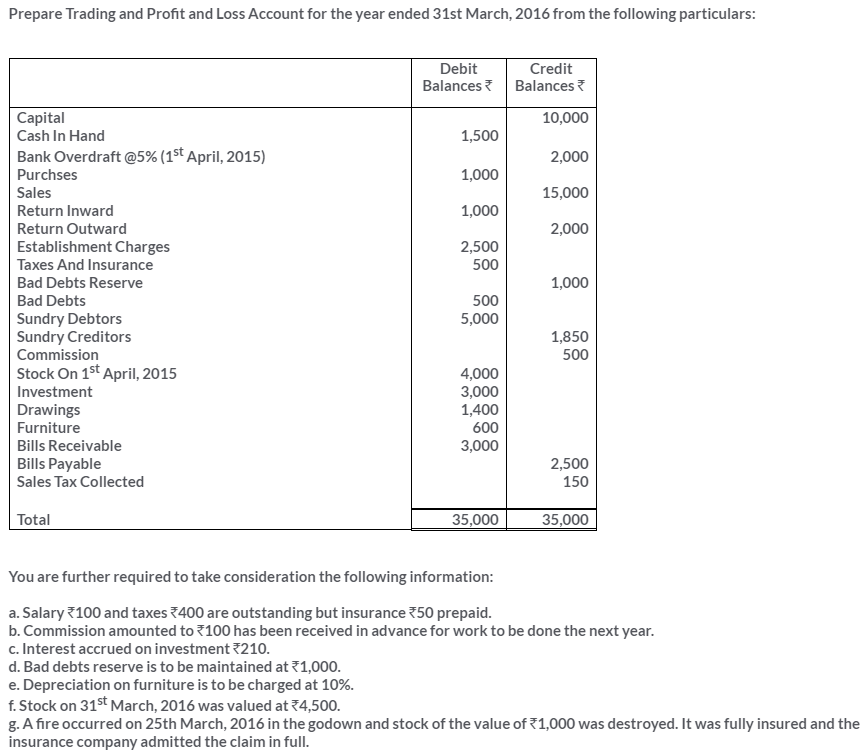
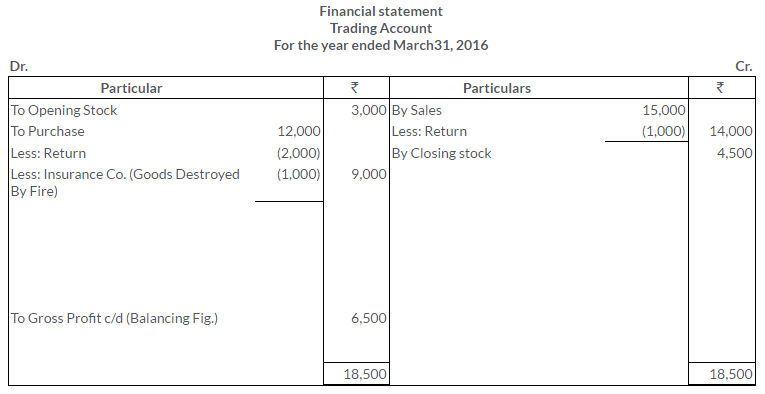
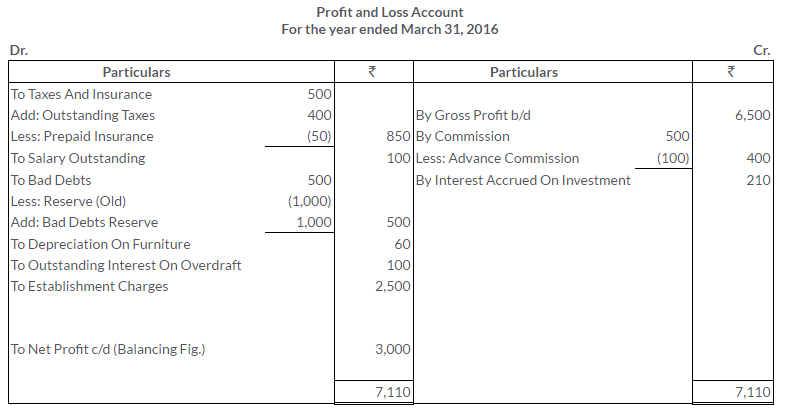
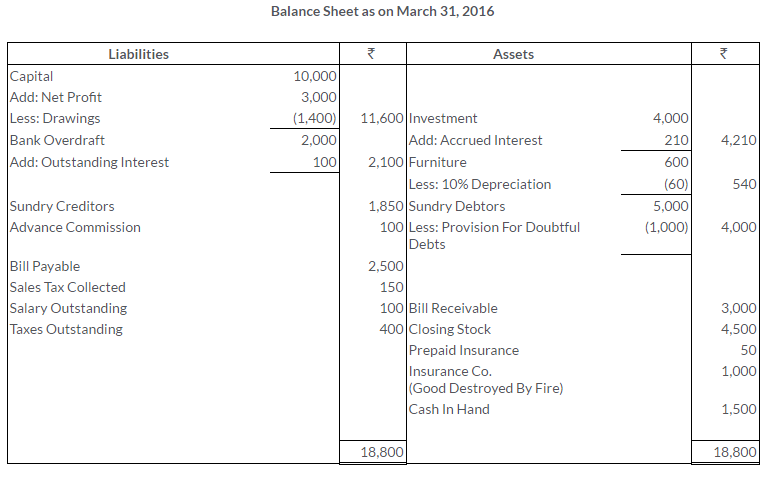
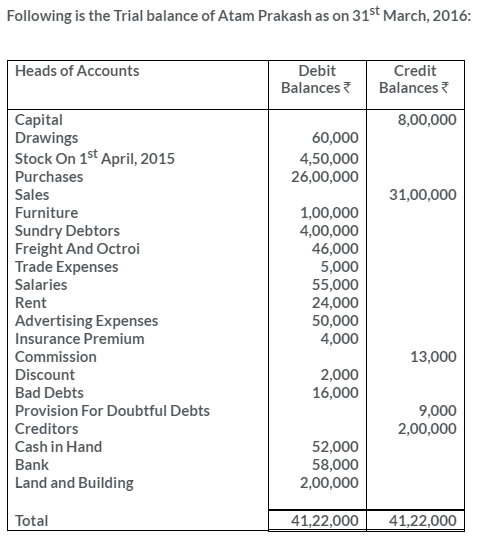
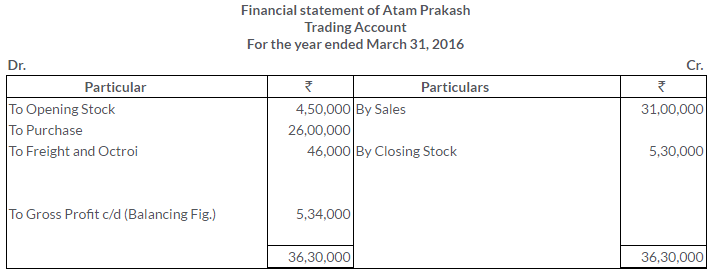
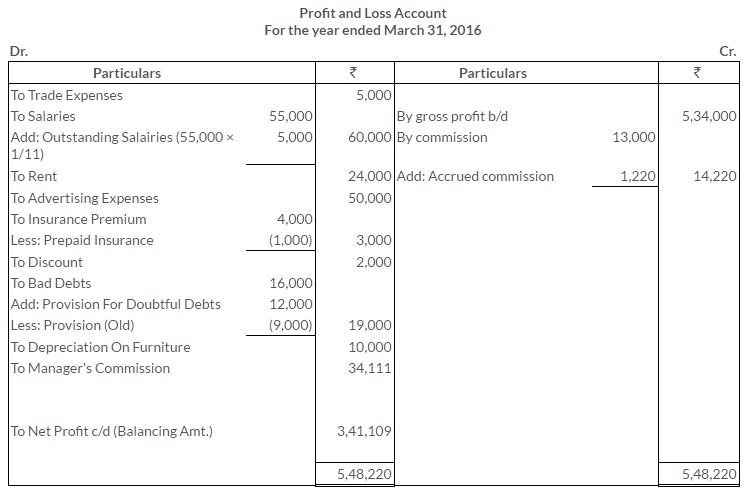
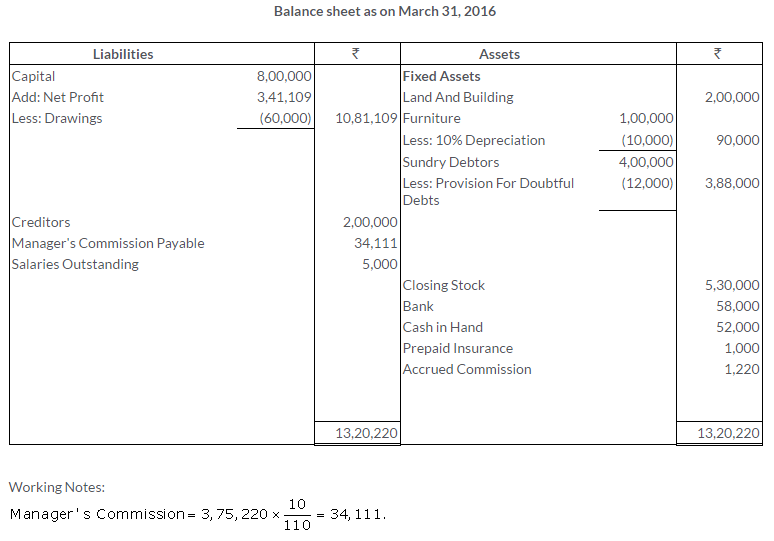
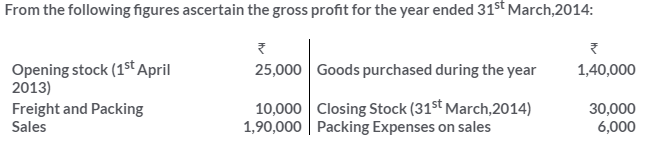
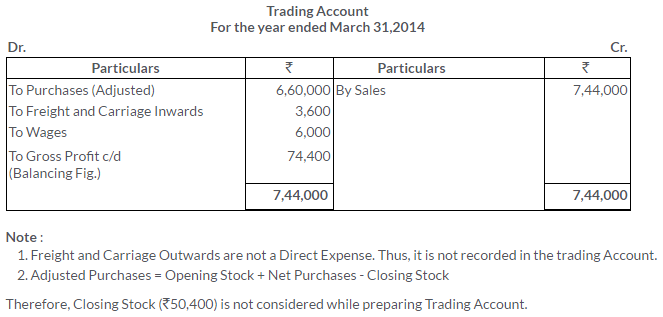
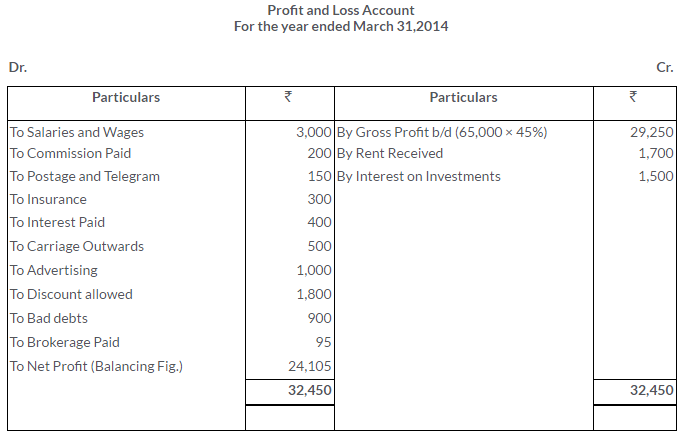
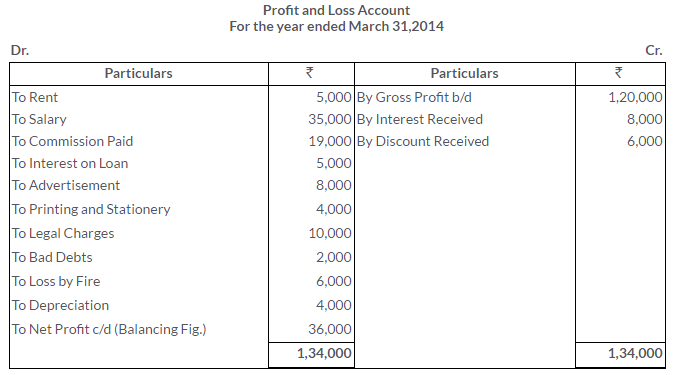
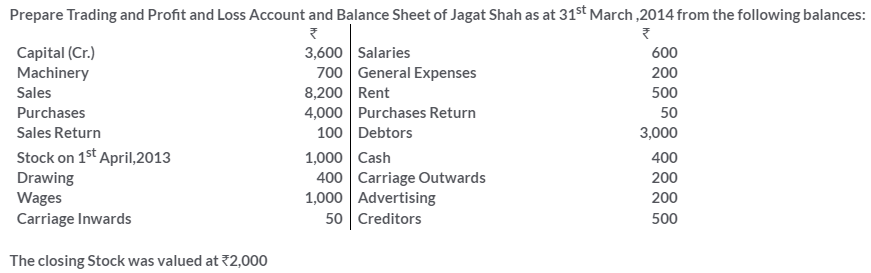
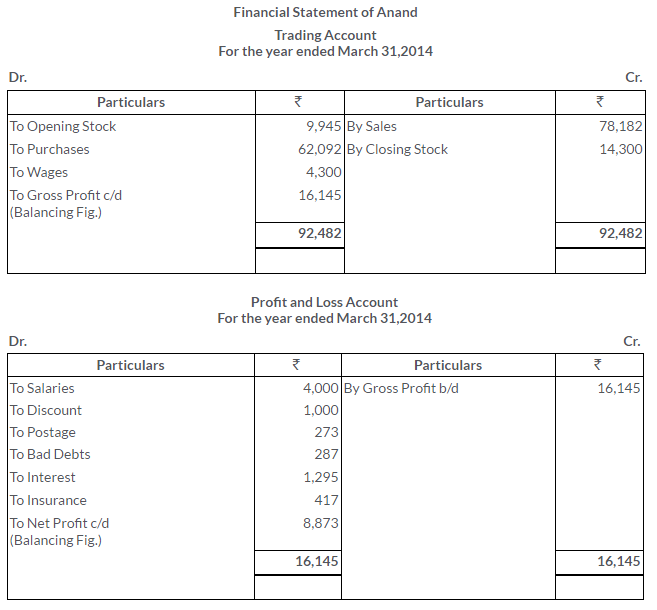
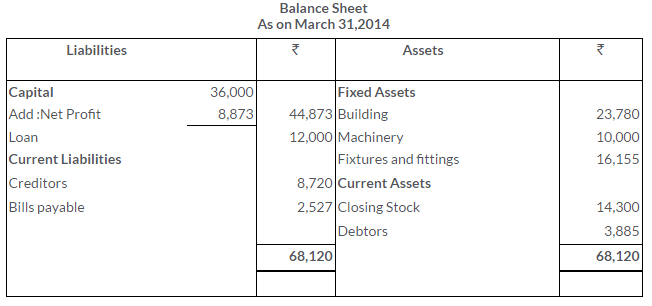
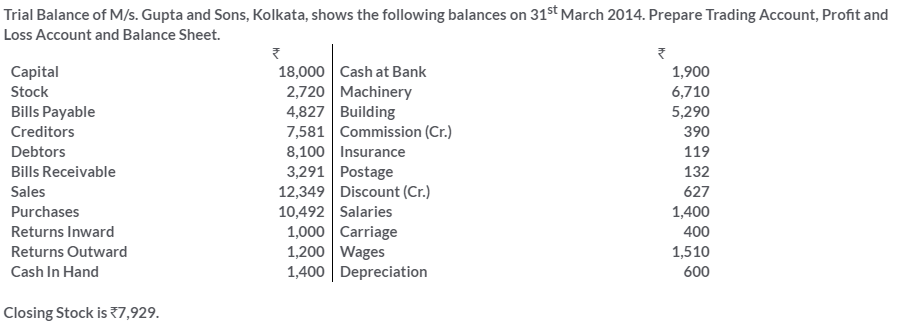
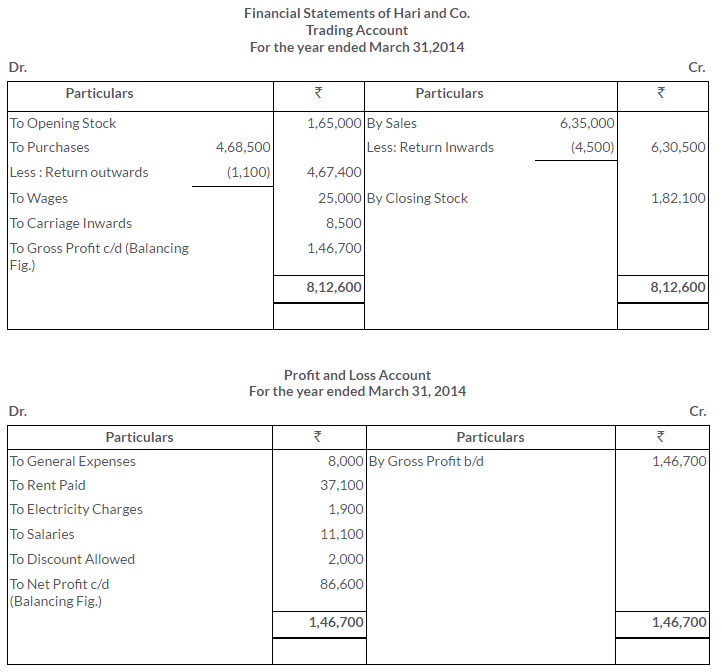
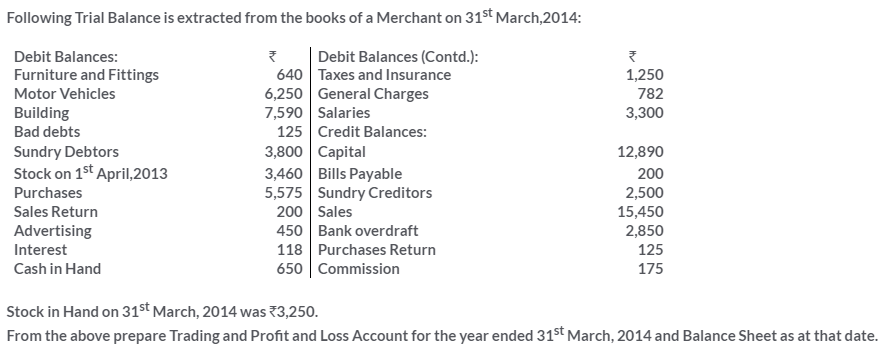
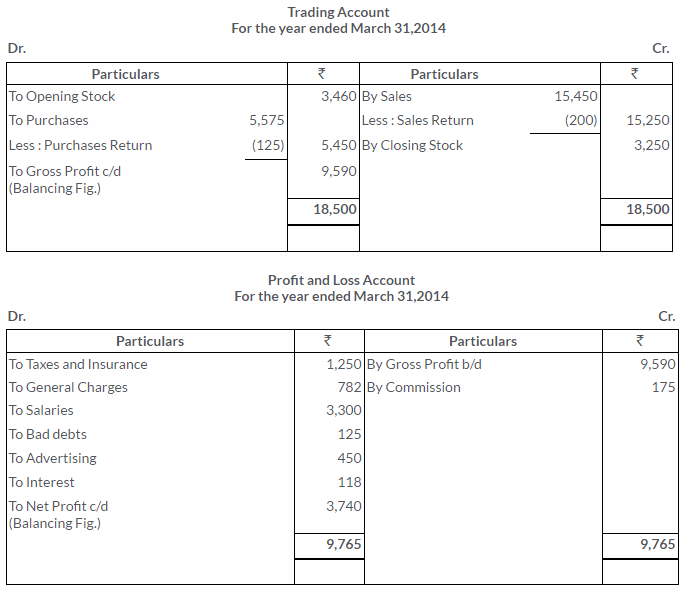
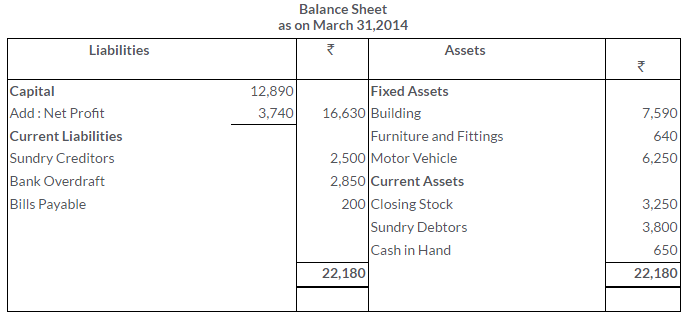
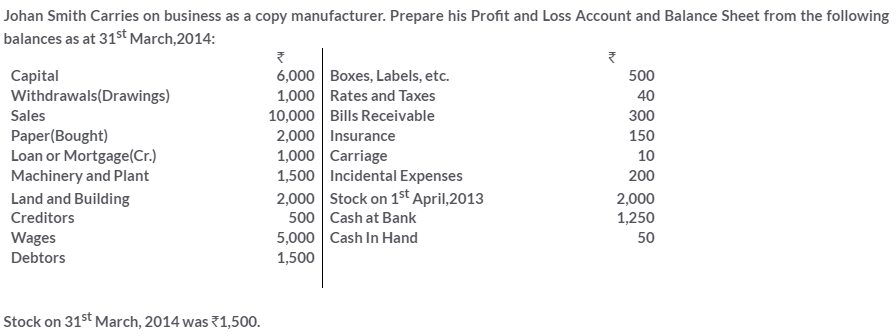
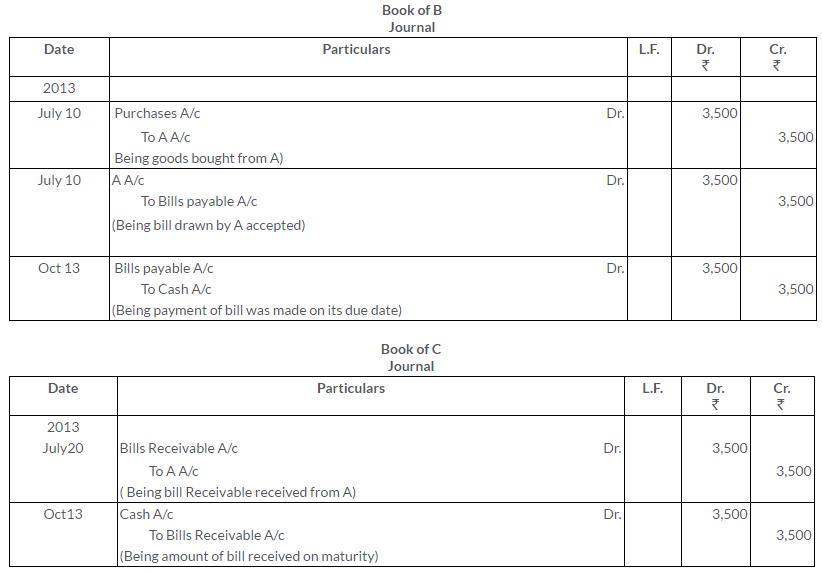
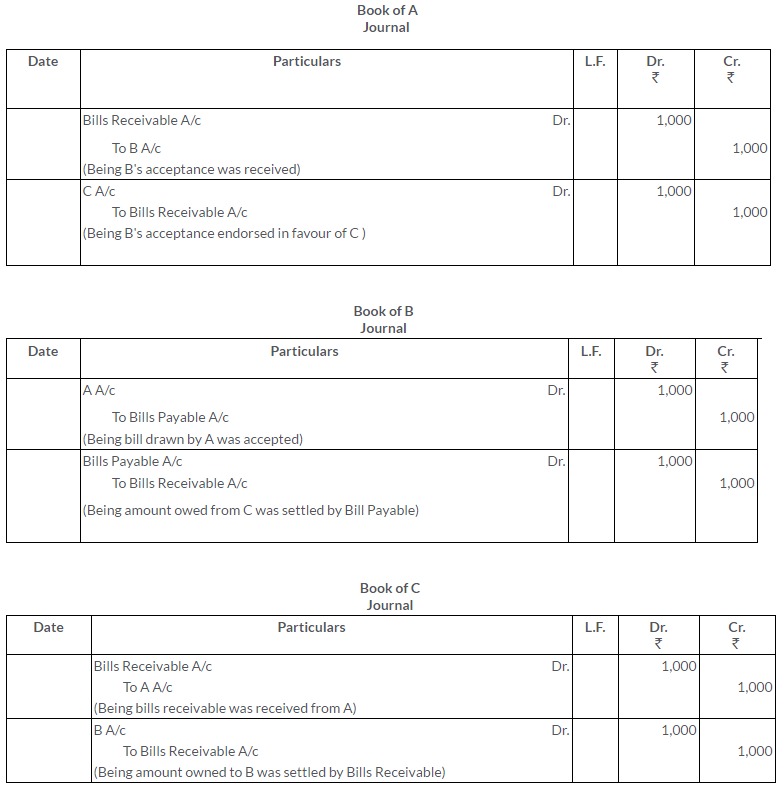
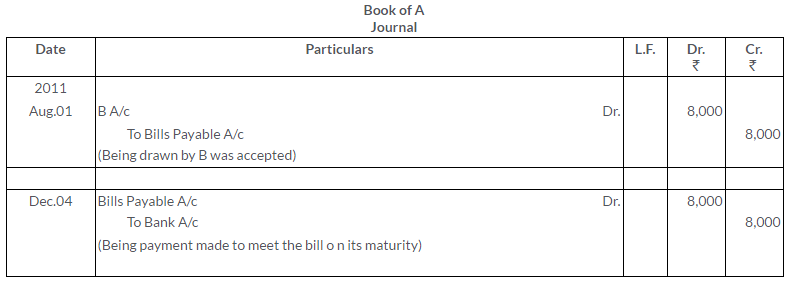
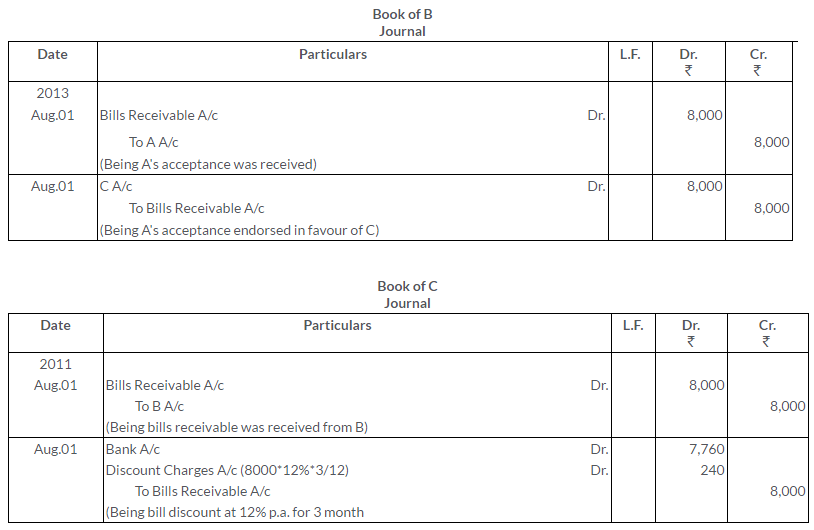
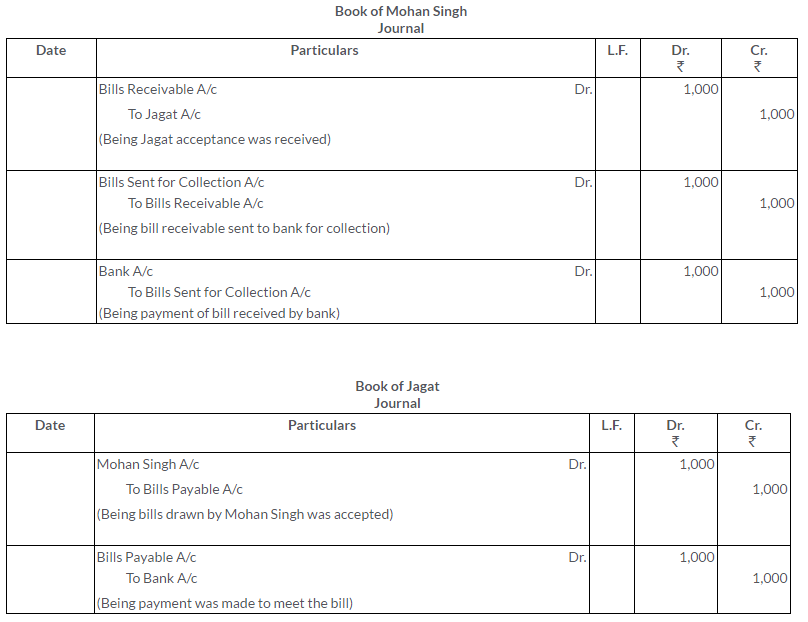
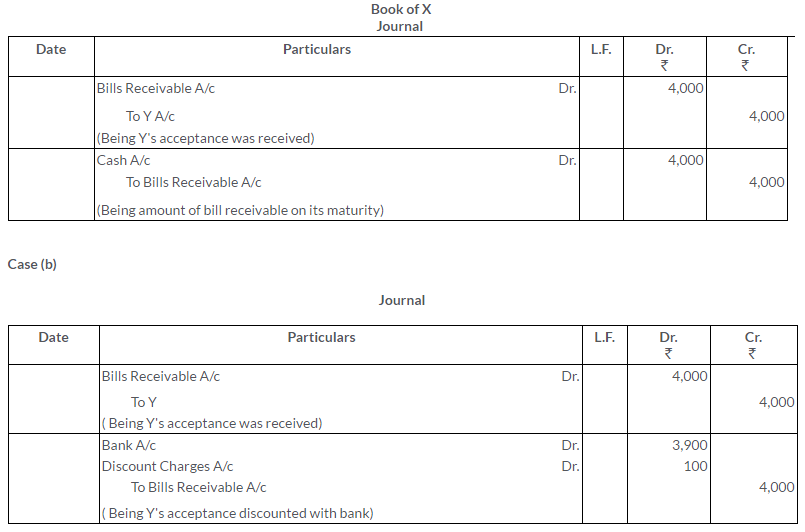
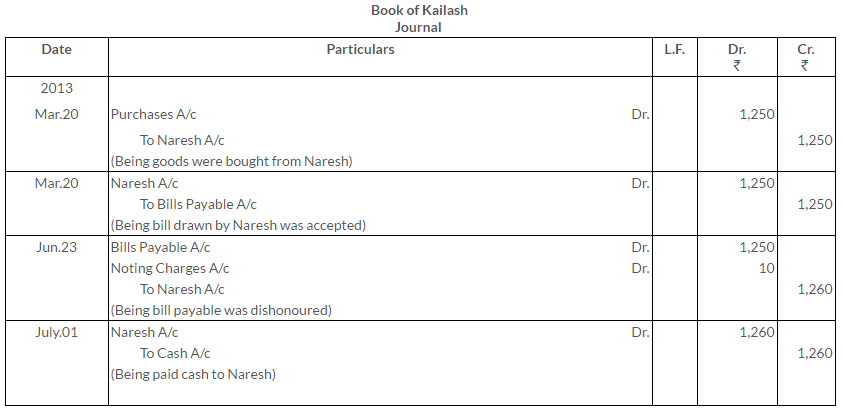
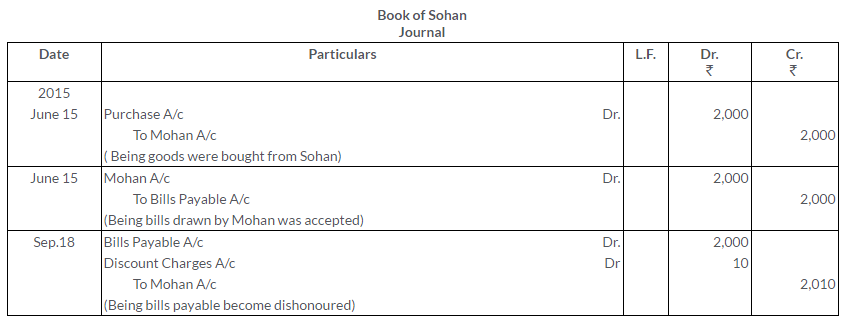
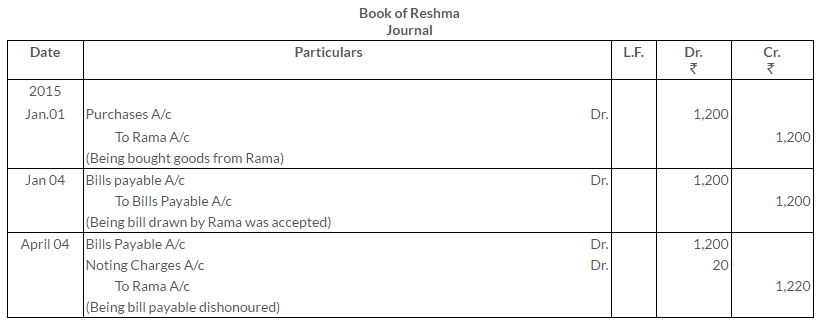
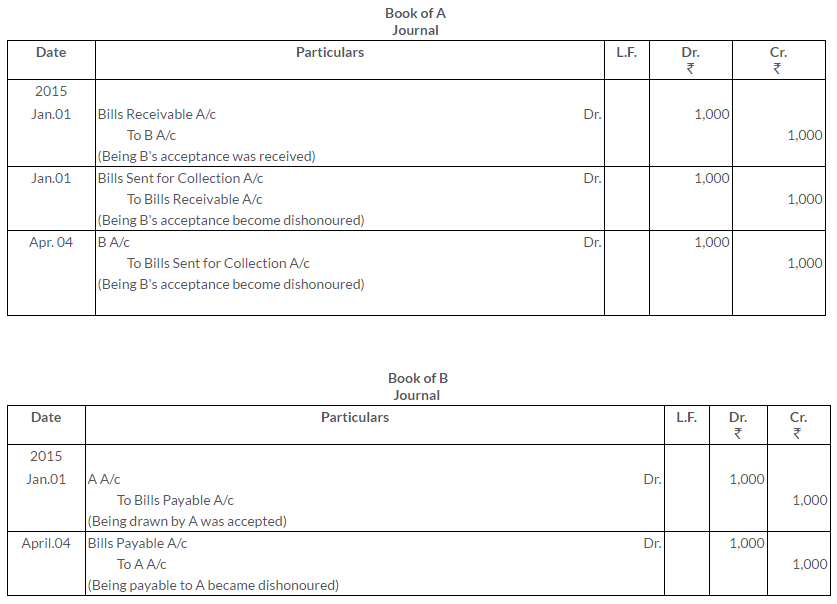
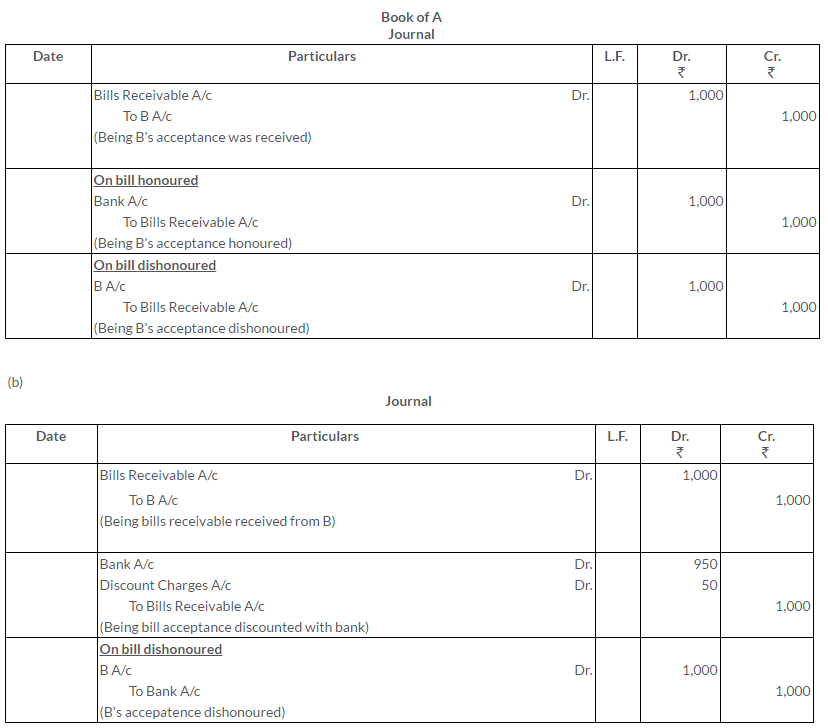
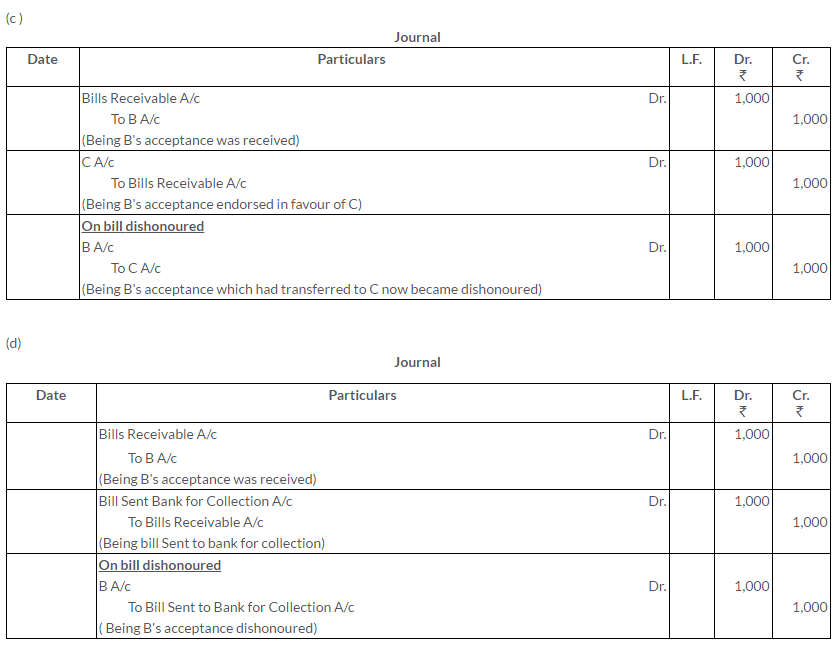
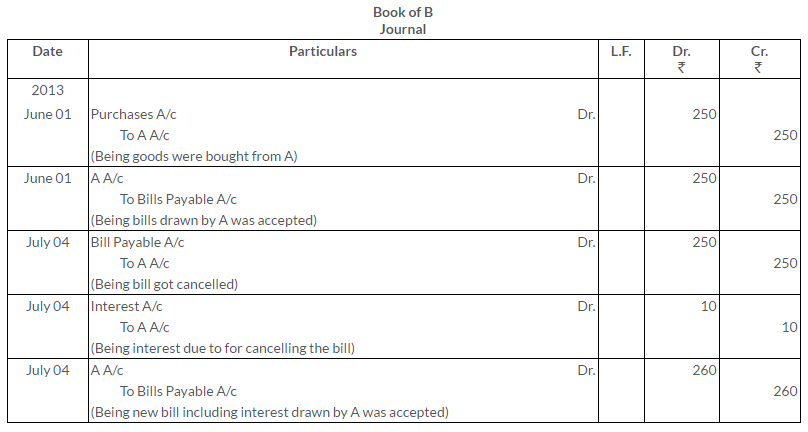
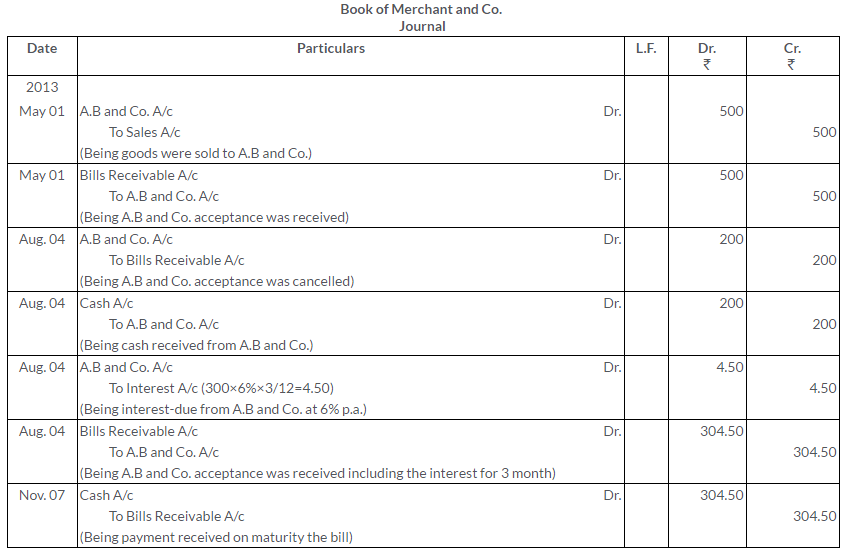
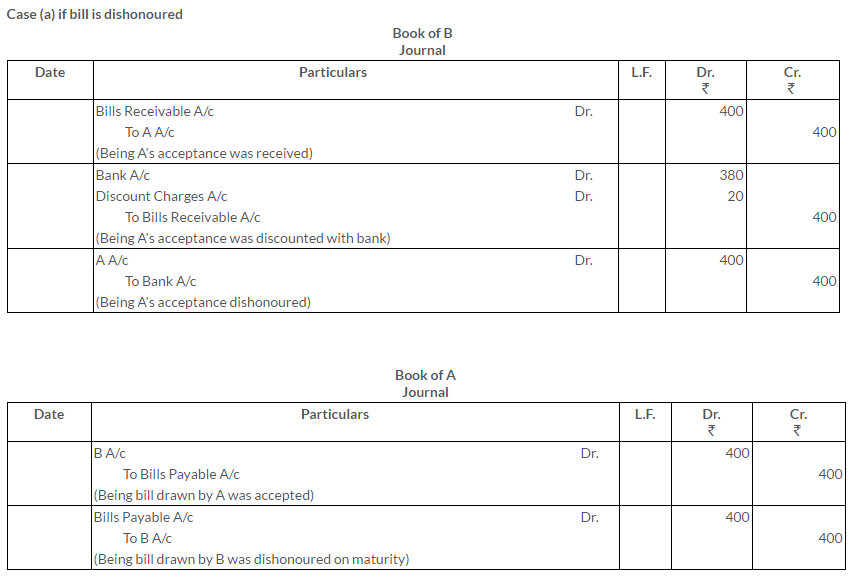
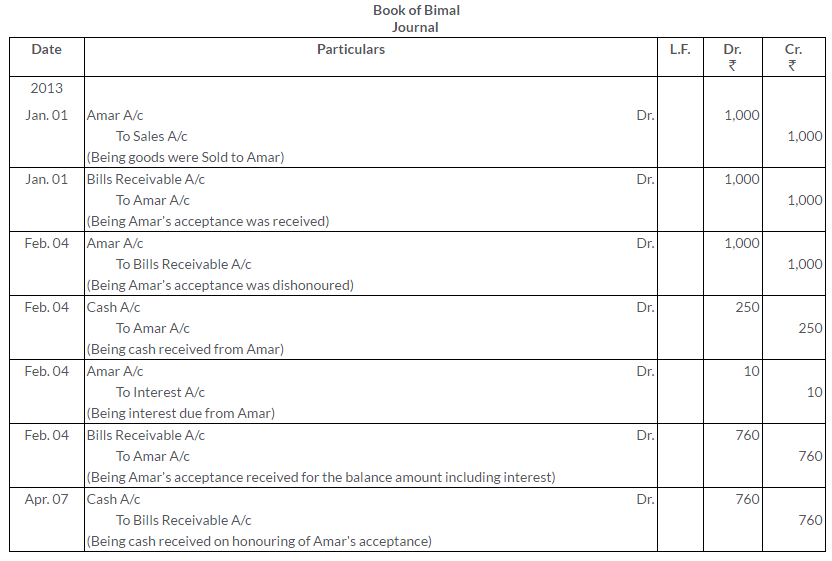
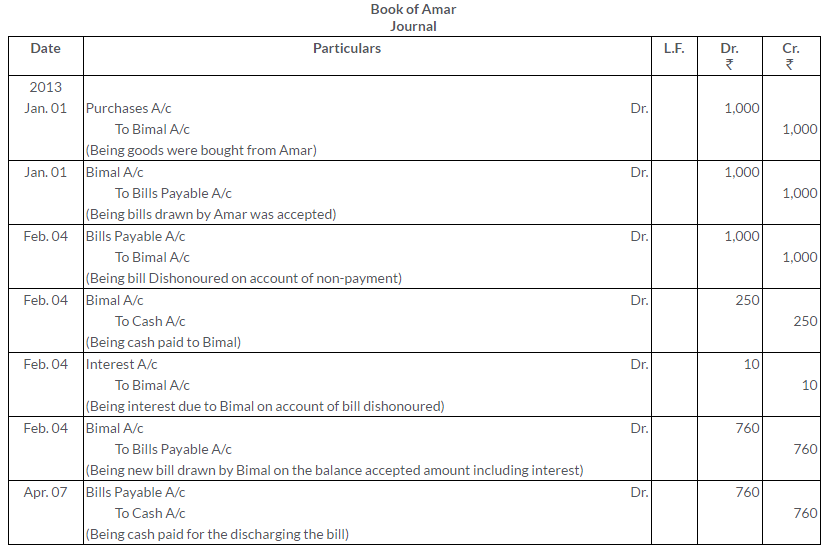
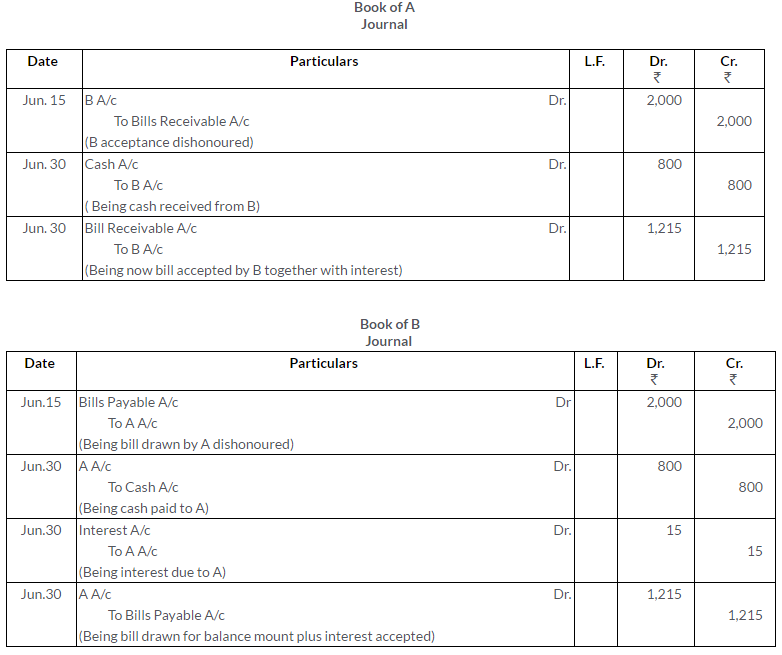
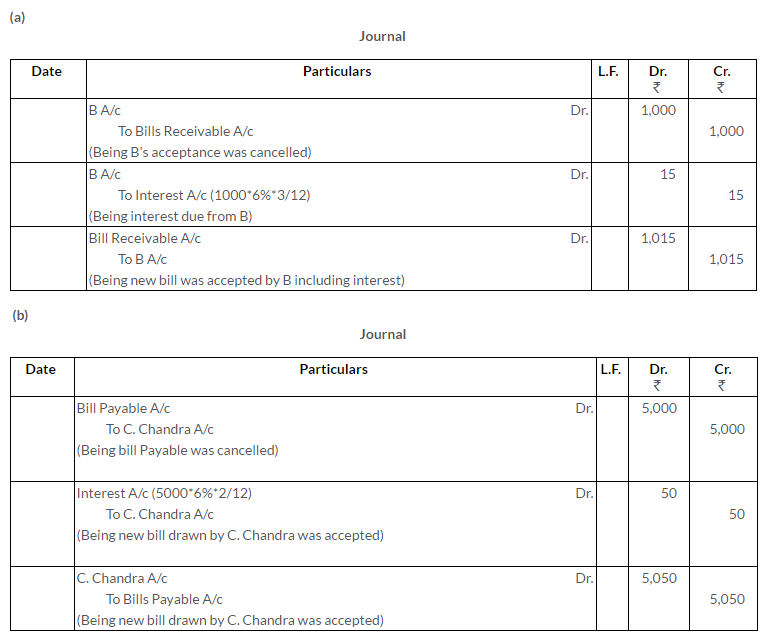
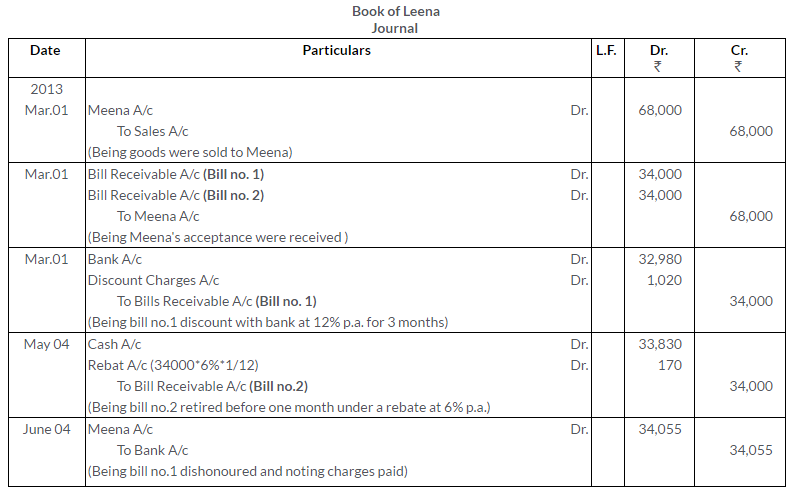
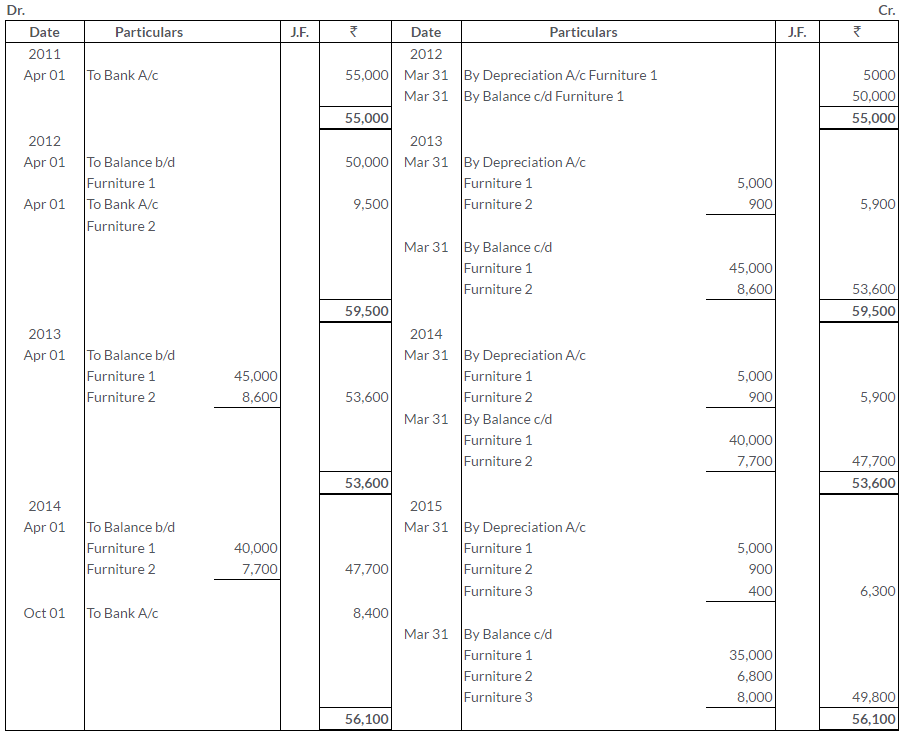
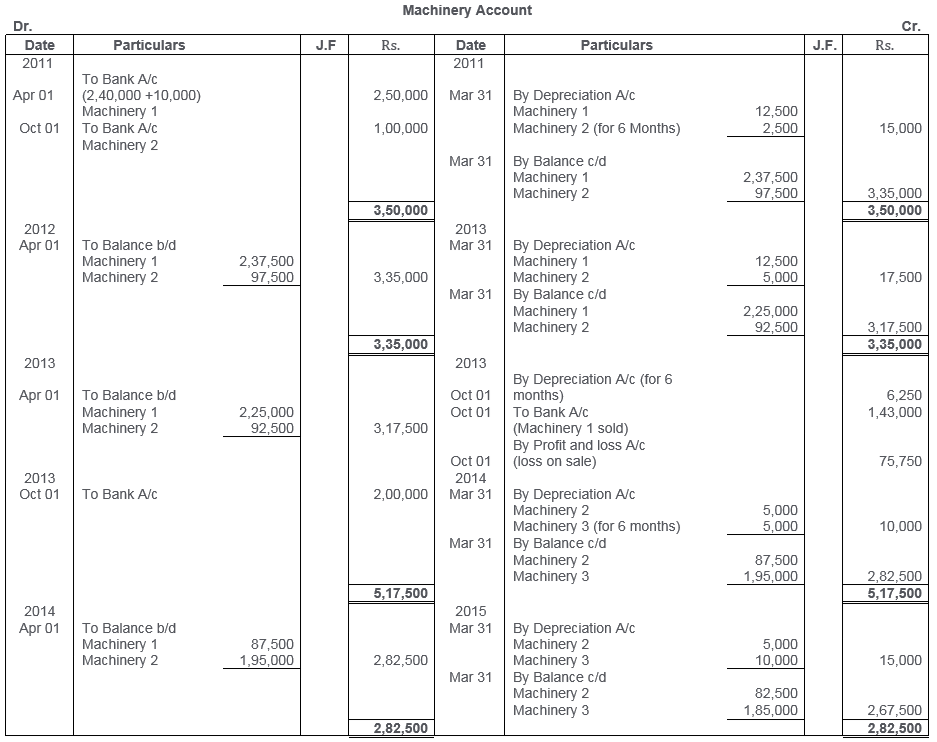
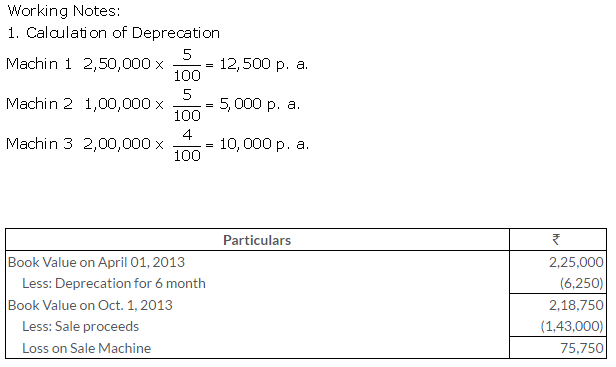
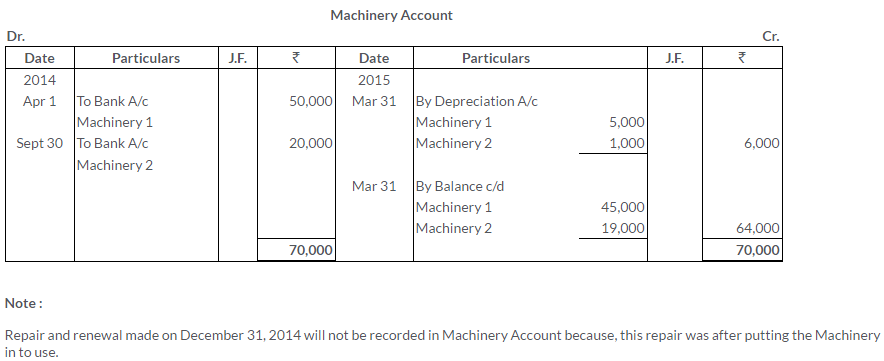
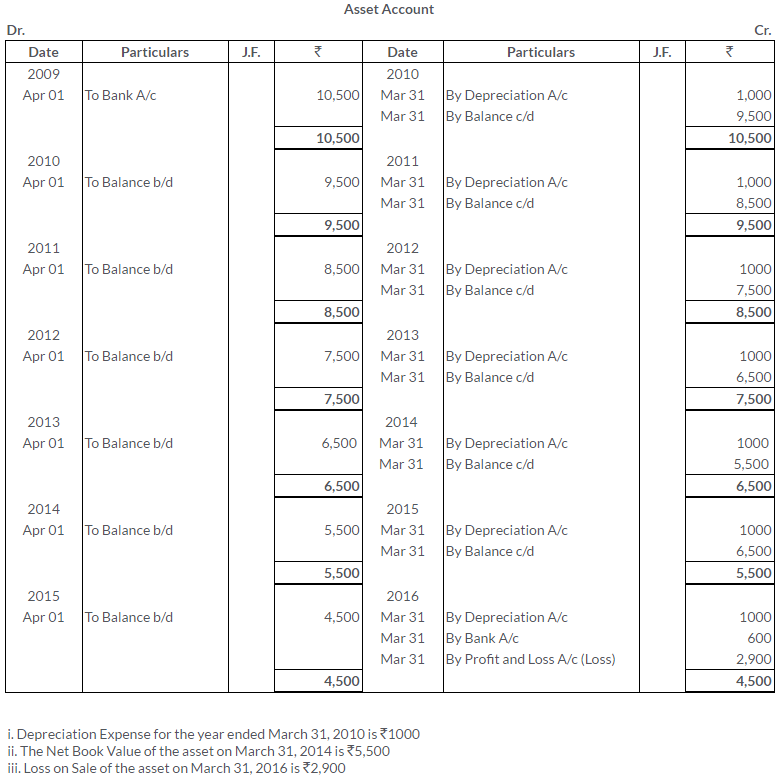
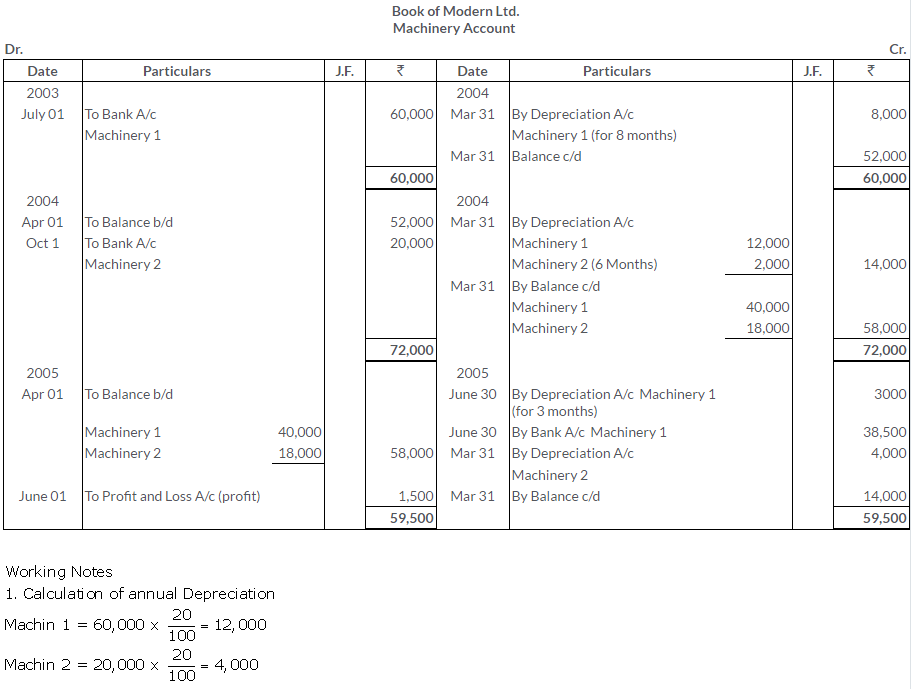
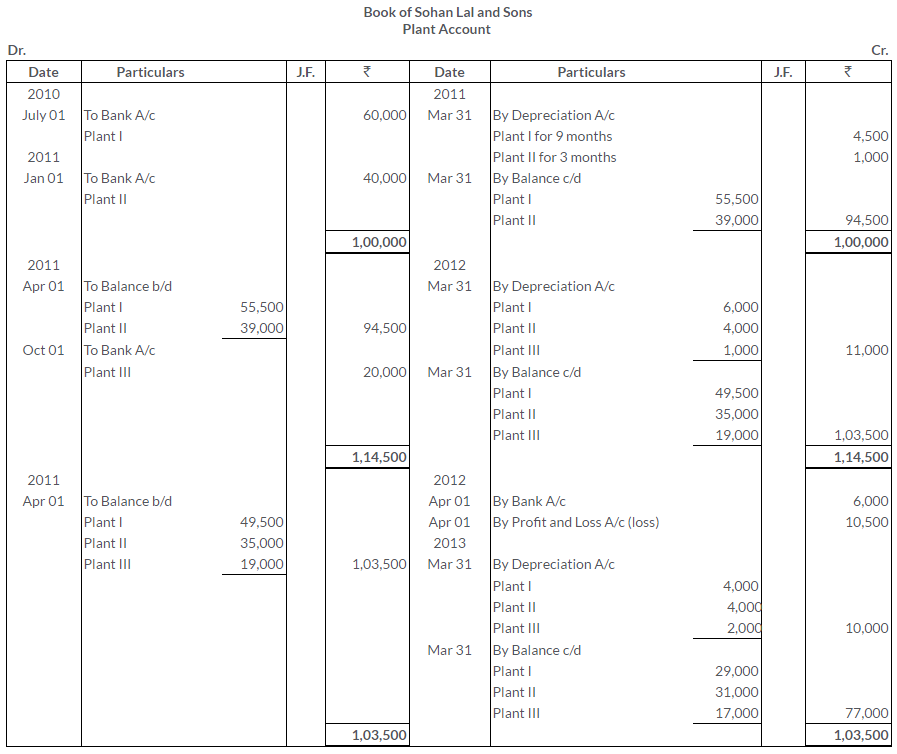
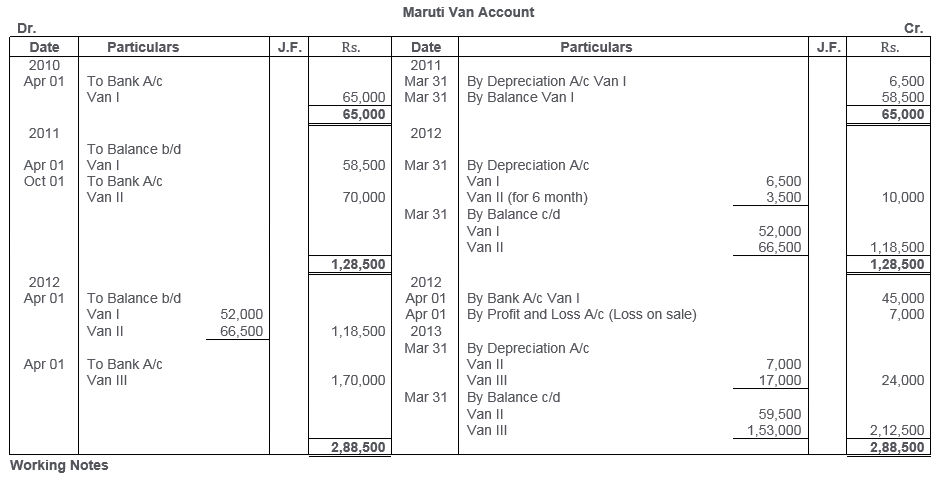
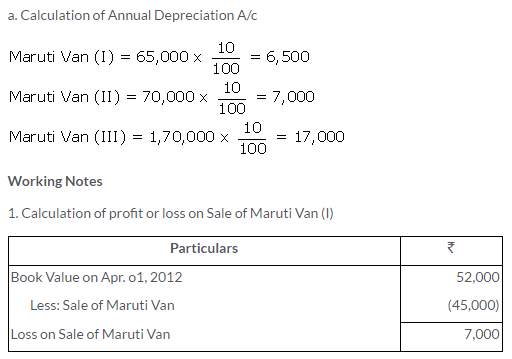
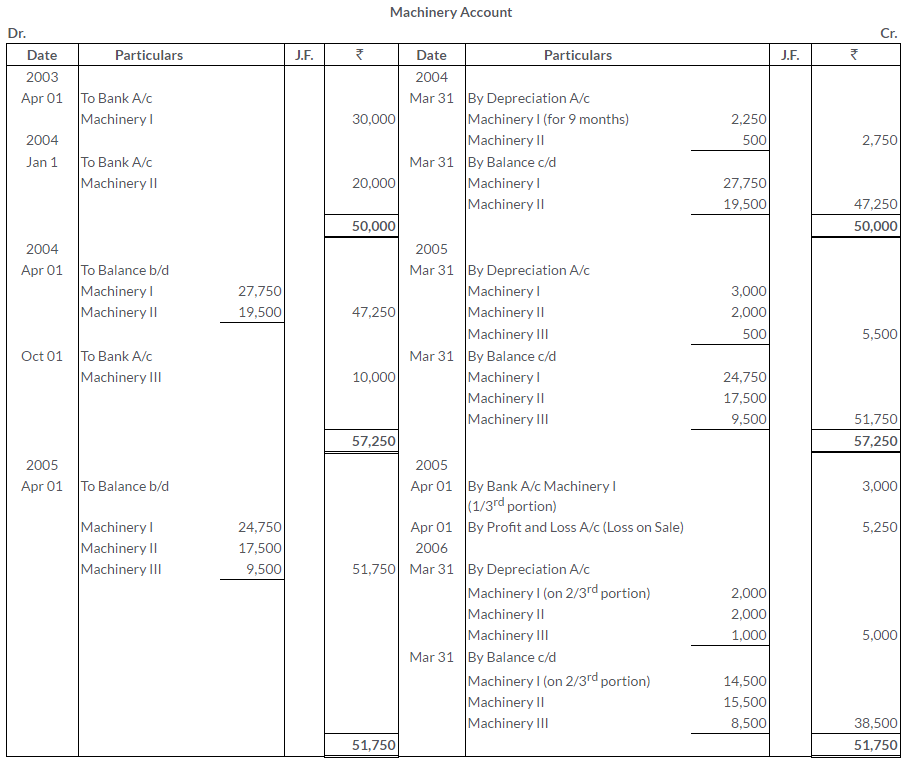
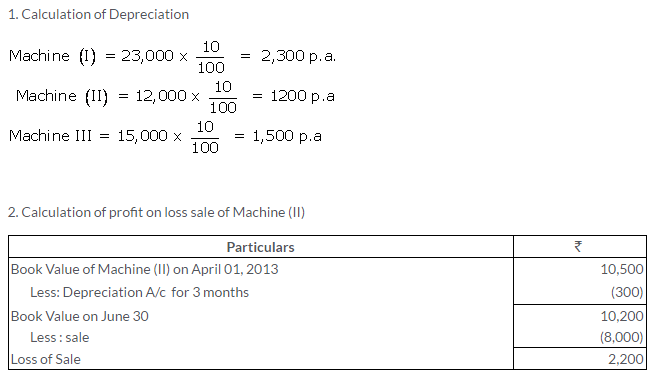
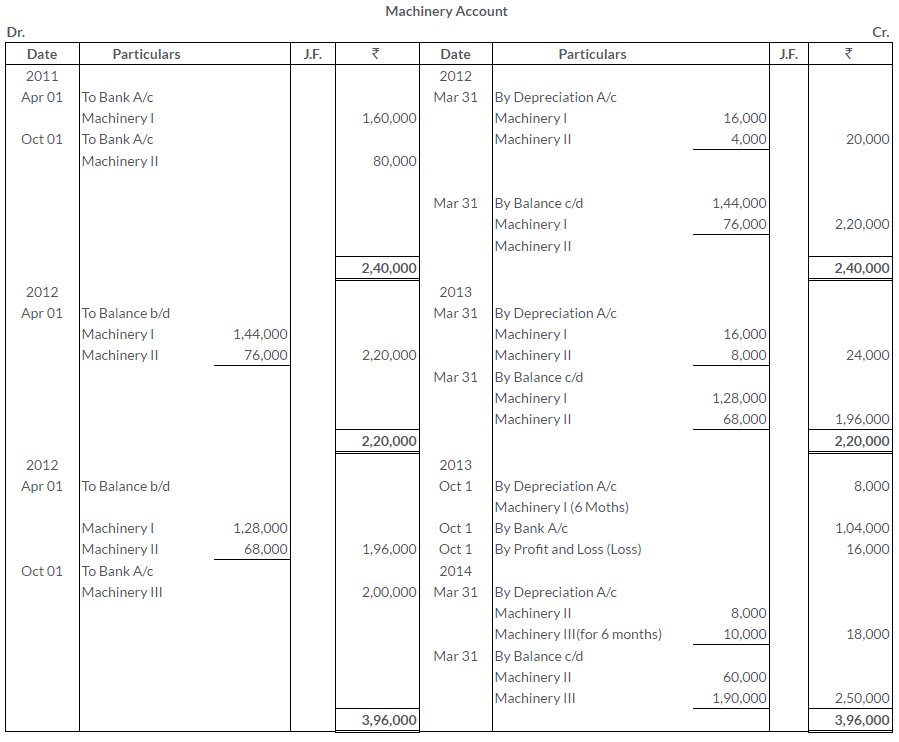
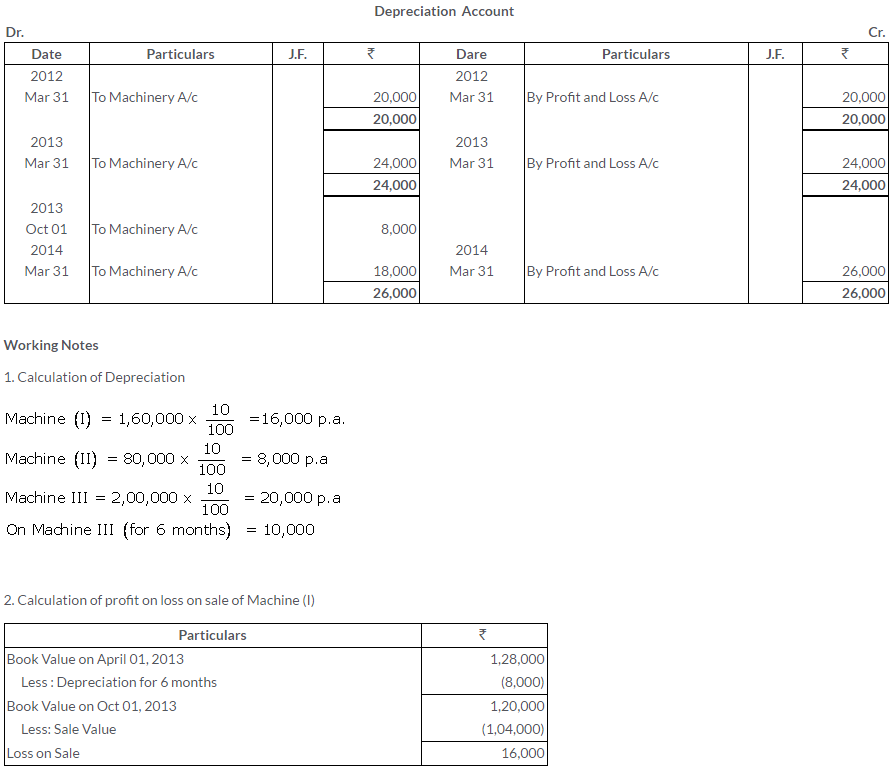
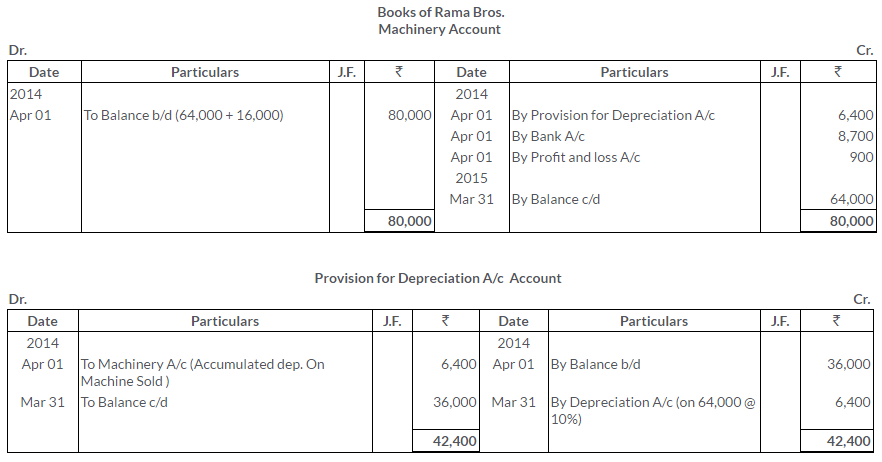
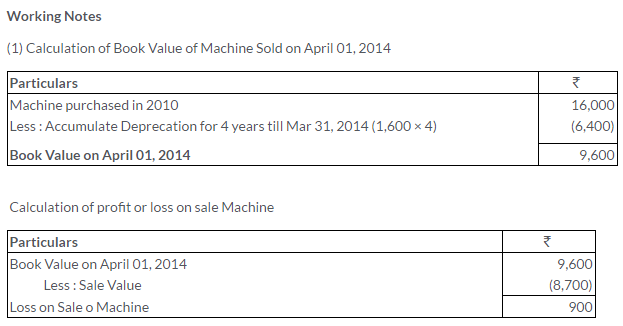
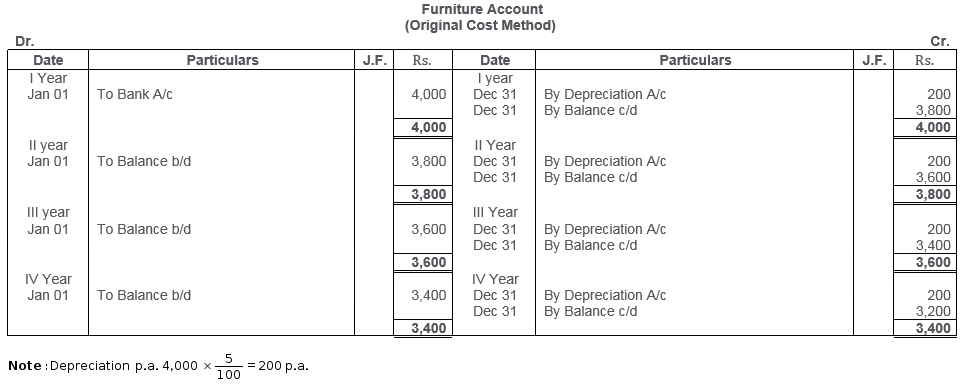
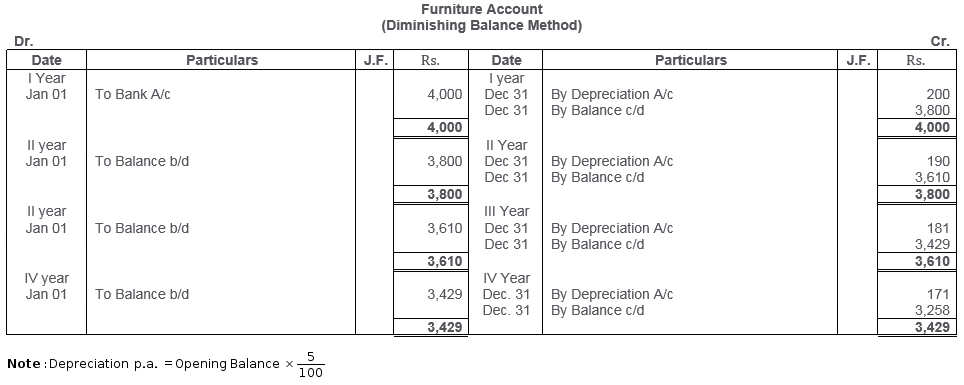
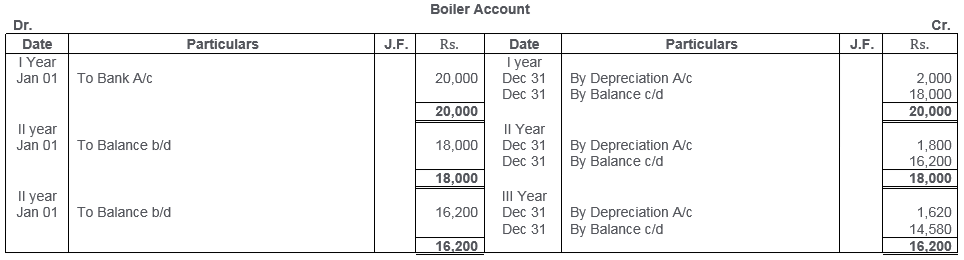
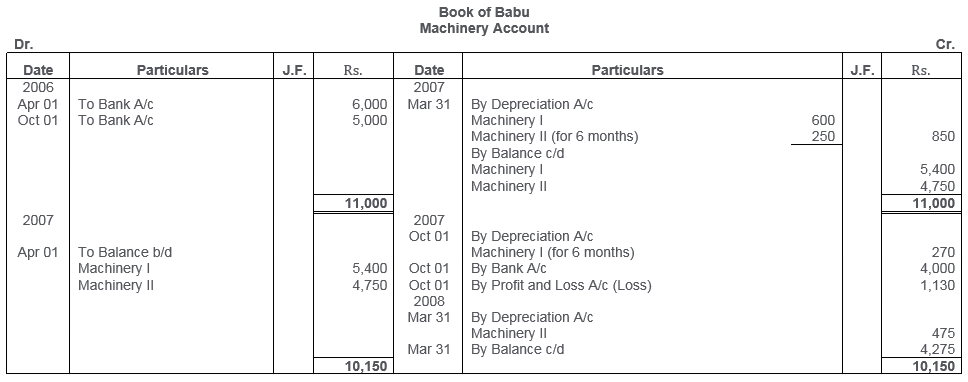
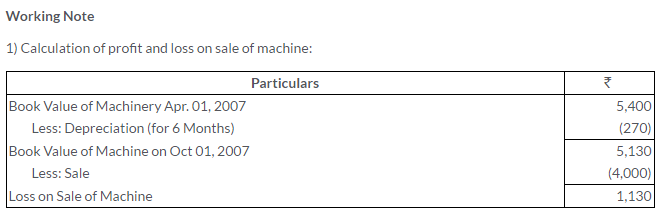
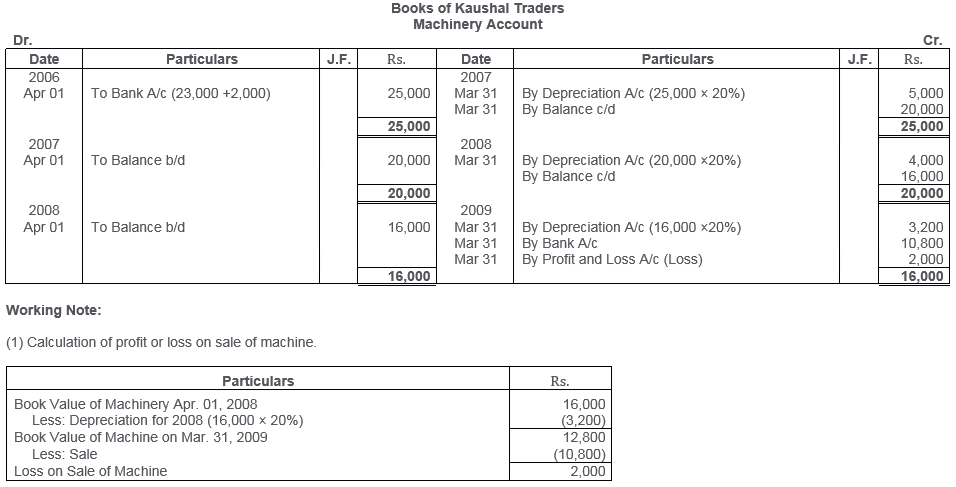
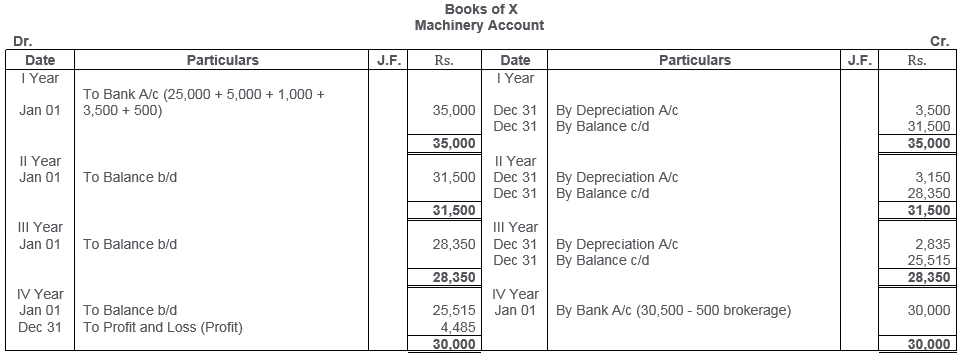
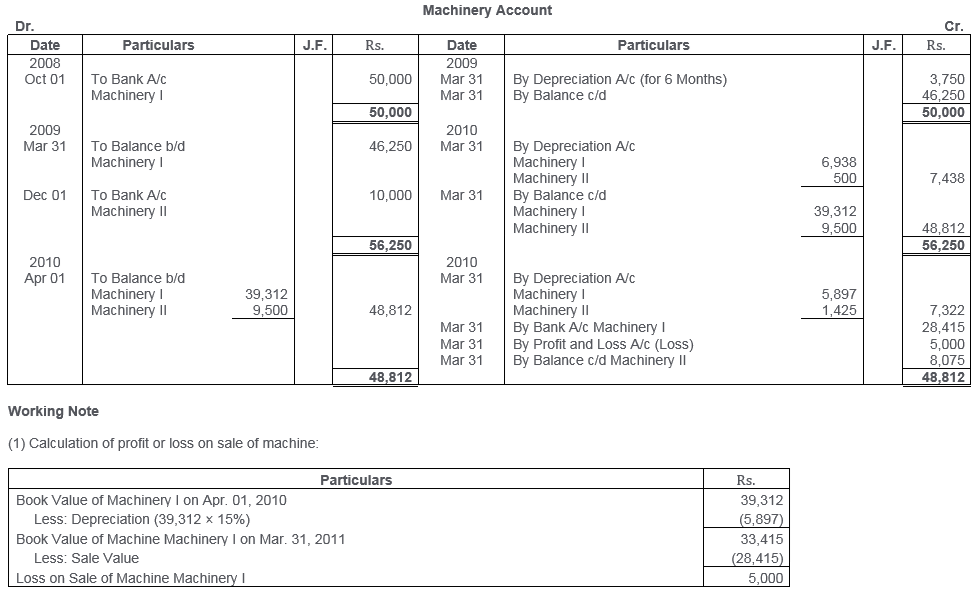
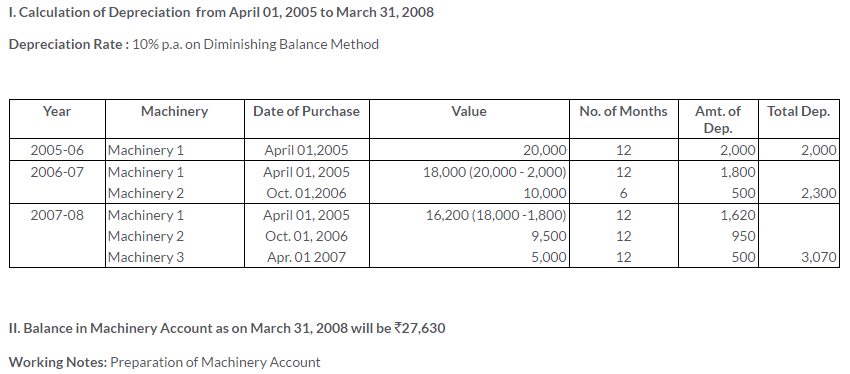
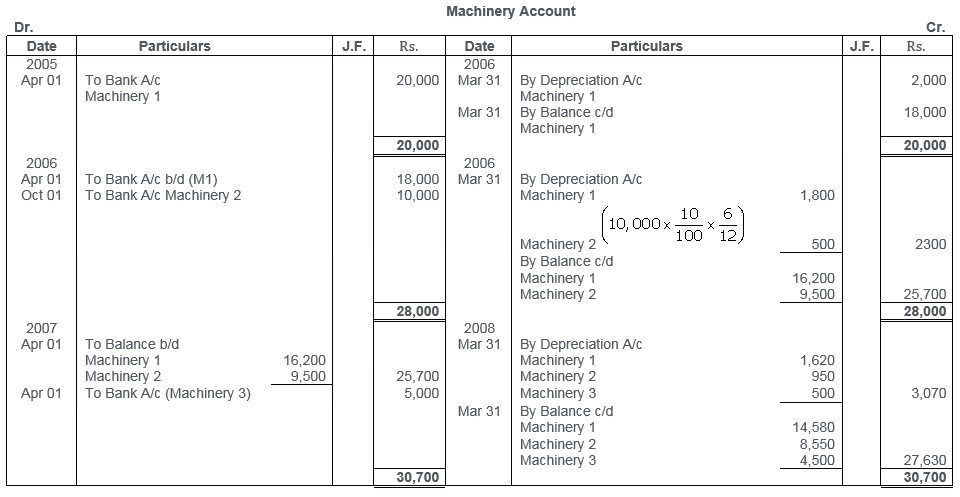
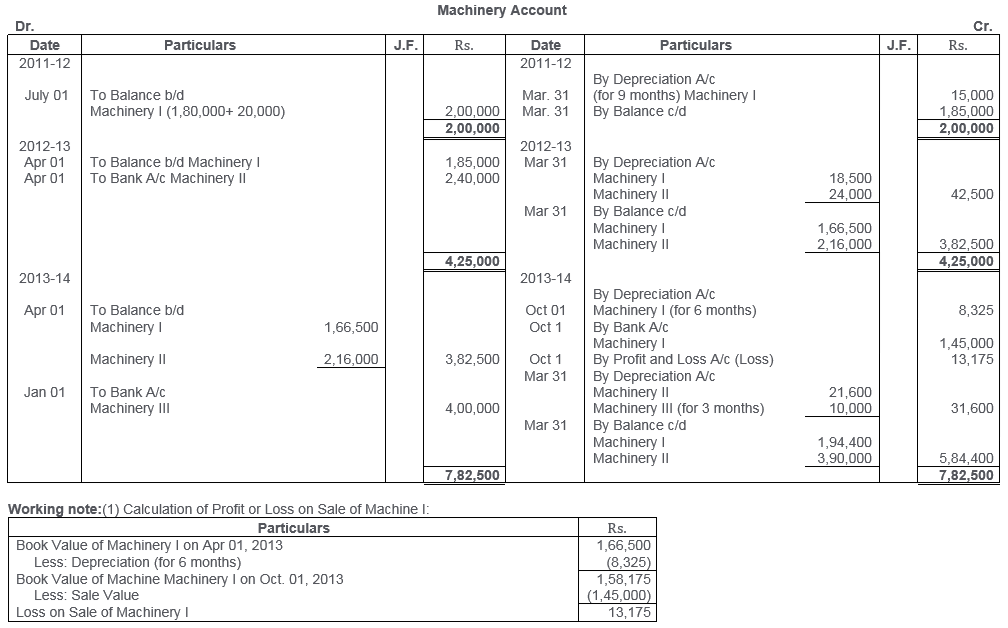
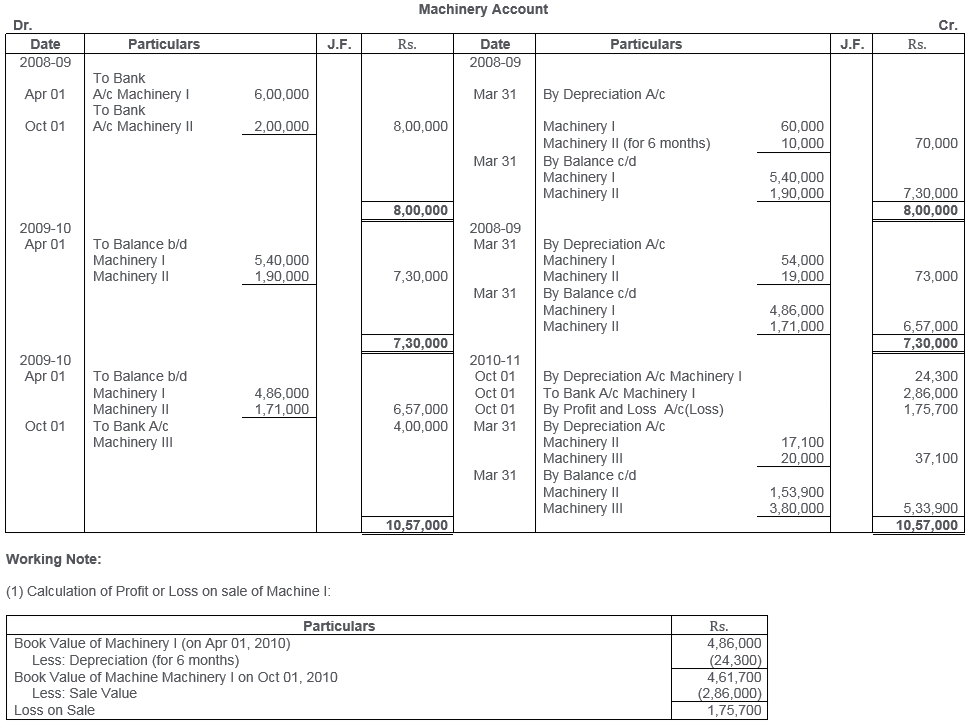
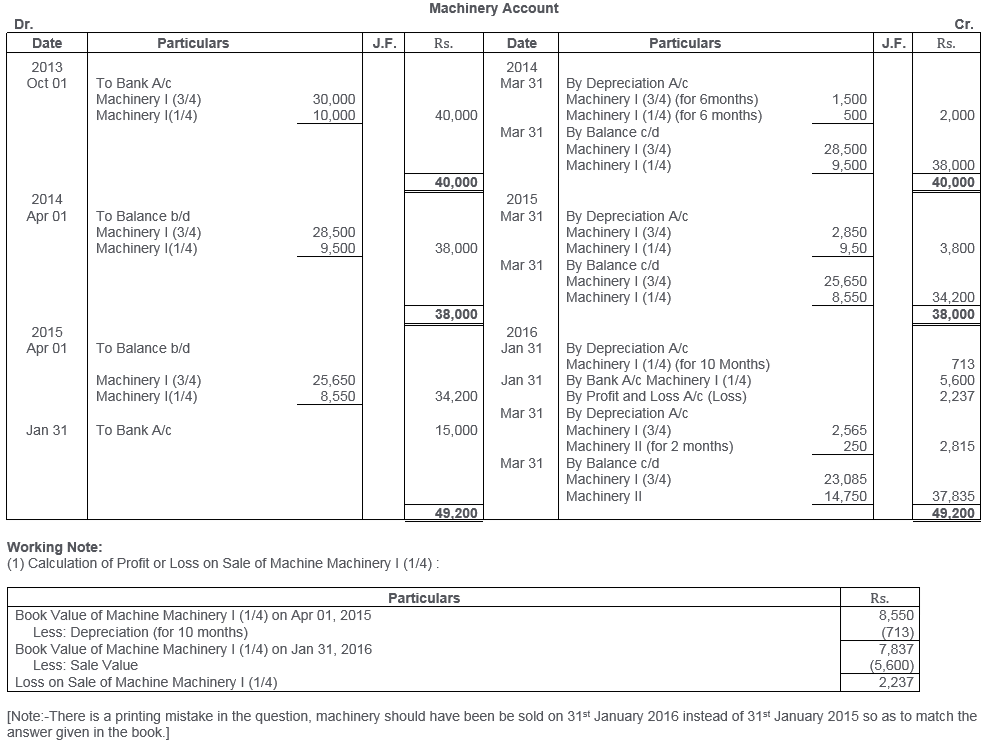
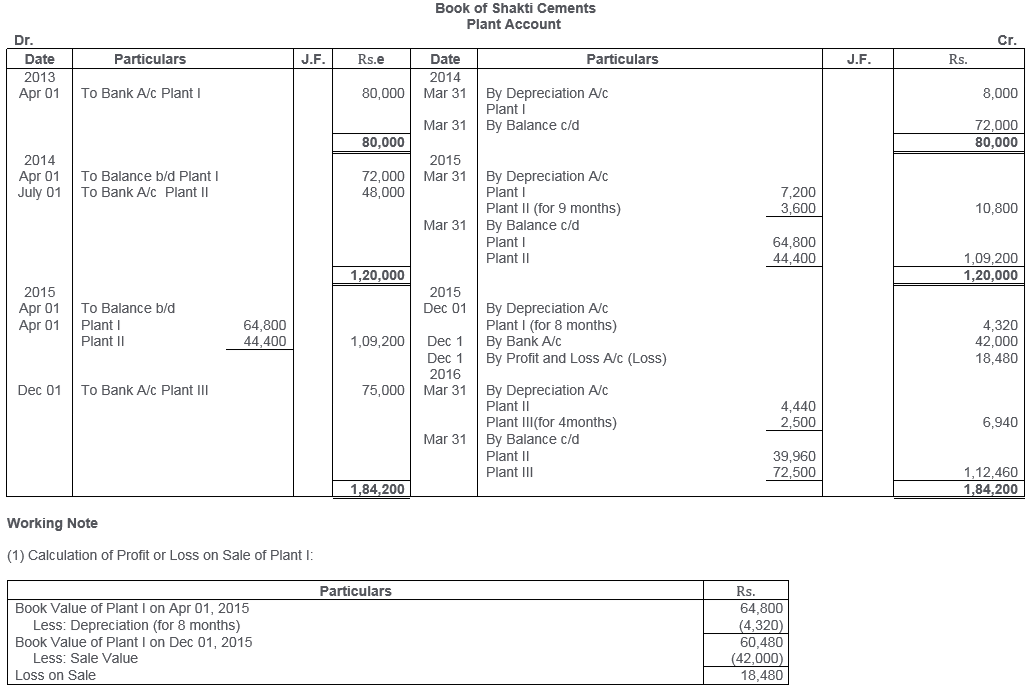
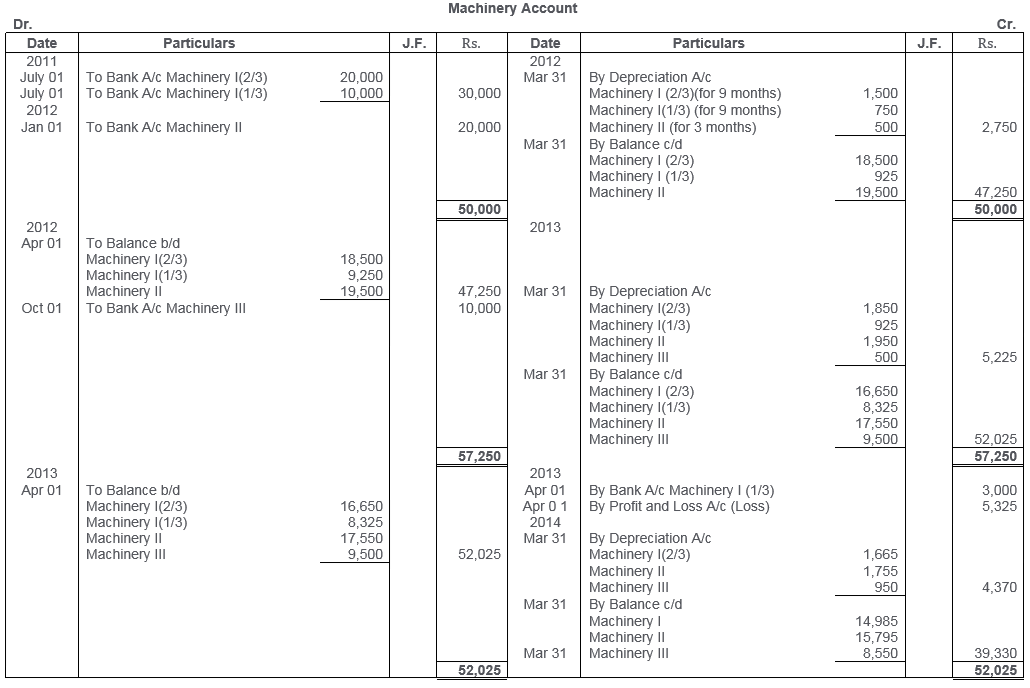
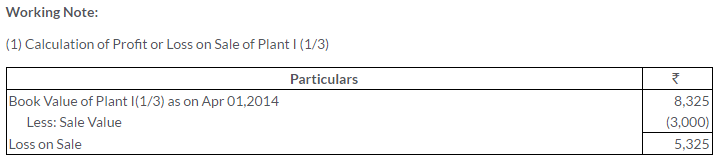
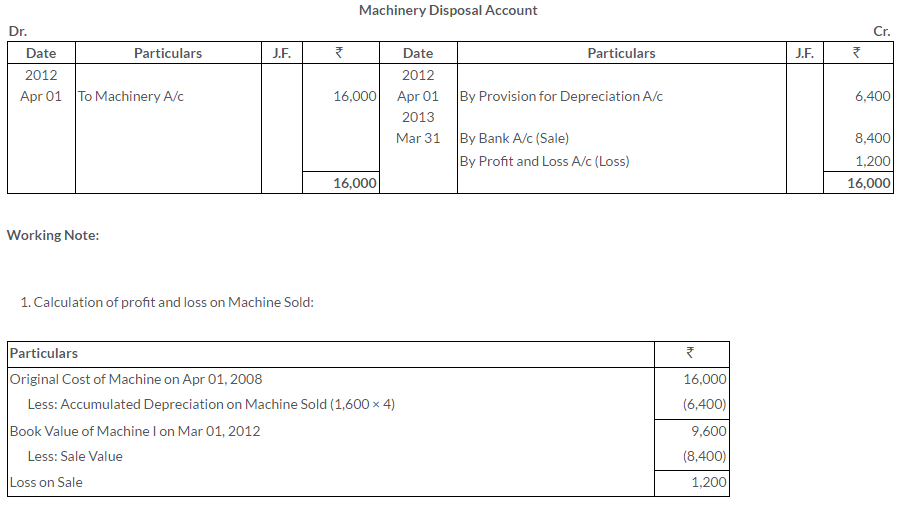
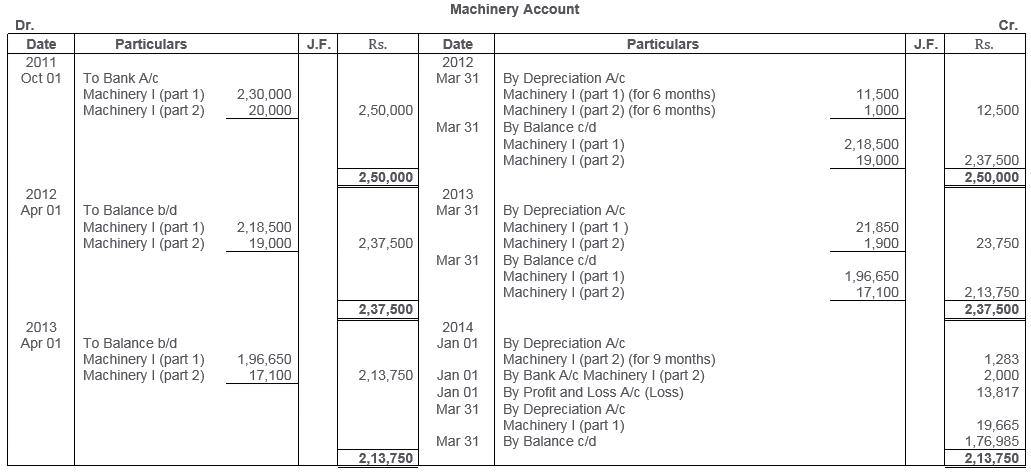
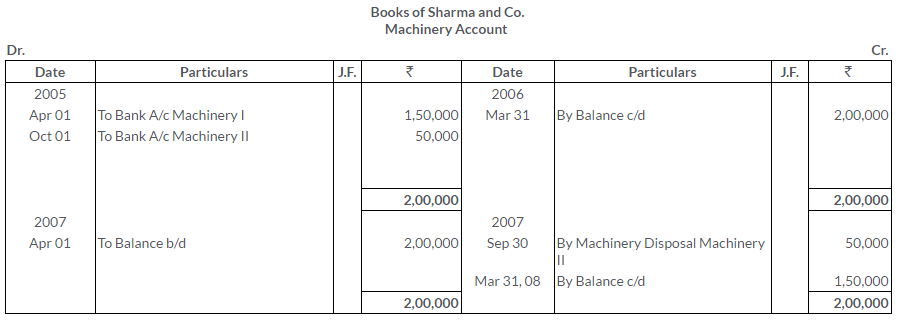
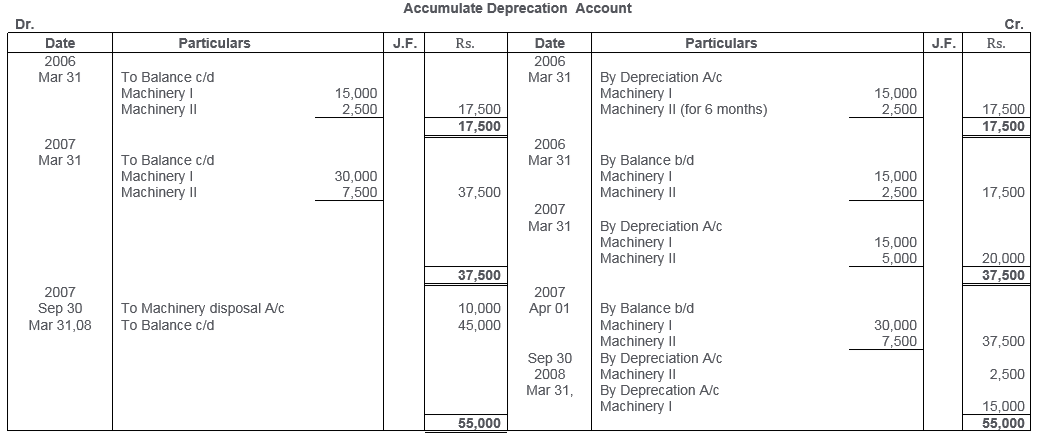
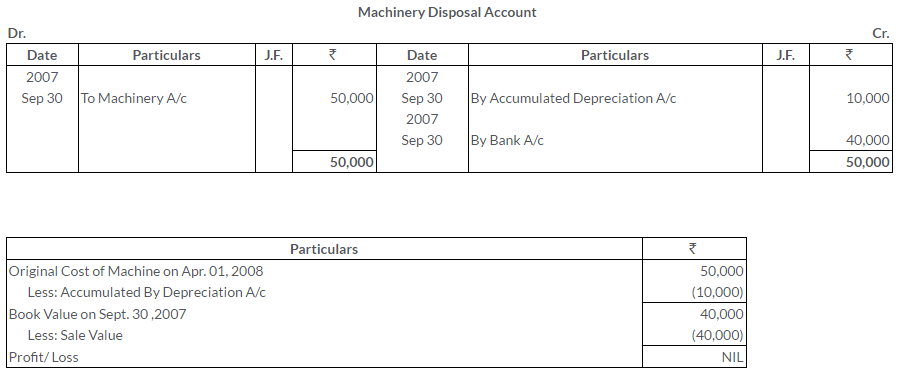
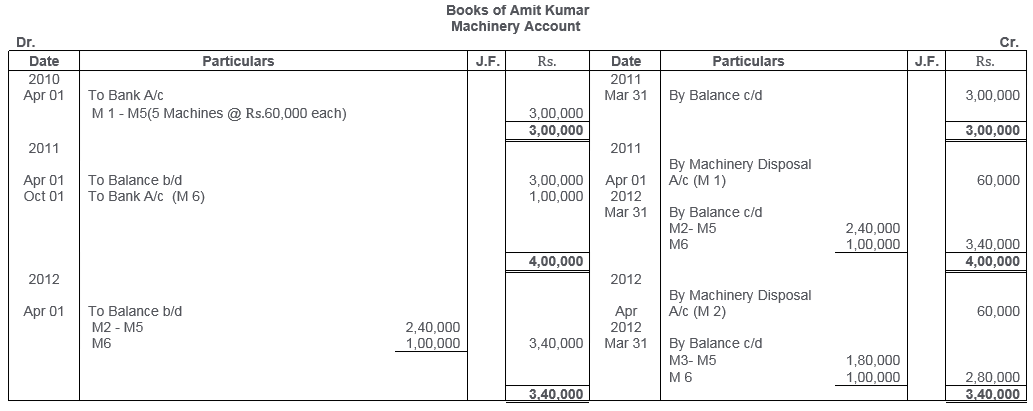
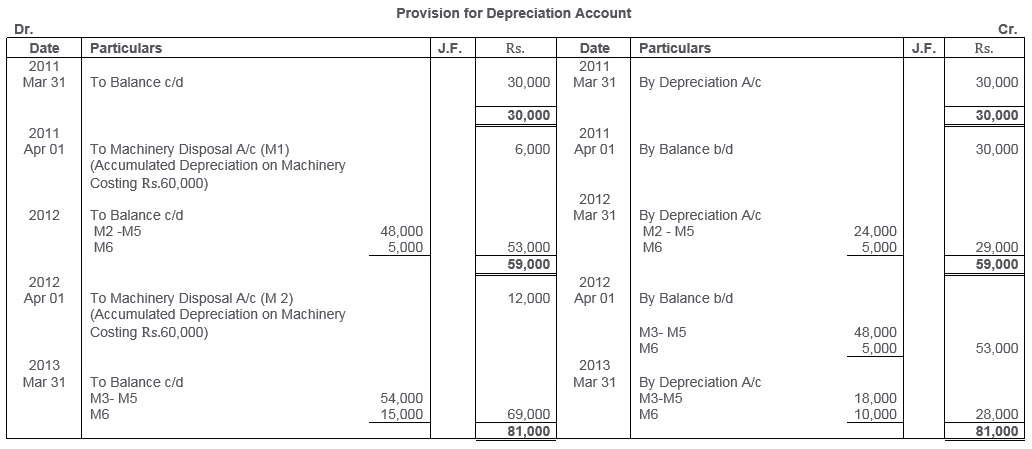
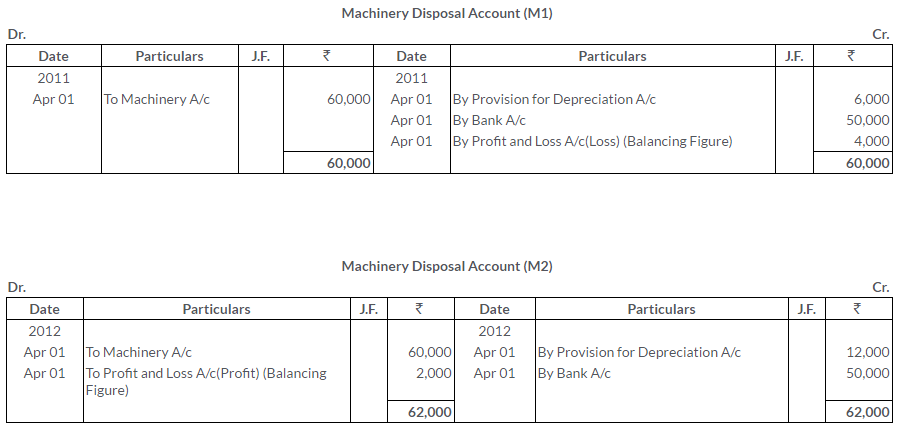
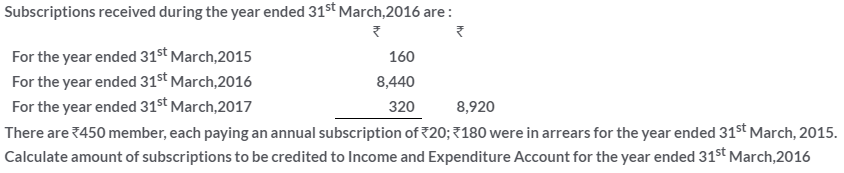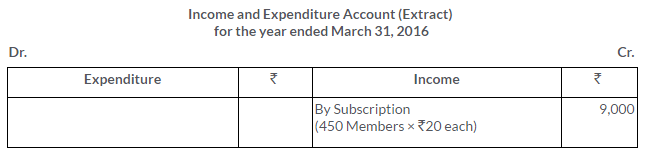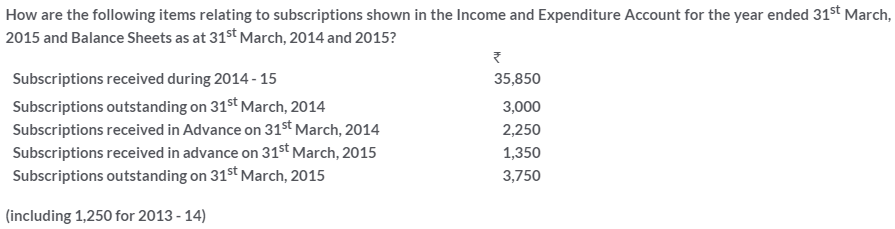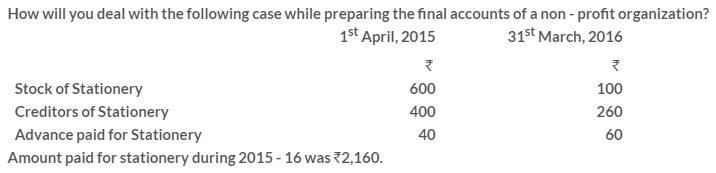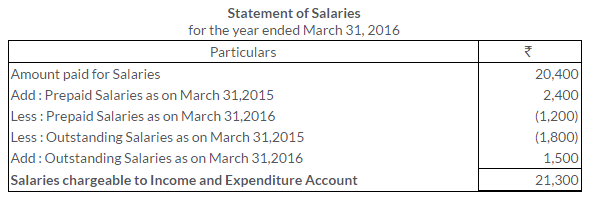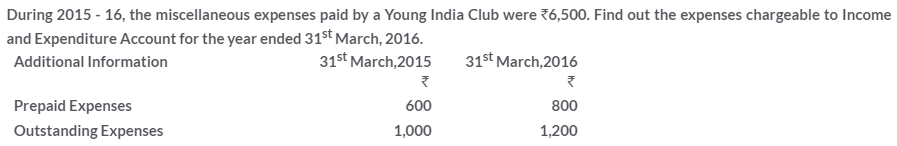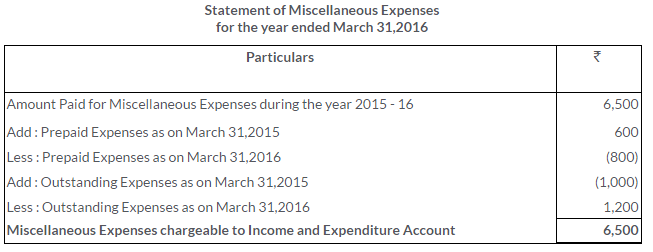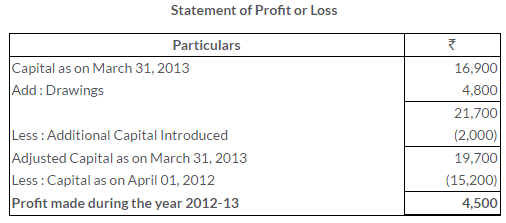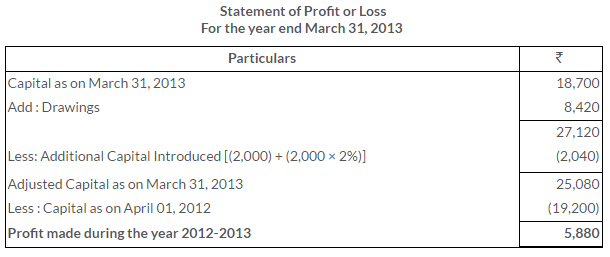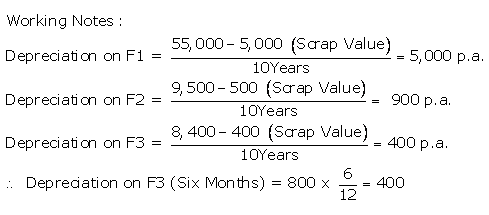TS Grewal Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 16 – Rectification of Errors
Question 1.
How will you rectify the following errors?
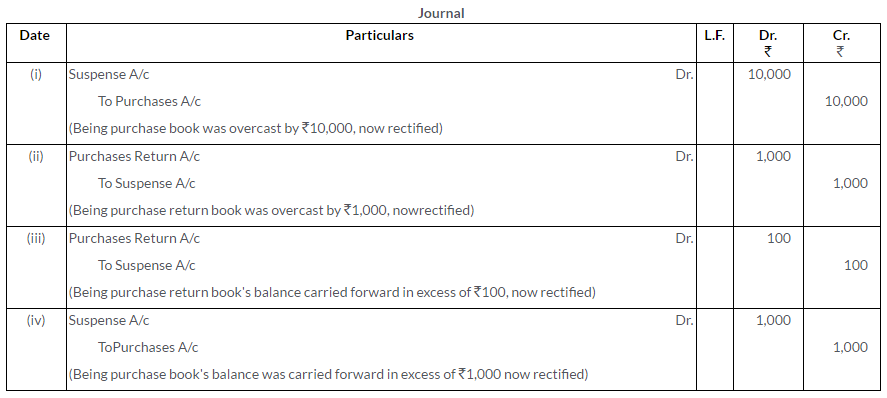
i. Purchases Book is overcast by Rs.10,000.
ii. Purchases Return Book is overcast by Rs.1,000.
iii. Purchases Return Book’s balance is carried forward in excess by Rs.100.
iv. Purchases Book’s balance is carried forward in excess by Rs.1,000.
Note: The above errors have been detected before the preparation of Trial Balance.
Solution:
Question 2.
How will you rectify the following errors?
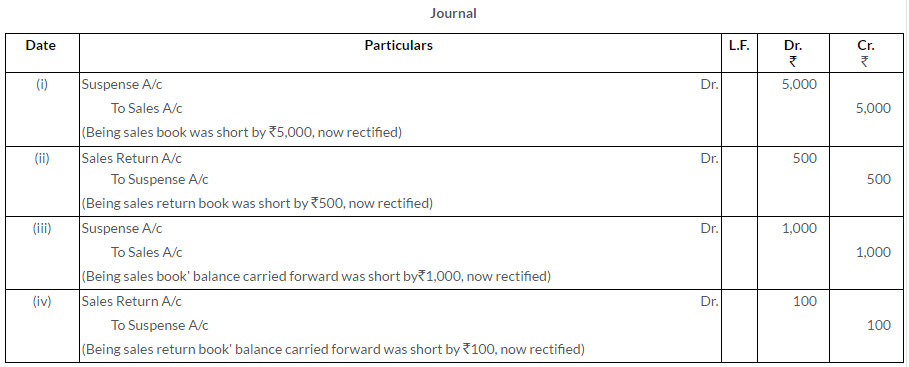
i. Sales Book is short casted by Rs.5,000.
ii. Sales Return Book is short casted by Rs.500.
iii. Balance of Sales Book is carried forward short by Rs.1,000.
iv. Balance of Sales Return Book is carried forward short by Rs.100.
Solution:
Question 3.
How will you rectify the following errors?
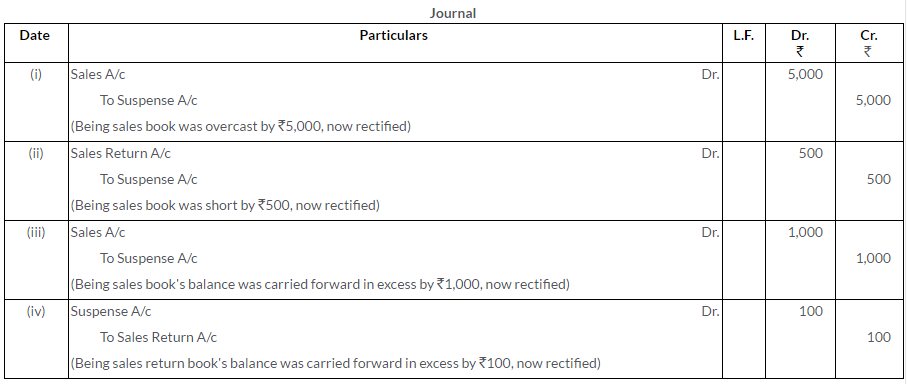
i. Sales Book is overcast by Rs.5,000.
ii. Sales Return Book is short casted by Rs.500.
iii. Balance of Sales Book is carried forward in excess by Rs.1,000.
iv. Balance of Sales Return Book is carried forward in excess by Rs.100.
Solution:
Question 4.
Rectify the following errors assuming that there is no Suspense Account:
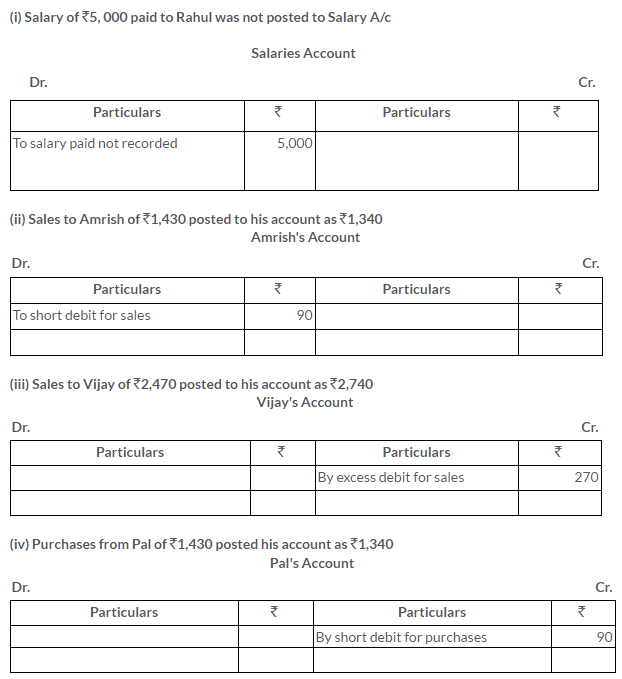
i. Salary of Rs.5,000 paid to Rahul was not posted to Salaries Account.
ii. Sales to Amrish of Rs.1,430 posted to his account as Rs.1,340.
iii. Sales to Vijay of Rs.2,470 posted to his account as Rs.2,740.
iv. Purchases from Pal of Rs.1,430 posted to his account as Rs.1,340.
Solution:
Question 5.
Which of the following errors will affect the Trial Balance?
i. The total of the Sales Book has not been posted to the Sales Account.
ii. Rs.1,000 paid as installation charges of a new machine has been debited to Repairs Account.
iii. Goods costing Rs.4,000 taken by the proprietor for personal use have been debited to Debtor’s Account.
iv. Rs.1,000 paid for repairs to building have been debited to Building Account.
[The total of the Sales Book has not been posted to Sales Account will affect the Trial Balance.]
Solution:
Total of Sales book has not been posted to Sales Account will affect the Trial Balance because due to undercast of Sales Accounts results in undercasting of credit side of the Trial Balance.
Question 6.
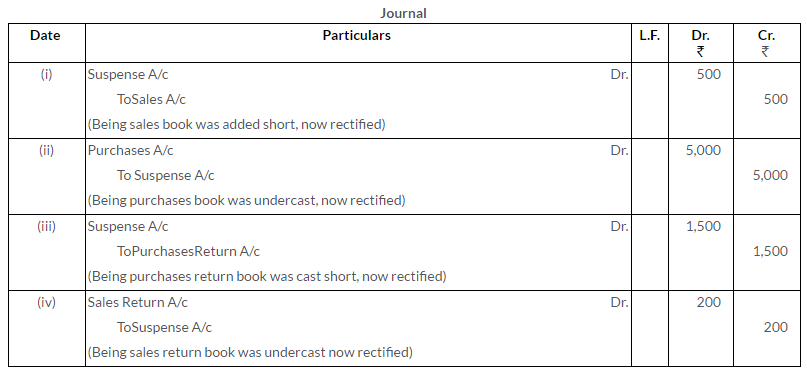
Rectify the following errors:
i. The Sales Book of December was added short by Rs.500.
ii. A periodical total of the Purchases Book was cast short by Rs.5,000.
iii. The total of Purchases Return Book has been undercast by Rs.1,500.
iv. The Sales Return Book is added Rs.200 short.
Solution:
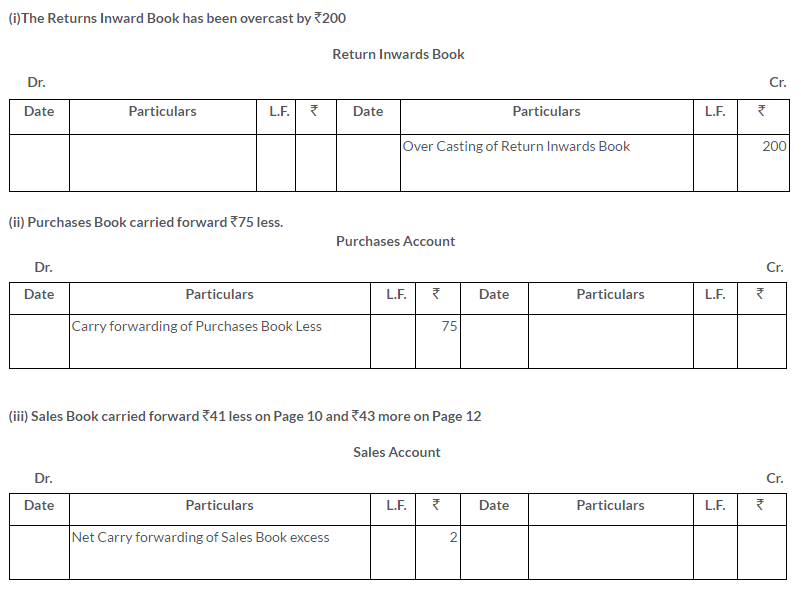
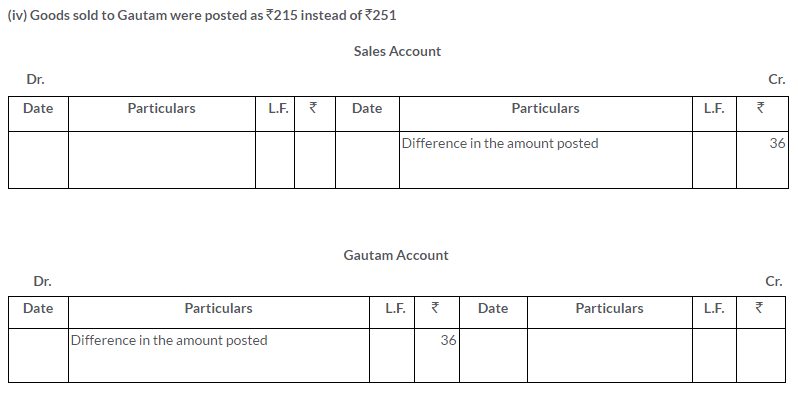
Question 7.
Rectify the following errors assuming that there is no Suspense Account:
i. The Returns Inward Book has been overcast by Rs.200.
ii. Purchases Book carried forward Rs.75 less.
iii. Sales Book carried forward Rs.41 less on Page 10 and Rs.43 more on Page 12
iv. Goods sold to Gautam were posted as Rs.215 instead of Rs.251.
Solution:
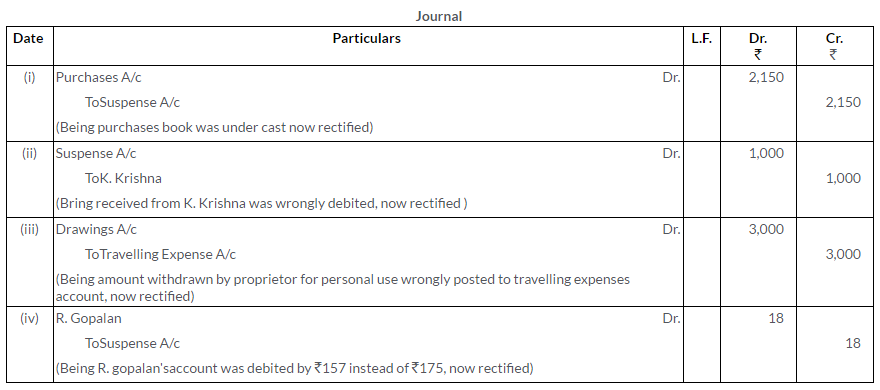
Question 8.
Following errors are discovered in the books of Sit Ram Lal. Make the necessary entries to rectify them:
i. Purchases Journal was Rs.2,150.
ii. Rs.500 received from K. Krishna was debited to his account.
iii. An amount of Rs.3,000 withdrawn by the proprietor of the firm for his personal use was posted to the Travelling Expense Account.
iv. An amount of Rs.175 for a credit sale to R. Gopalan correctly entered in the Sale Book, has been debited to his account as Rs.157
Solution:
Question 9.
Pass the Journal entries rectifying the following errors:
i. Purchases of Rs.10,000 was omitted to be recorded.
ii. Purchases of office furniture of Rs.10,000 was recorded in Purchases Book.
iii. Office Rent of Rs.15,000 was debited to the Personal Account of the landlord.
iv. Old machine was sold for Rs.5,000 was credited to Sales Account.
Solution:
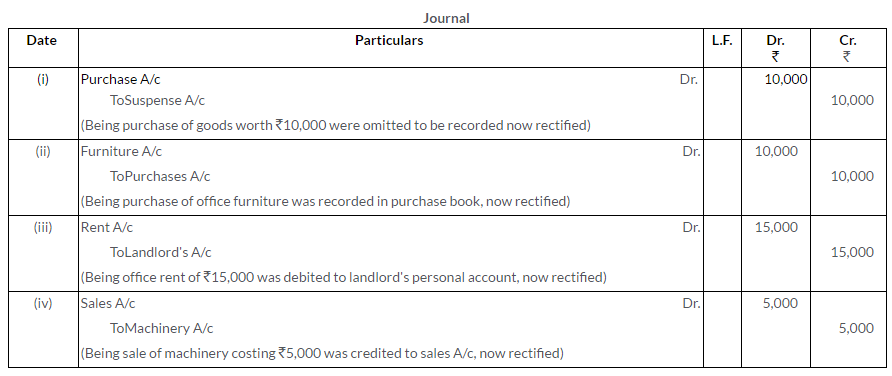
Question 10.
Following errors affecting the accounts for the year 2015 were detected in the books of Dasand Co., Meerut:
i. Sale of old furniture for Rs.5,000 was treated as sales of goods.
ii. Rent of proprietor’s residence Rs.6,000 was debited to Rent Account.
iii. Cash received from Rajesh Rs.2,150 was credited to Brajesh.
Pass the rectifying Journal entries. State the nature of each of these mistakes.
Solution:
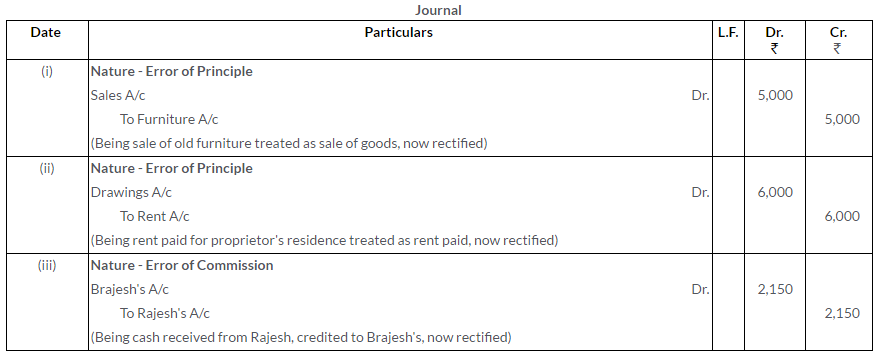
Question 11.
Rectify the following errors:
i. Purchases Book has been undercast by Rs.1,000.
ii. Credit sale to Anu Prakash Rs.7,000 was recorded in Purchases Book.
iii. Credit sale to Rahul Rs.7,000 was recorded as Rs.700.
Solution:
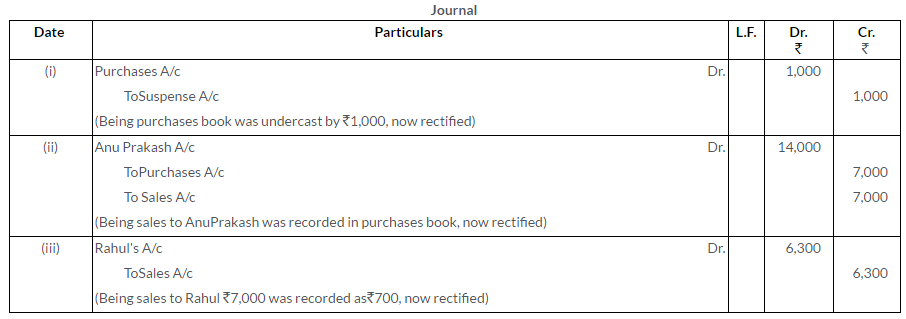
Question 12.
Rectify the following errors:
i. Total of one page of the Sales Book was carried forward to the next page as Rs.2,785 instead of Rs.2,587.
ii. A cheque of Rs.400 received from Mohan was dishonoured and had been posted to the debit side of the ‘Allowance Account’.
iii. Return of goods worth Rs.5,000 by a customer was entered in the Purchase Return Book.
iv. Sum of Rs.200 owed by ‘X’ has been included in the list of Sundry Creditors.
v. Sale of old furniture worth Rs.430 was credited to the Sales Account as Rs.340.
(KVS 2005)
Solution:
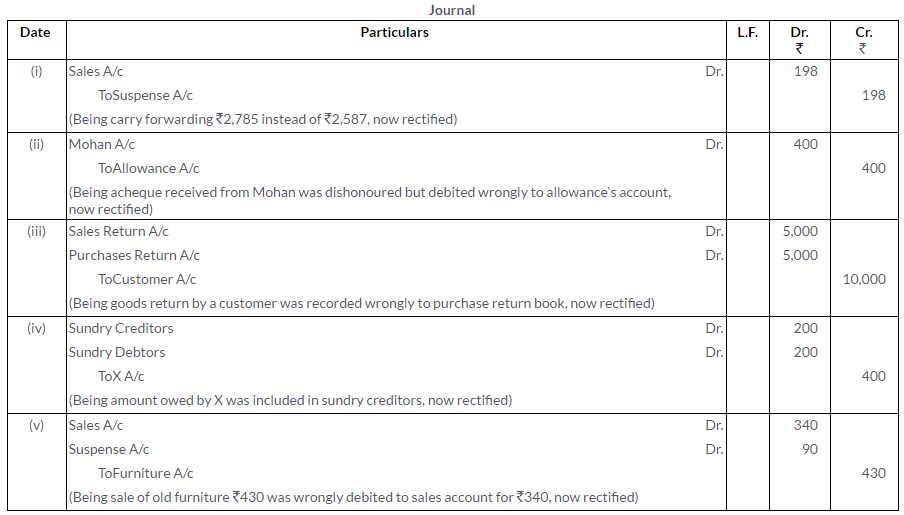
Question 13.
Rectify the following errors:
i. Purchases Book is overcast by Rs.500.
ii. Salary paid to an employee, Mr. Ajay, is debited to his Personal Account Rs.3,000.
iii. Goods sold to Shashi on credit Rs.300 have been wrongly passed through the Purchases Book.
iv. Total of returns inward has been added Rs.9 short.
v. Purchase of chair from Happy Traders for Rs.35 has been entered in the Purchases Book as Rs.53.
Solution:
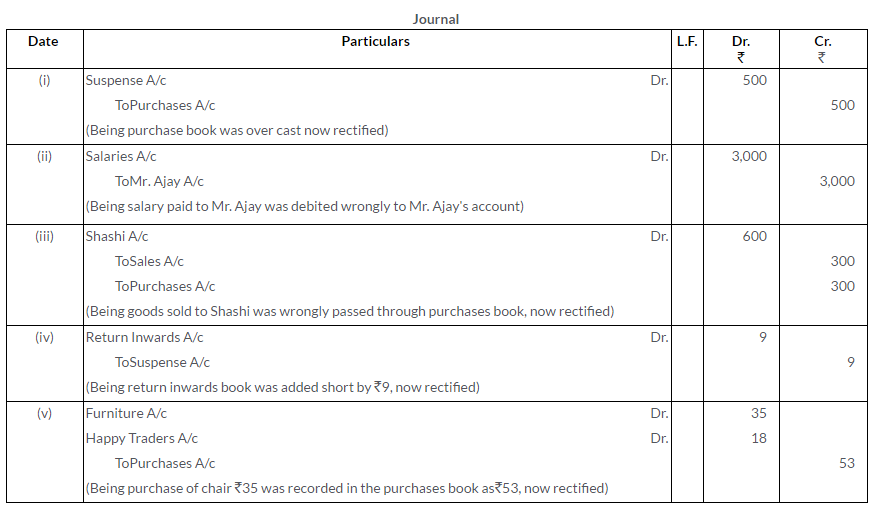
Question 14.
Correct the following errors in Mohan Lal’s Book:
i. A payment of Rs.5,000 for salaries (to Mr. Ram) has been posted twice to the Salaries Account.
ii. Rs.750 received from Rajesh are entered on the debit side of the Cash Book. No posting was done in Rajesh’s Account.
iii. Sales Book was overcast by Rs.3,000.
iv. Goods (Cost Rs.2,000, Sales Price Rs.2,500) distributed as free samples among prospective customers were not recorded anywhere.
Solution:
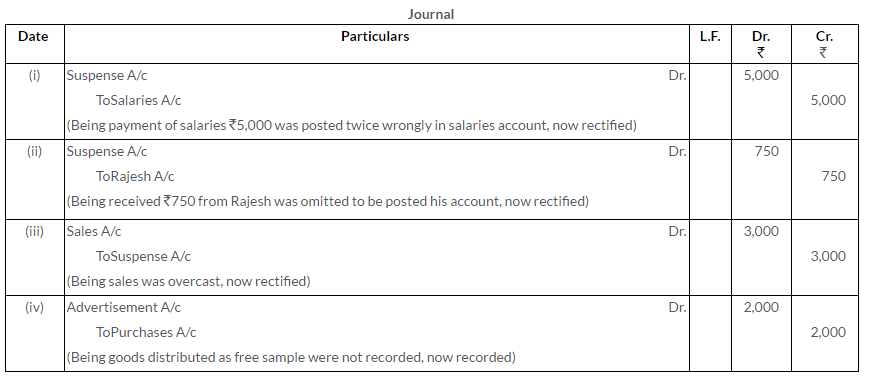
Question 15.
Rectify the following errors:
i. Sales to Vinod of Rs.143 posted to his account as Rs.134.
ii. Sales to Vinod of Rs.143 debited to his account as Rs.134.
iii. Sales to Vinod of Rs.143 credited to his account as Rs.134.
Solution:
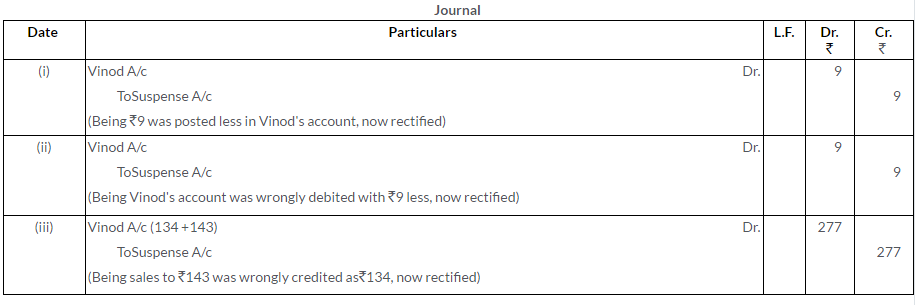
Question 16.
Give the rectifying entries of the following:
i. Sales of Rs.20,000 to Manoj were recorded as Rs.2,000 in the Sales Book.
ii. An amount of Rs.25,000 spent for the extension of machinery has been debited to the Wages Account.
iii. Discount received from Ram and Co. Rs.350, has not been entered in the discount column of the Cash Book.
iv. Goods of Rs.3,000 sold to Mahesh were recorded in the Purchases Book.
Solution:
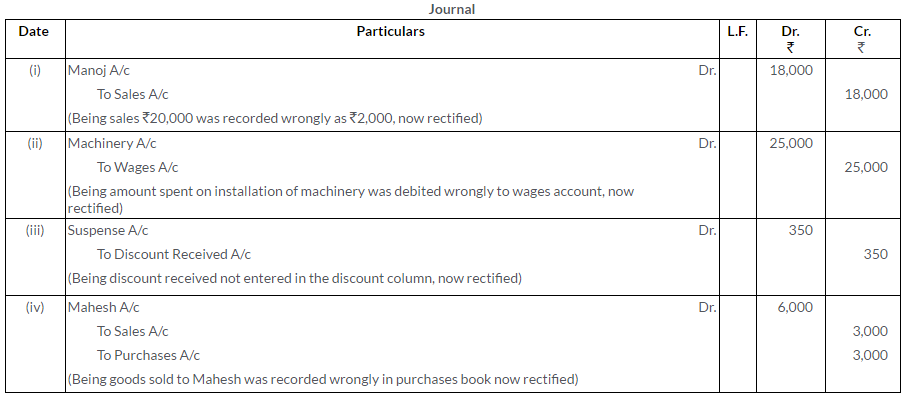
Question 17.
Correct the following errors in Mohan Lars Book:
i. A sum of Rs.1,500 written off as depreciation on furniture has not been debited to the Depreciation Account.
ii. Returns Outward Journal has been overcast by Rs.85.
iii. Basudev returned goods worth Rs.500; his account was debited by this amount.
iv. Purchase from Krishna Mohan of Rs.2,250 has been debited to his account.
Solution:
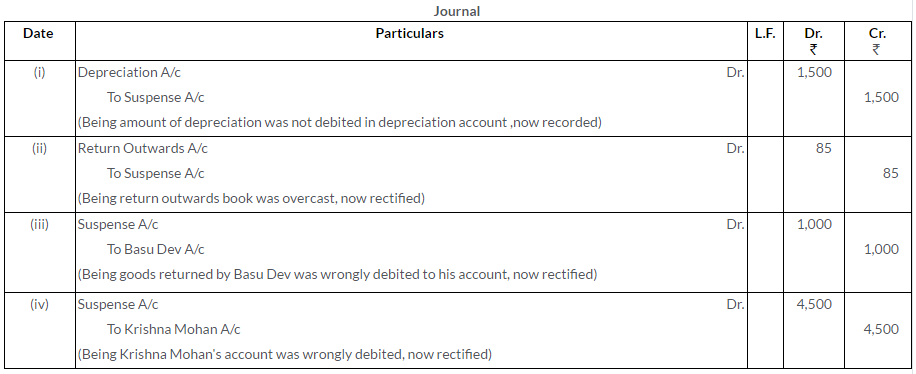
Question 18.
Correct the following errors in Hari’s Books:
i. Credit sale of Rs.132 to R. Krishan correctly entered in Sales Journal but posted to his account as Rs.312.
ii. The total of the credit side of Ramesh’s Account was overcast by Rs.2,000.
iii. Total of the Purchases Journal of Rs.5,250 has been posted to Purchases Account as Rs.5,205.
iv. Printer purchased from R. Ltd. forRs.4,000 on credit was entered in the Purchases Book.
v. An item of`2,000 entered in the Sales Return Book was posted to the debit of Pandey who had returned the goods.
Solution:
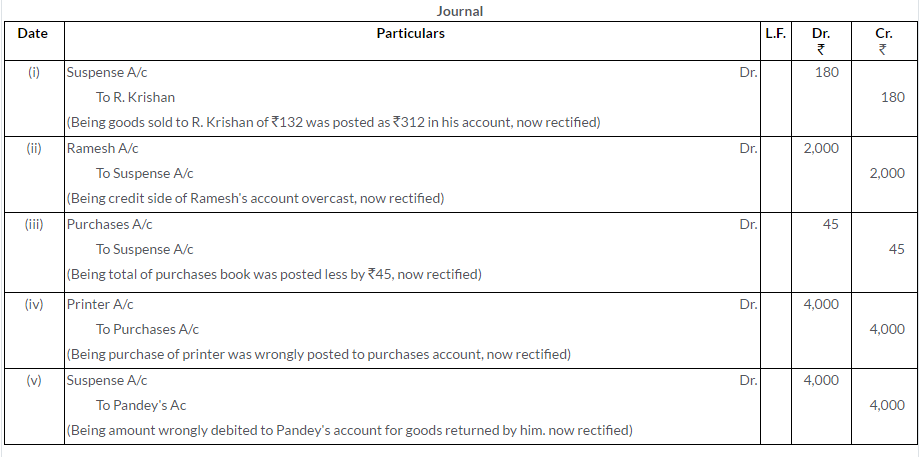
Question 19.
Rectify the following errors:
i. A purchase of Rs.5,000 from Ram was omitted to be entered in the Purchases Book.
ii. A credit sale of Rs.257 to Messrs. Goodluck and Co. was recorded as Rs.275.
iii. A purchase of office furniture for Rs.500 from Salwan Furnitures was entered through the Purchases Book.
iv. Rent paid to Landlord Rs.500 was debited to his Personal Account.
v. A debit balance of Rs.2000 on the Personal Account of Mr. John (correctly shown in the Ledger) has been omitted when extracting a Trial Balance.
Solution:
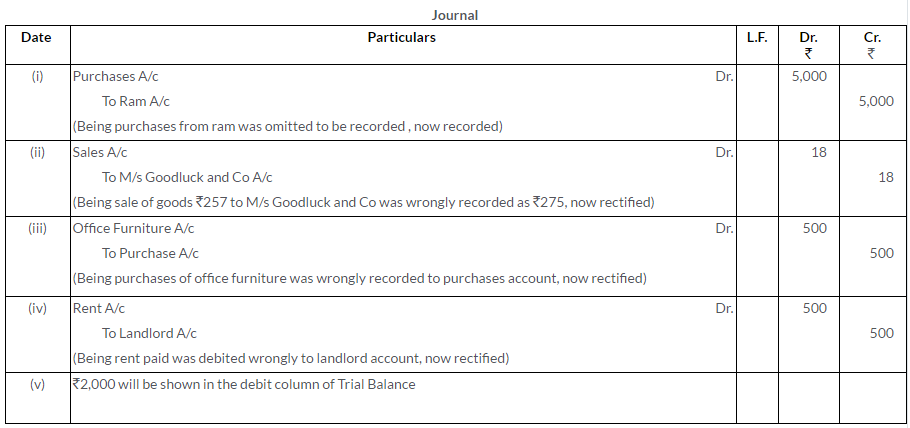
Question 20.
Pass the Journal entries to rectify the following errors:
i. Credit sales to Ram Rs.170 debited to his account as Rs.710.
ii. Credit purchases from Rs.229 recorded as Rs.292.
iii. Sales Book was undercast by Rs.200.
iv. Credit purchase of goods of Rs.2,100 from Sohan posted as Rs.1,200.
v. An addition in the Returns (Inward) Book had been cast Rs.100 short.
Solution:
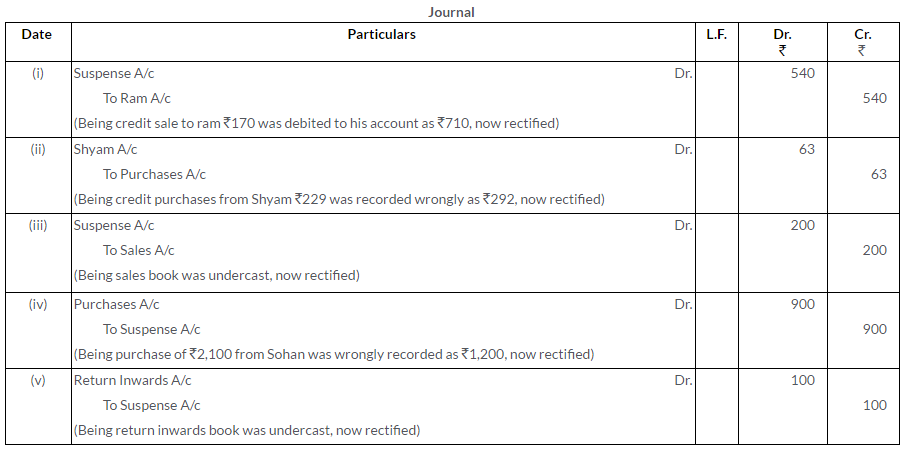
Question 21.
Pass the rectifying entries for the following:
i. Sales of goods Rs.6,000 to Madan were recorded as Rs.600 in the Sales Book.
ii. Credit purchase of goods from Mohan amounting to Rs.2,000 has been wrongly passed through the Sales Book.
iii. Return of goods worth Rs.500 by a customer was entered in ‘Purchases Return Book’.
iv. Cheque of Rs.400 received from Ranjan was dishonoured and debited to the Discount Account.
v. Bill for Rs.820 received from Ramesh for repair of machinery was entered in the Purchases Book as Rs.720.
(Delhi 2003)
Solution:
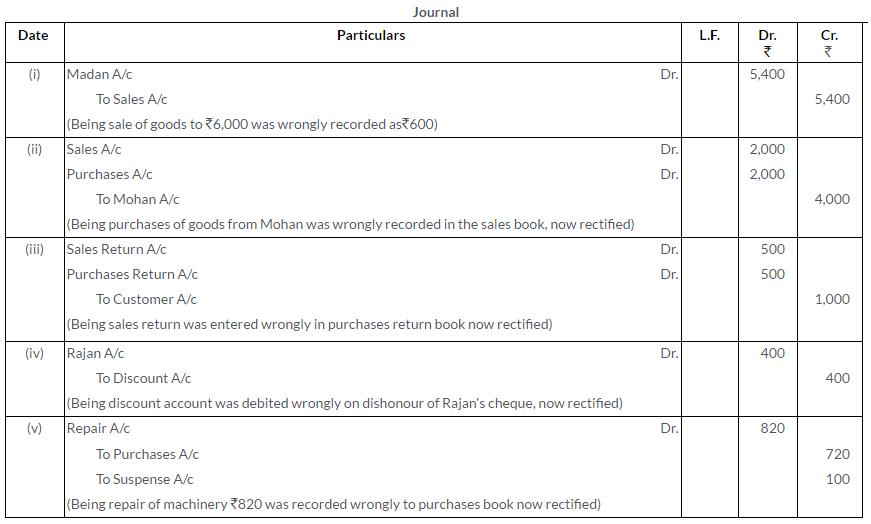
Question 22.
Give rectifying Journal entries for the following errors:
i. Sales of goods to Madan Rs.6,000 were entered in the Sales Book as Rs.600.
ii. Credit purchase of Rs.1,500 from Ajay has been wrongly passed through the Sales Book.
iii. Repairs to building Rs.300 were debited to Building Account.
iv. Rs.2,050 paid to Rohit is posted to the debit of Mohit’s Account as Rs.5,020.
v. Purchases Return Book is overcast by Rs.400.
(MSE Chandigarh 2007)
Solution:
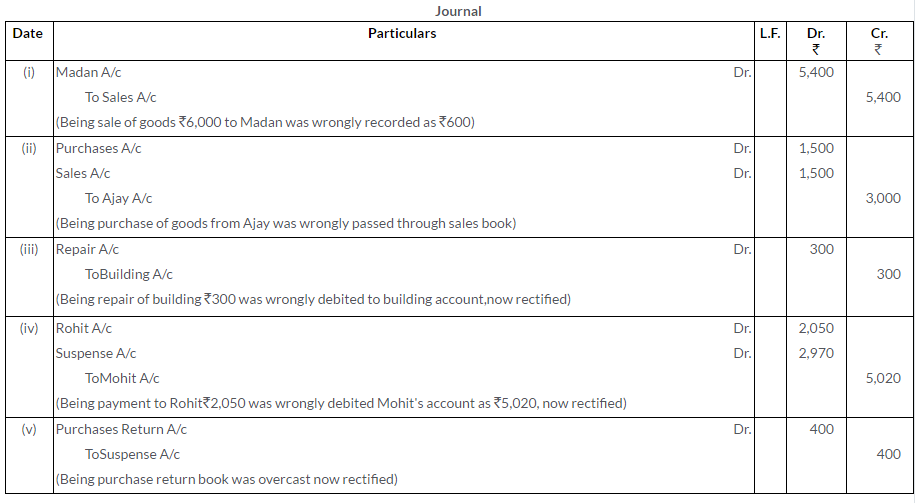
Question 23.
Give rectifying entries for the following:
i. Rs.5,400 received from Mr. A was posted to the debit of his account.
ii. The total of Sales Return Book overcast by Rs.800.
iii. Rs.2,740 paid for repairs to motor car was debited to Motor Car Account as Rs.1,740.
iv. Returned goods to Shyam Rs.1,500 were passed through Returns Inward Book.
(MSE Chandigarh 2008)
Solution:
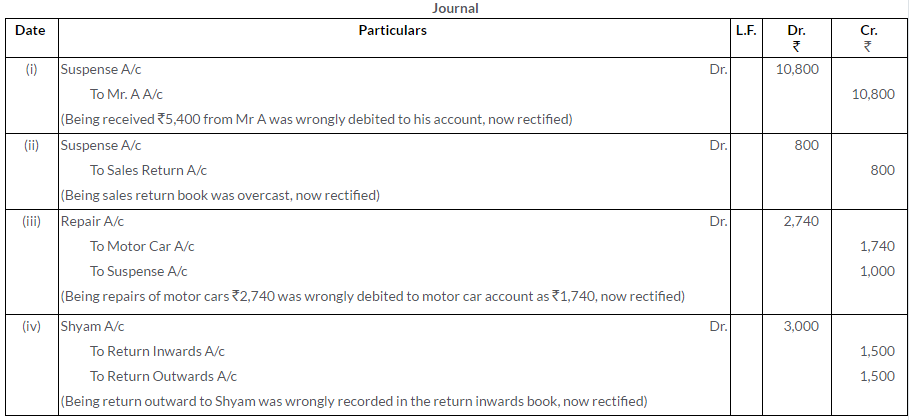
Question 24.
Pass Journal entries rectifying the following errors:
i. A cheque for Rs.10,000 was received from Ranjan on which Rs.200 Cash Discount was allowed. The cheque was not honoured on due date and the amount of discount was credited to Discount Received Account.
ii. Rs.2,000 paid as wages for machinery installation was debited to Wages Account.
iii. Rs.5,000 received from Rakesh were credited to his Personal Account. The amount had been written off as bad debt earlier.
iv. Repair bill of machinery was recorded as Rs.100 against the bill amount of Rs.1,000.
Solution:
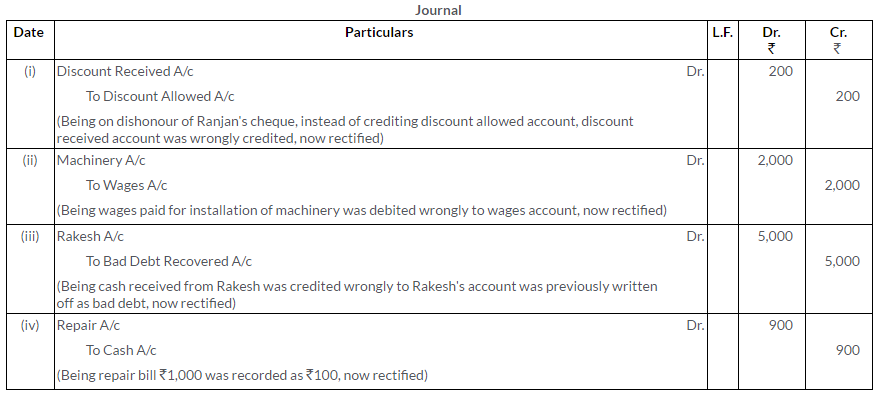
Question 25.
Rectify the following errors:
i. Sales Book has been totaled Rs.1,000 short.
ii. Goods worth Rs.1,500 returned by Green and Co. have not been recorded anywhere.
iii. Goods purchased worth Rs.2,500 have been posted to the debit of the supplier, Gupta and Co.
iv. Furniture purchased from Gulaband Co. worth Rs.10,000 has been entered in Purchases Book.
v. Cash received from A Rs.2,500 has not been posted in his account.
(KVS 2008)
Solution:
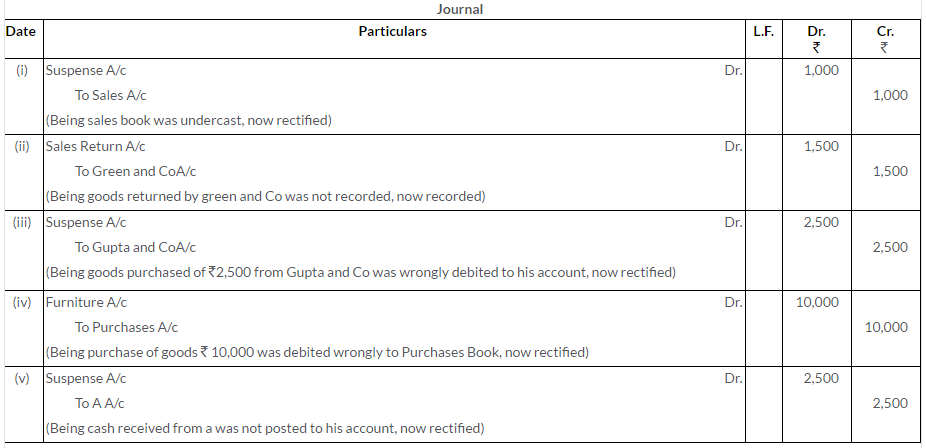
Question 26.
How will you rectify the following errors?
i. Rs.500 spent on building repairs has been debited to the Building Account.
ii. Furniture worth Rs.5,000 purchased from X on credit omitted from being recorded in the books.
iii. Total of Returns Inward Book was added by Rs.200 instead of Rs.250.
iv. Sales Book was overcast by Rs.500.
v. Sale of old machinery amounting toRs.600 has been credited to the Sales Account.
Solution:
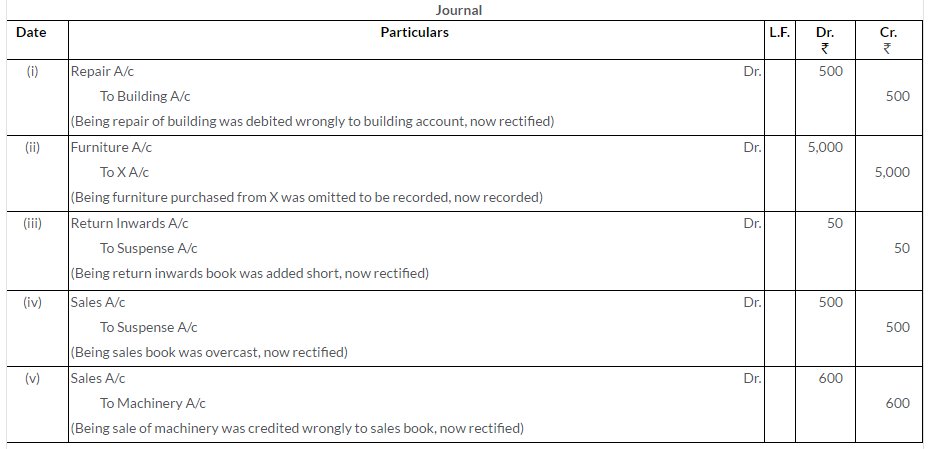
Question 27.
Pass Journal entries to rectify the errors in the following cases:
i. A purchase of goods from David amounting to Rs.150 has been wrongly passed through the Sales Book.
ii. A credit sale of goods of Rs.120 to Peter has been wrongly passed through the Purchases Book.
iii. Rs.200, salary paid to Cashier, B. Naidu, stands wrongly debited to his Personal Account.
iv. Rs.100 received from Shaw and Co. have been wrongly entered as from Shah and Co.
v. Ramesh’s Account was credited with Rs.840 twice instead of once.
Solution:
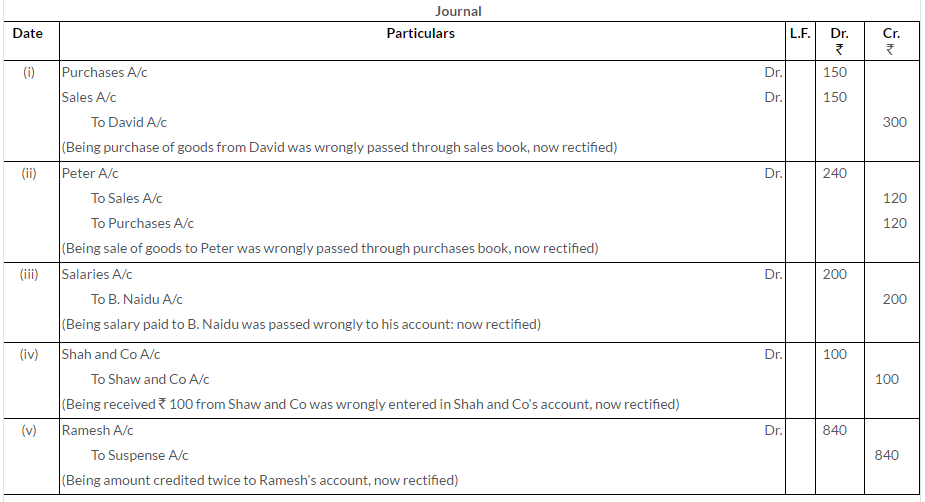
Question 28.
A. What are the different causes that make a Trial Balance incorrect?
B. Pass the rectifying Journal entries:
i. A credit sale of goods for Rs.2,500 to Krishna has been wrongly passed through the Purchases Book.
ii. Rs.5,000 paid for freight on machinery purchased was debited to the Freight Account as Rs.500.
iii. The Returns Inward Book has been wrongly overcast by Rs.100.
iv. An amount of Rs.500 due from Ramesh which had been written off as bad debt in previous year was recovered and had been posted to the Personal Account of Ramesh.
v. A sum of Rs.460 owed by Hari had not been included in the list of debtors.
(MSE Chandigarh 2003)
Solution:
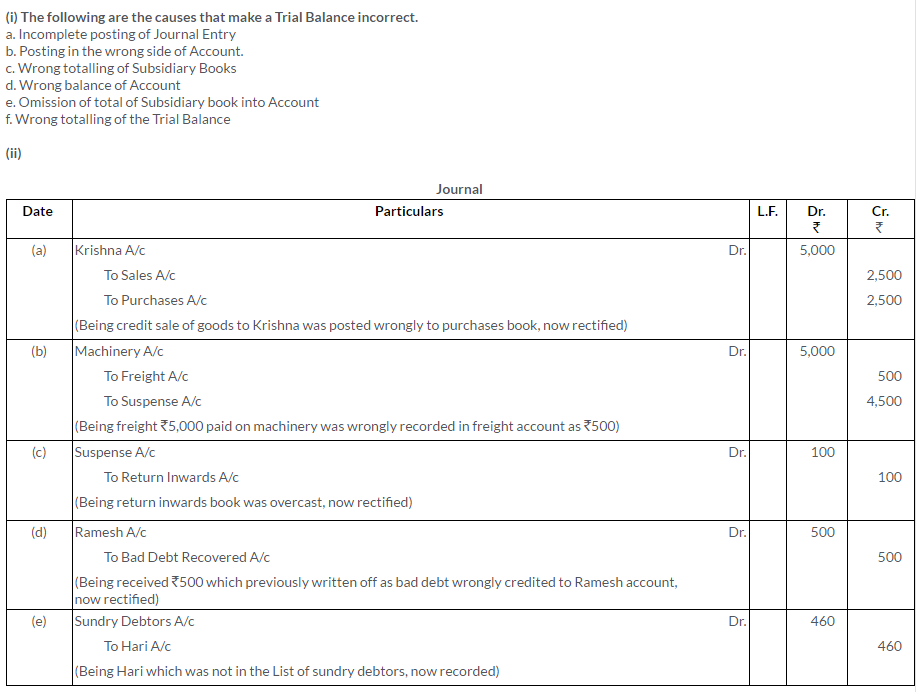
Question 29.
Rectify the following errors:
i. Wages paid for the construction of office debited to the Wages Account, Rs.5,000.
ii. Machinery purchased for Rs.35,000 was passed through the Purchases Book.
iii. Old furniture sold for Rs.1,000, passed through the Sales Book.
iv. Rs.2,000 paid to Mehta Bros. against acceptance were debited to Malhotra Bros Account.
v. Sales of Rs.204 to Ram debited to his account as Rs.402 and purchases ofRs.1,012 from Shyam credited to his account as Rs.1,210.
Solution:
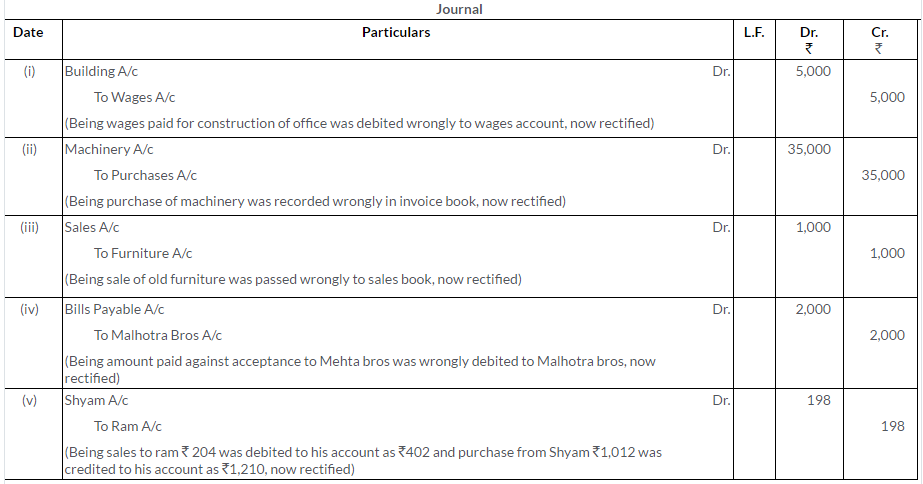
Question 30.
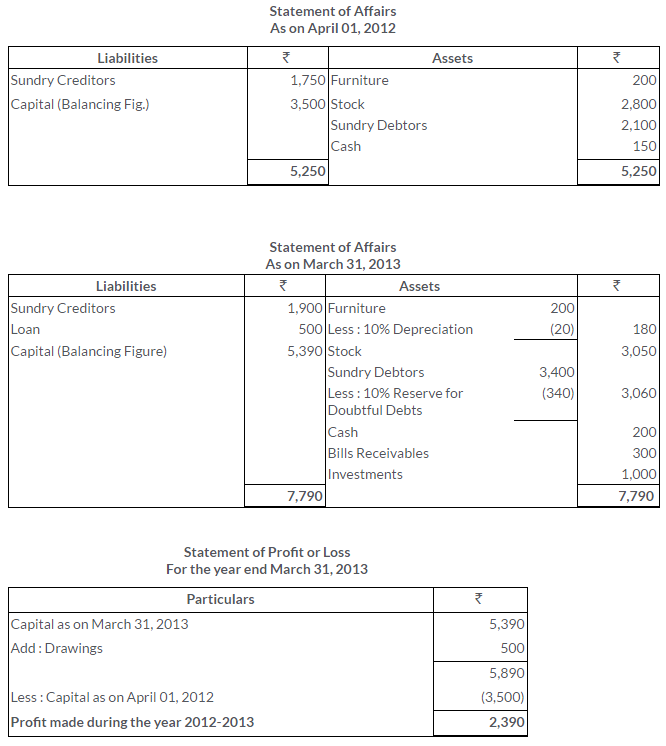
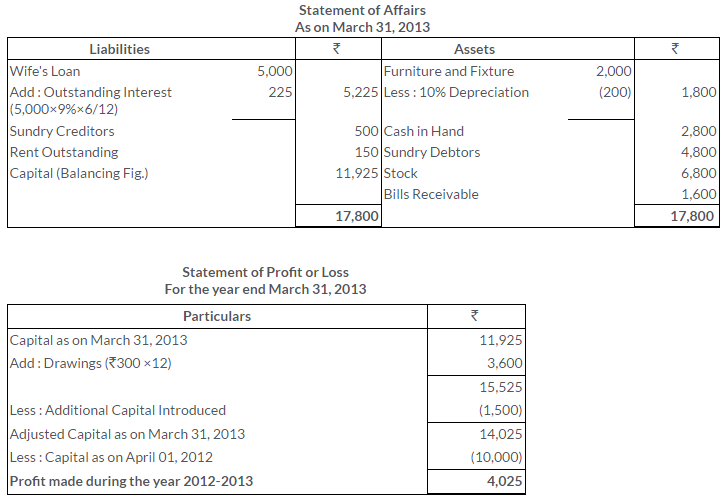
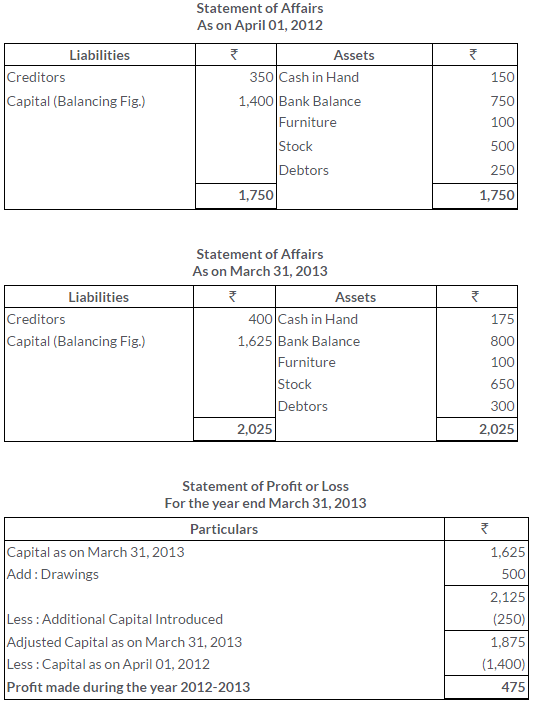
There was an error in the Trial Balance of Ram Gopal on 31st March, 2013 and the difference in books was carried to the Suspense Account. On going through the books, you find that:
i. Rs.540 received from M. Mehta was posted to the debit side of his account.
ii. Rs.100 being purchases return was posted to the debit of the Purchases Account.
iii. Discount of Rs.300 received was posted to the debit of the Discount Account.
iv. Rs.374 paid for motor car repairs was debited to the Motor Car Account as Rs.717
v. Rs.400 paid to C. Das was debited to the account of G. Dass.
Pass the Journal entries to rectify the above errors and state what amount was carried to the Suspense Account.
Solution:
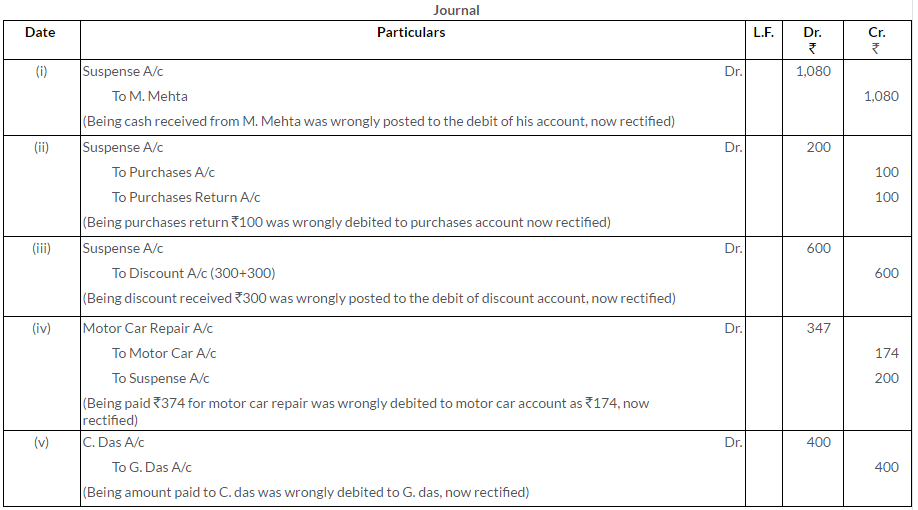
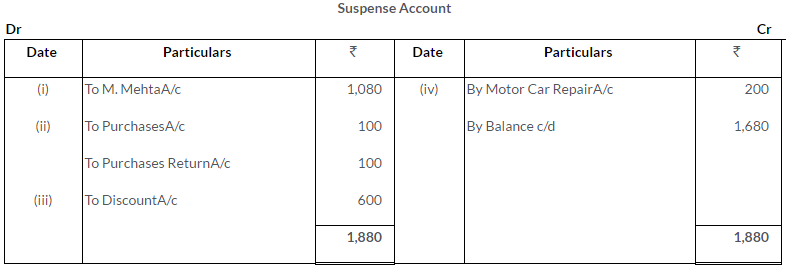
Question 31.
Trial Balance of a bookkeeper shows an excess of debits over credits by Rs.261. This difference is placed in a Suspense Account to facilitate books closure. Later on the following errors were discovered:
i. A credit item of Rs.349 has been debited to a Personal Account as Rs.439.
ii. A sum of Rs.625 written off from fixtures as depreciation has not been posted to Depreciation Account.
iii. Rs.9,000 paid for furniture bought have been charged to the Purchases Account.
iv. A discount allowed to a customer has been credited to him as Rs.145 in place of Rs.154.
v. A sale of Rs.594 was posted as Rs.495 in the Sales Account.
vi. The total of Returns Inward Book has been added Rs.10 short.
Pass the Journal entries to correct these errors and prepare the Suspense Account.
Solution:
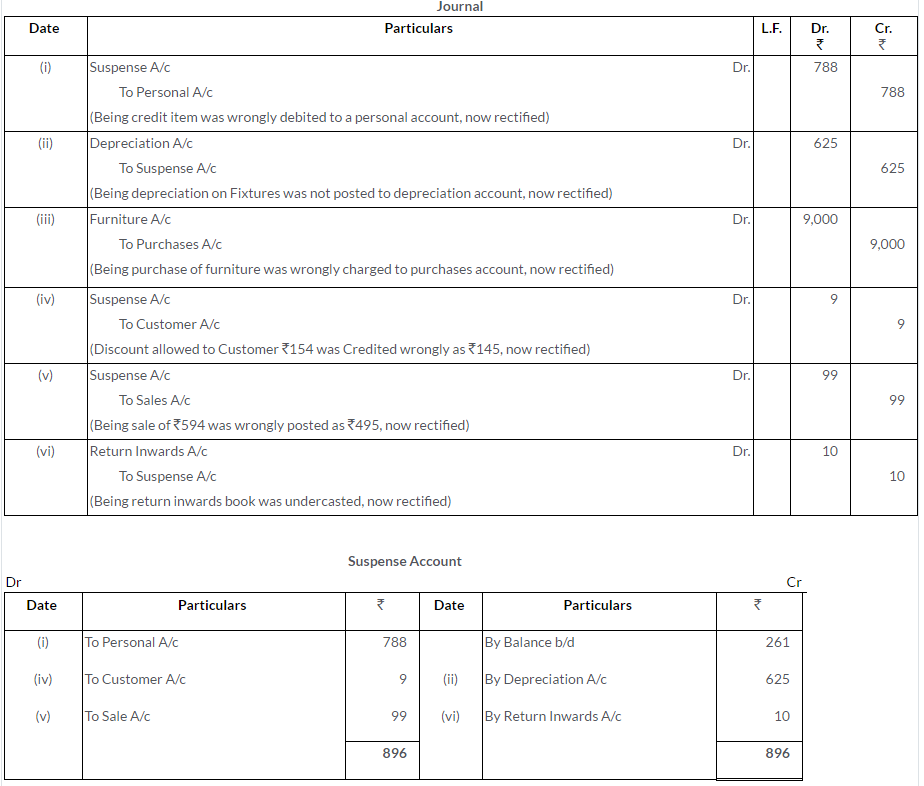
Question 32.
The accountant of a firm finds that the Trial Balance as on 31st December, 2015 is out by an excess debit of Rs.283. He placed the amount in the Suspense Account. In the first week of January, 2016, he discovered the following errors. Pass the Journal entries necessary to rectify these errors and show the Suspense Account as it would appear at the end of the week. Have you any comment to make?
i. Cash paid to Amar Nath, Rs.75, was posted to the credit of Amar Singh’s Account as Rs.57.
ii. Discount allowed by Brijesh of Rs.5 was not entered in the Cash Book but Brijesh stands debited correctly.
iii. No entry was made for goods worth Rs.40 taken away by proprietor for personal use.
iv. Rs.500 received from Jhaveri Bros. for interest on loan advanced to them were recorded in the Cash Book. But the entry was not posted in the Ledger.
v. The total of Returns Outward Book was short by Rs.100.
Solution:
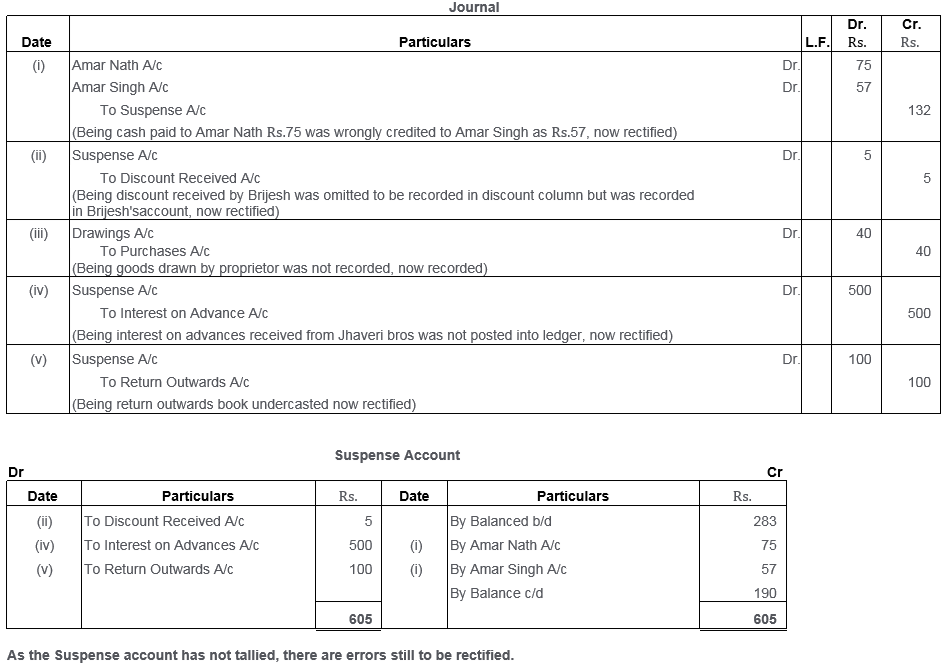
Question 33.
You are presented with a Trial Balance showing a difference which has been carried to the Suspense Account and the following errors are revealed:
i. Rs.1,700 paid in cash for an office equipment was charged to Office Expenses Account.
ii. A cash sale of Rs.5,000 to Black, correctly entered in the Cash Book, was posted to the credit of Black’s Account in the Ledger.
iii. Goods amounting to Rs.800, returned by Blue, were entered in the Sales Book and posted there from to the credit of Blue’s Account.
iv. Furniture purchased for Rs.8,100 was posted to Furniture Account as Rs.810.
v. Goods amounting to Rs.10,000 sold to Red were correctly entered in Sales Book but posted to Red’s Account for Rs.18,000.
vi. Sales Return Book was overcast by Rs.100.
You are required to pass the necessary rectification entries in respect of the above.
Solution:
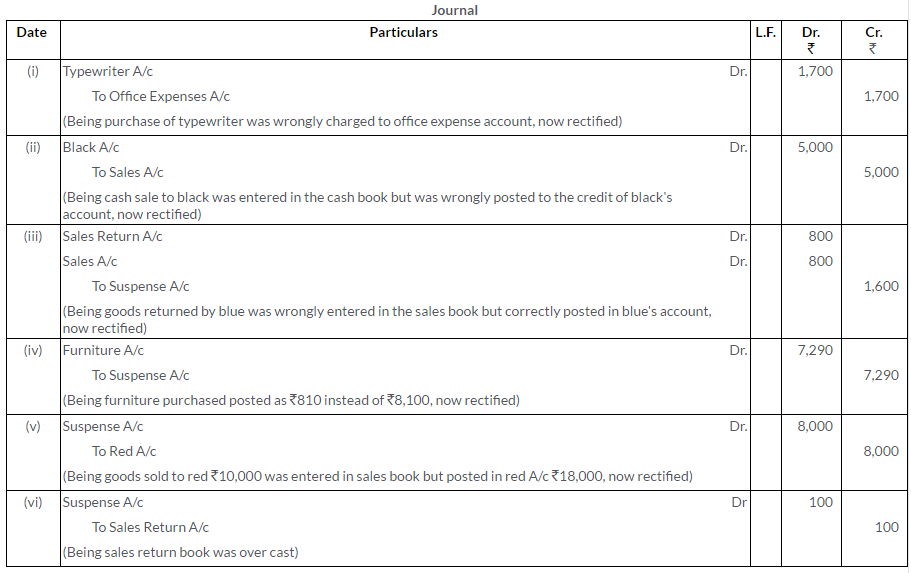
Question 34.
The bookkeeper of a firm found that his Trial Balance was out (excess credit) by Rs.742. He I placed the amount in a Suspense Account and subsequently found the following errors:
i. A discount of Rs.178 was allowed to Ramesh but in his account only Rs.100 is recorded.
ii. The total of the Purchases Book was Rs.1,000 short.
iii. A sale of Rs.375 to Kohli was entered in the Sales Book as Rs.735.
iv. From the Purchases Book, Bose’s Account was debited with Rs.175.
v. Cash Rs.250 received from Maitra against debt previously written off was credited to his account.
vi. Purchase of office furniture worth Rs.750 on credit from Delhi Furnitures was entered in the Purchases Book.
vii. While carrying forward the total of the Sales Book from one page to another the amount of Rs.11,358 was written as Rs.11,538.
viii. The proprietor took goods of the value of Rs.150 for his domestic consumption. No record of it has been made in the books.
ix. Repairs bill for the proprietor’s personal car Rs.410, has been paid by the firm and debited to the Repairs Account.
x. A sale to Kassim of Rs.700 has been entered in the Purchases Book.
Rectify the errors by means of suitable Journal entries and show the Suspense Account.
Solution:

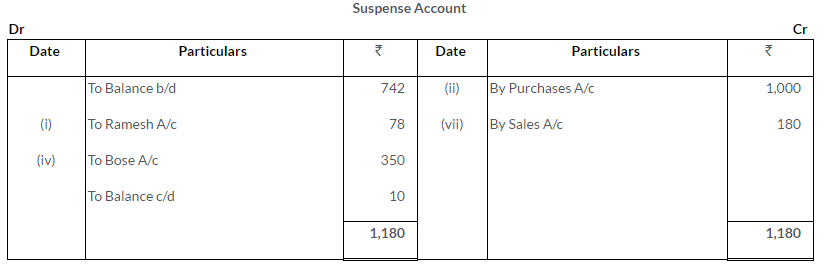
Question 35.
Rectify the following errors found in the books of Mr. B. Trial Balance had Rs.930 excess credit. The difference has been posted to a Suspense Account:
i. The total of Returns Inward Book has been cast Rs.1,000 short.
ii. The purchase of an office table costing Rs.3,000 has been passed through the Purchases Book.
iii. Rs.3,750 paid for wages to workmen for making showcases had been charged to the Wages Account.
iv. A purchase of Rs.670 had been posted to the Creditors Account as Rs.600.
v. A cheque for Rs.2,000 received from Mr. P.C. Joshi had been dishonoured and was passed to the debit of the Allowances Account.
After rectification reflect the transactions in the Suspense Account.
Solution:
Question 36.
Pass the rectification entries for the following transactions:
i. An amount of Rs.2,000 received from Mohan on 1st April, 2013 had been entered in the Cash Book as having been received on 31st March, 2013.
ii. The balance in the account of Mr. Rahim Rs.1,000 had been written off as bad but on other account has been debited.
iii. An addition in the Returns Inward Book had been cast Rs.100 short.
iv. A cheque for Rs.200 drawn for the Petty Cash Account has been posted in the account of Asif.
v. A cheque of Rs.150 received from Sharad has been dishonoured and debited in the Discount Account.
vi. Ramesh’s Account was credited with Rs.840 twice instead of once.
Solution:
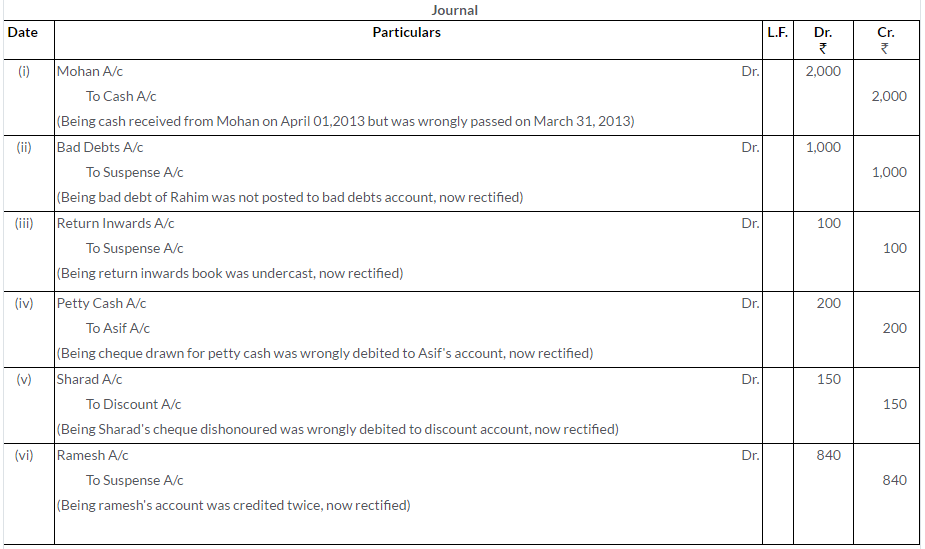
Question 37.
The Trial Balance of M/s. Gupta and Sons shows a difference of Rs.52,200. To prepare the Final Account on 31st March, 2009, this difference is placed in a Suspense Account Afterwards the following errors were disclosed. Pass the necessary entries to rectify them and show the Suspense Account.
i. Purchases Book total had been undercasted by Rs.20,000.
ii. A cheque received from Vasudev for Rs.7,800 had been debited in the Cash Book but not posted in Vasudev’s Personal Account.
iii. Returns Outward Book had been overcasted by Rs.10,000.
iv. Goods returned by Yash Pal worth Rs.15,000 have been entered in Returns Outward Book. However, Yash Pal’s Account is correctly posted.
(Delhi 2006)
Solution:
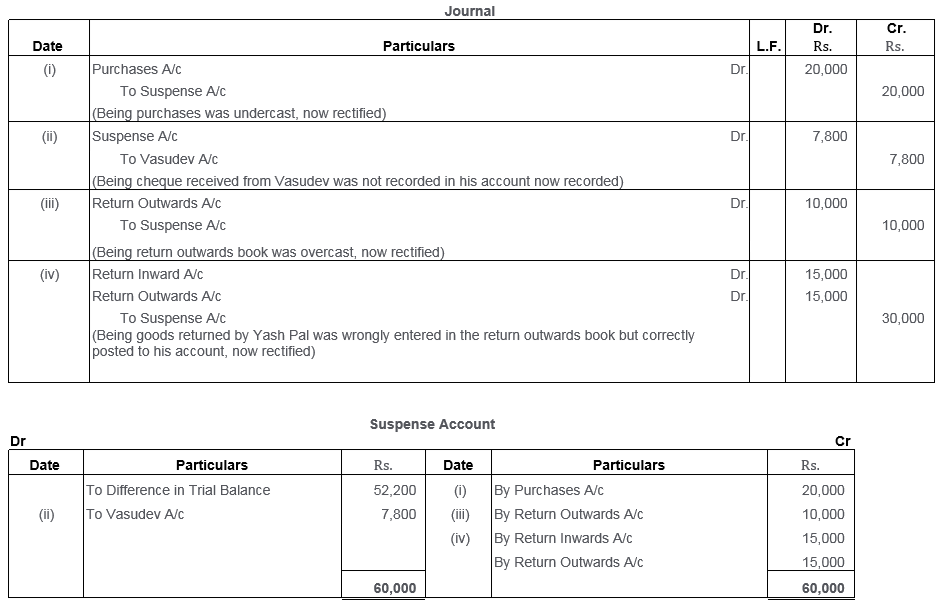
Question 38.
A Trial Balance disclosed a difference of Rs.417 placed on the credit side of the Suspense Account. Later on the following errors were located:
i. Goods worth Rs.200 purchased from Sohan had been posted to his account as Rs.250.
ii. A purchase of furniture for Rs.500 was recorded in the Purchases Book.
iii. Instead of crediting Gian’s Account with Rs.512, it was debited with Rs.215.
iv. Goods worth Rs.130 returned by Gian were entered in the Sales Book and posted therefrom to the credit of Gian’s Personal Account.
Pass the rectifying entries and prepare a Suspense Account.
(MSE Chandigarh 2006)
Solution:
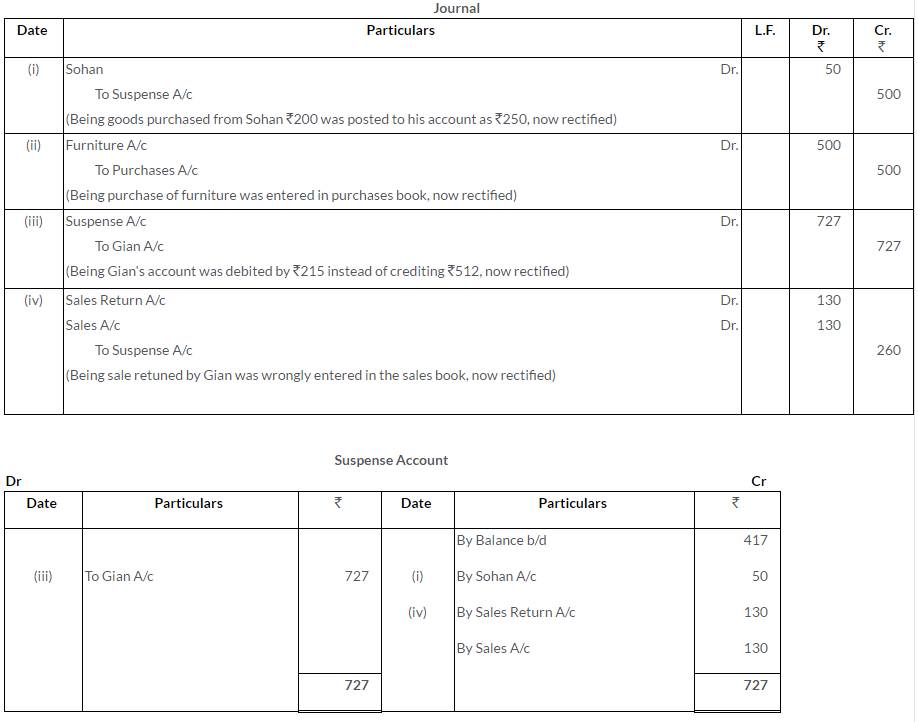
Question 39.
There was a difference of Rs.720 in the Trial Balance which has been transferred to the credit side of the Suspense Account. Pass the rectifying entries and prepare a Suspense Account to rectify the following errors:
i. An amount of Rs.375 now posted on the debit side of the Commission Account instead of Rs.275.
ii. Credit amount of Rs.260 posted to the debit of the Personal Account as Rs.360.
iii. Goods sold to Surinder recorded in Purchases Book Rs.300.
iv. D’s bill for erection of godown at a cost of Rs.1,200 has been charged to the Repairs Account.
(MSE Chandigarh 2005)
Solution:
Question 40.
Rectify the following errors by means of Journal entries:
i. A cheque of Rs.5,000 received from Ashish was dishonoured and was debited to Discount Account.
ii. Purchases of Rs.540 from Ramneek was written in Sales Book but was correctly posted to correct side of Ramneek’s Account.
iii. Salary paid to Miss Yugakshi Rs.1,000 was debited to her Personal Account as Rs.900.
iv. Furniture costing Rs.500, purchased from Jyoti, was wrongly entered in Purchases Book as Rs.450.
(Delhi 2008)
Solution:
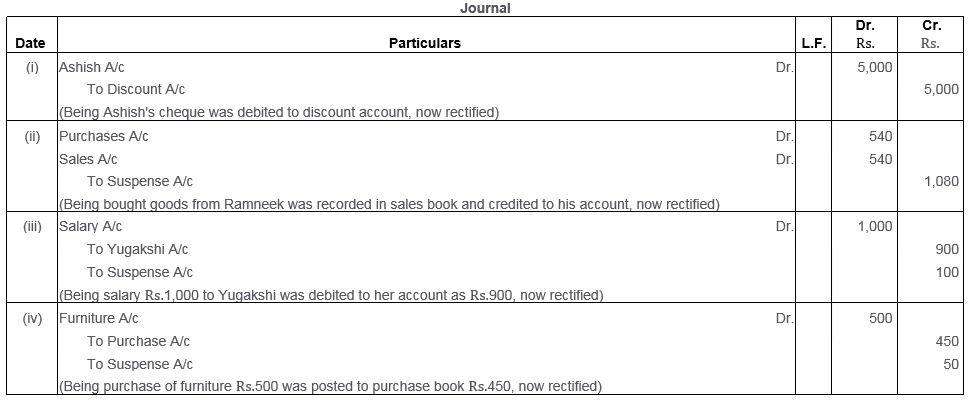
Question 41.
The Trial Balance of S. Sen did not agree and the difference in books was carried to a Suspense Account. Pass the entries required to rectify the following errors which accounted for the difference. Also, prepare the Suspense Account:
i. A Sales Invoice for Rs.1,000 for goods sold on credit to B. Basu was entered in the Purchases Book but in the Ledger, the amount was correctly debited to the account of B. Basu.
ii. Goods bought on credit from Ram Lal for Rs.1,500 were wrongly debited to his account as Rs.5,100.
iii. An amount of Rs.275 was posted as Rs.325 to the debit side of the Commission Account.
iv. The Sales Book for the month of April was undercast by Rs.100.
v. Rs.460 paid for building repairs was debited to the Building Account as Rs.640.
[Suspense Account opened with a Credit of Rs.8,930]
Solution:
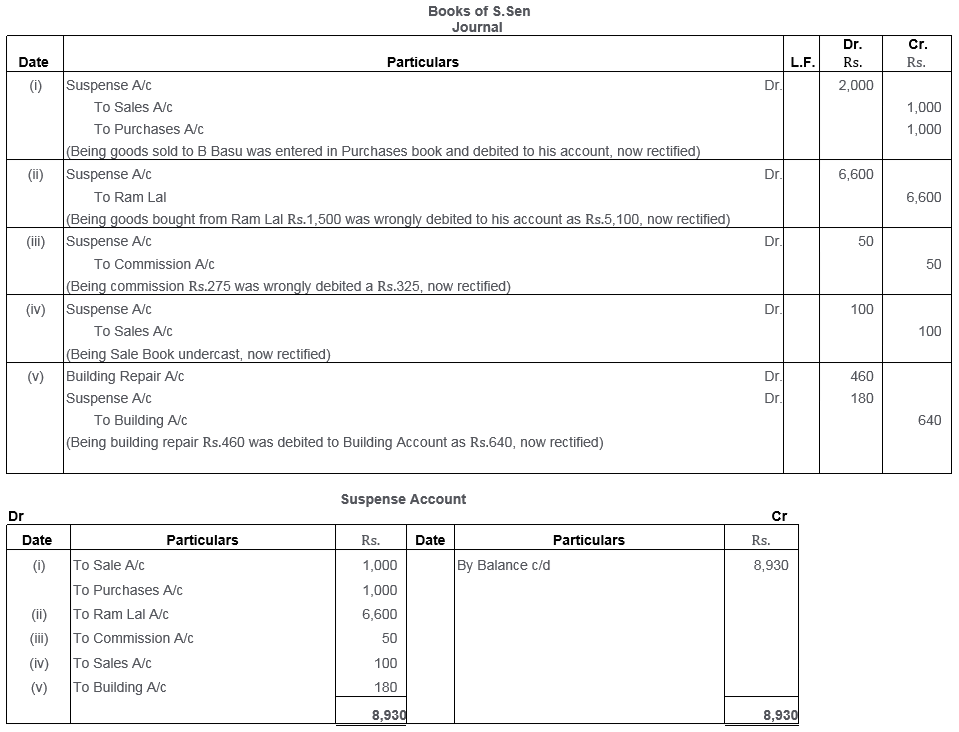
Question 42.
Rectify the following errors:
i. Sale of old furniture worth Rs.3,000 treated as sales of goods.
ii. Sales Book added Rs.5,000 short.
iii. Rent of proprietor’s residence, Rs.6,500 debited to Rent Account.
iv. Goods worth Rs.11,970 returned by Manav posted to his debit as Rs.11,790.
(Delhi 2010)
Solution:
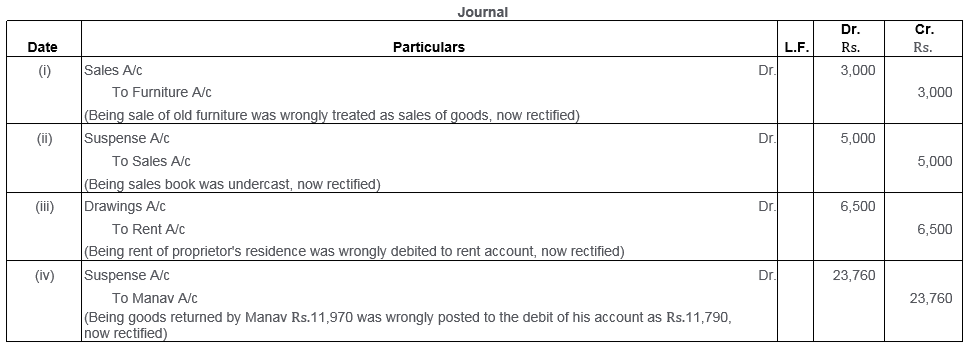
Question 43.
There was a difference in the Trial Balance of M/s. Jain and Sons, prepared for the year ended 31st March, 2009. The accountant put the difference in Suspense Account. The following errors were found:
i. Purchases Return Book total Rs.400 has not been posted to Ledger Account.
ii. Rs.5,100 spent on legal expense for the newly acquired Building was debited to the Building Account as Rs.1,500.
iii. A sale of Rs.6,540 to Rajat has been credited to his account.
Rectify the errors and show the Suspense Account with Nil closing balance.
(KVS 2010)
Solution:
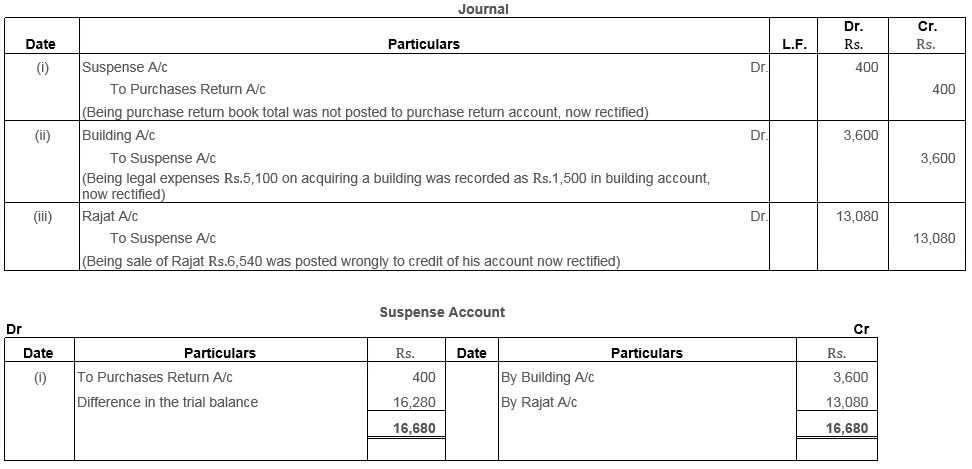
Question 44.
Give the Journal entries to rectify the following errors:
i. Purchases Book was overcast by Rs.1,000.
ii. Installation charges on new machinery purchased Rs.500 were debited to Sundry Expenses Account as Rs.50.
iii. Radhey Shyam returned goods worth Rs.500 which was entered in the Purchases Return Book.
iv. Goods taken by the proprietor for Rs.5,000 have not been entered in the books at all.
(Delhi 2011)
Solution:

Question 45.
Rectify the following errors:
i. The total of one page of Sales Book was carried forward as Rs.371 instead of Rs.317.
ii. Rs.540 received from Yatin was posted to the debit of his Account.
iii. Purchases Returns Book was overcast by Rs.300.
iv. An item of Rs.1,062 entered in Sales Return Book had been posted to the debit of customer who returned the goods.
v. Rs.1,500 paid for furniture purchased had been charged to ordinary Purchase Account.
(MSE Chandigarh 2011)
Solution:
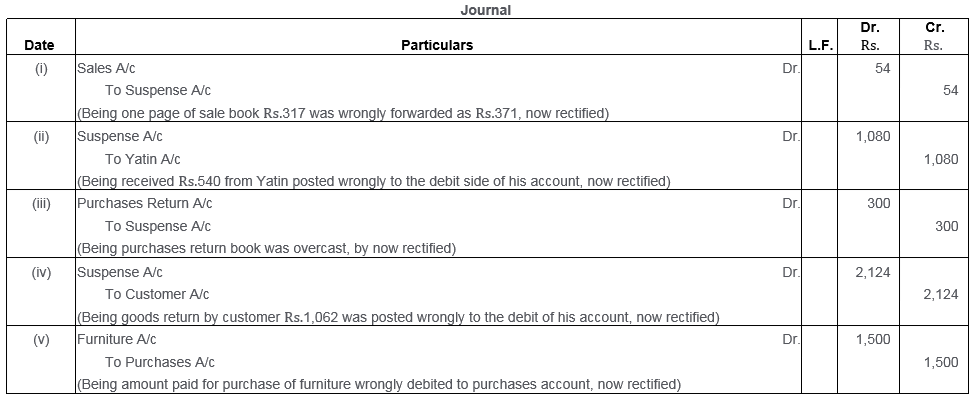
Question 46.
Rectify the following errors by passing Journal entries:
i. Old furniture sold for Rs.500 has been credited to Sales Account.
ii. Machinery purchased on credit from Raman for Rs.2,000 recorded through PurchaS Book as Rs.16,000.
iii. Cash received from Rajat Rs.5,000 was posted to the debit of Bhagat as Rs.6,000.
iv. Depreciation provided on machinery Rs.3,000 was posted to Machinery Account Rs.300.
(MSE Chandigarh 2013)
Solution:
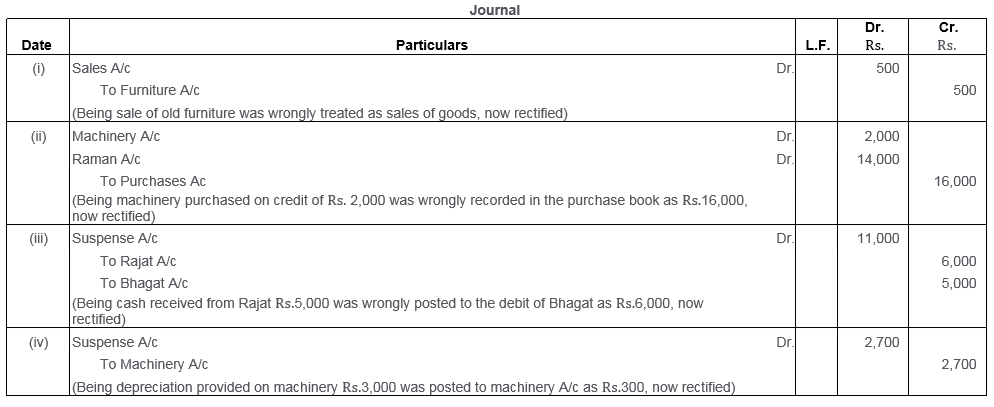
Question 47.
Rectify the following errors by passing Journal entries:
i. A sum of Rs.470 received from Ganga was posted to her debit as Rs.740.
ii. A debit balance of Rs.550 in the personal account of Mr. John was undercast.
iii. Bills Receivable from Brown for Rs.3,000 posted to the credit of Bills Payable Account and credited to Brown’s Account.
iv. Goods returned by Mridul Rs.225 have been entered in the Returns Outward Book.
(MSE Chandigarh 2015)
Solution:
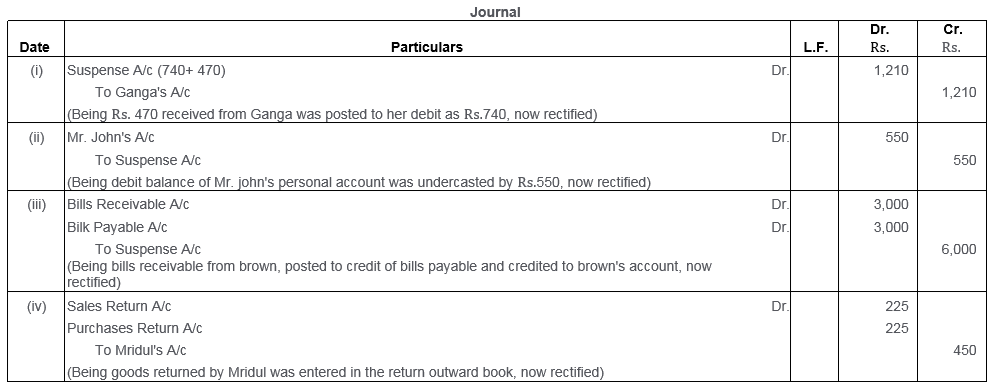
Question 48.
Pass the rectification entries for the following transactions:
i. A builder’s bill for Rs.25,000 for erection of a small shed was debited to Repairs Account.
ii. Repairs to plant amounting to Rs.2,000 had been charged to Plant and Machinery Account.
iii. Wages paid to the firm’s workmen for making certain additions to machinery amounting to Rs.1,340 were debited to Wages Account.
iv. A cheque for Rs.7,500 received from S. Desai was credited to the account of R. Gupta.
v. Goods to the value of Rs.7,000 returned by X were included in closing stock, but no entry was made in the books.
vi. Goods costing Rs.5,000 were purchased for various members of the staff and the cost was included in Purchases’. A similar amount was deducted from the salaries of the staff members concerned and the net payments to them debited to Salaries Account.
vii. Goods sold to Rs.4,750 have been wrongly entered in the Sales Journal as Rs.7,450.
viii. Debit and Credit totals of discount columns in the Cash Book which come to Rs.400 and Rs.370 respectively have not been posted to Discount Accounts.
Solution:
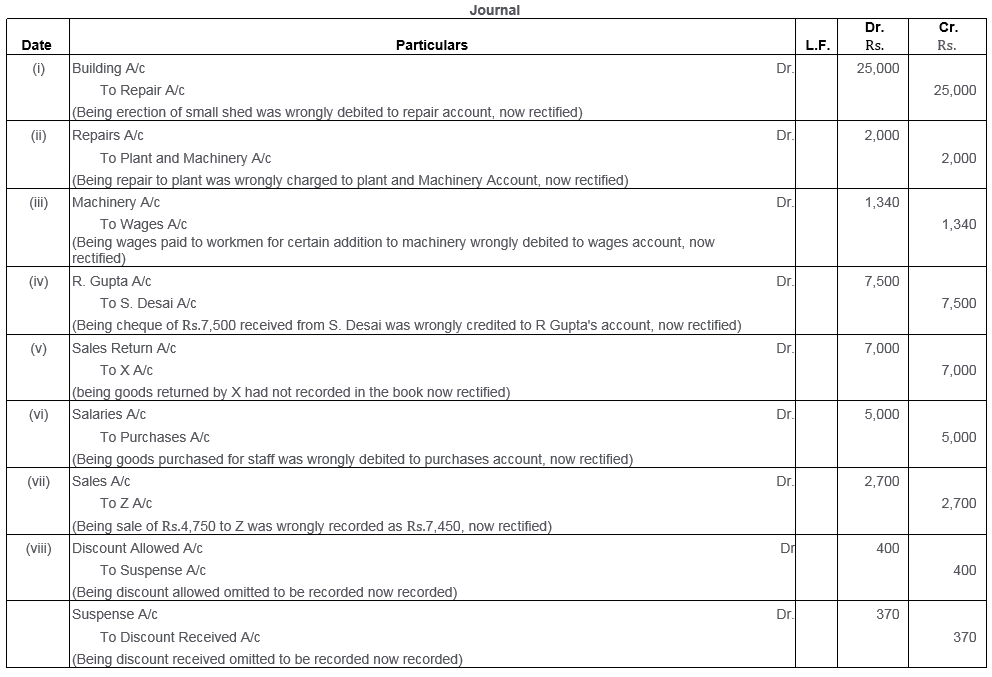
Question 49.
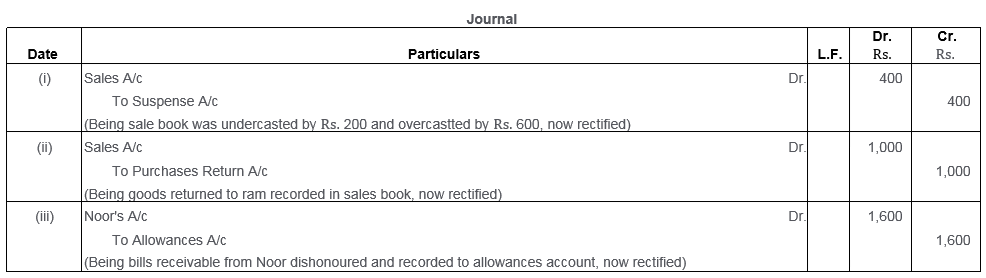
While trying to close his books for the year ended 31st March, 2014, Mahesh found that t Trial Balance did not agree. He traced the following errors:
i. In the Sales Book for the month of January total of Page No. 2 was carried forward to Page No. 3 as Rs.1,000 instead of Rs.1,200 and total of Page No. 6 was carried forward to Page No. 7 as Rs.5,600 instead of Rs.5,000.
ii. Goods returned to Ram Rs.1,000 were recorded in the Sales Book.
iii. Bill Receivable for Rs.1,600 from Noor was dishonoured and posted to debit of Allowances Account. Rectify the above errors.
(KVS 2015)
Solution: