Friction HC Verma Concepts of Physics Solutions
Friction HC Verma Concepts of Physics Solutions Chapter 6












































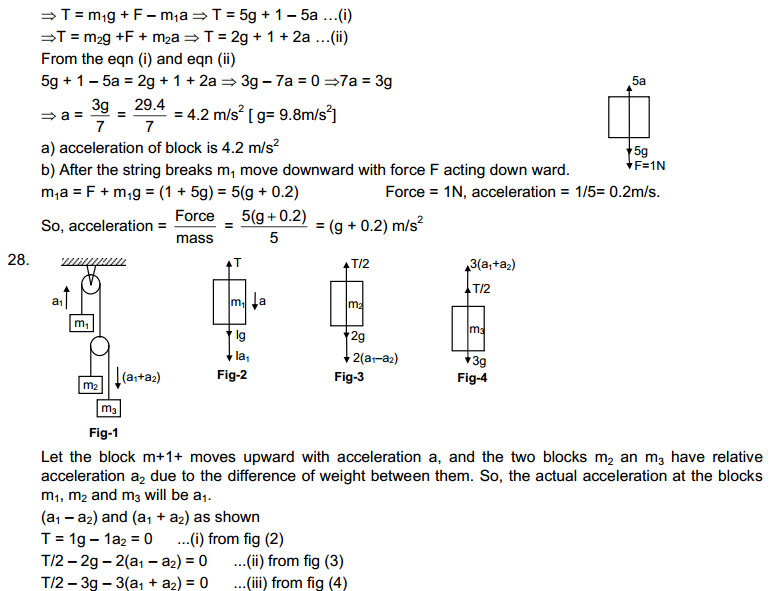


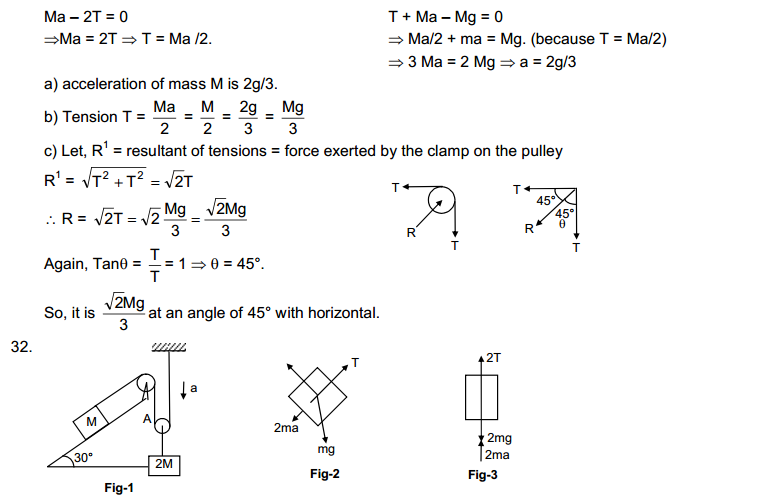
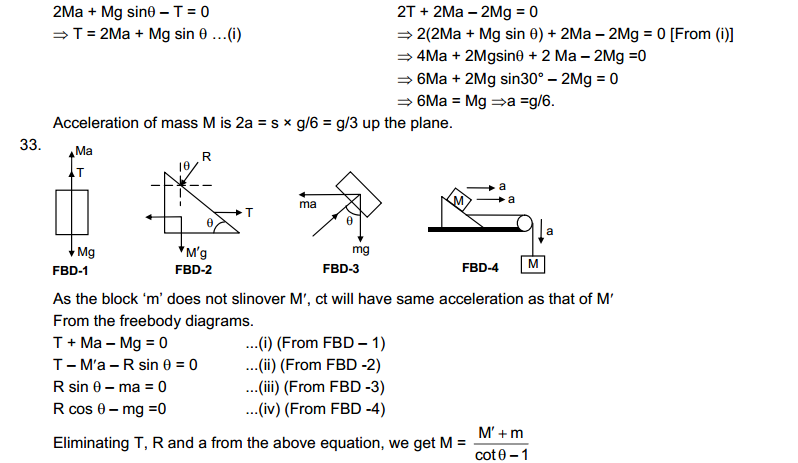

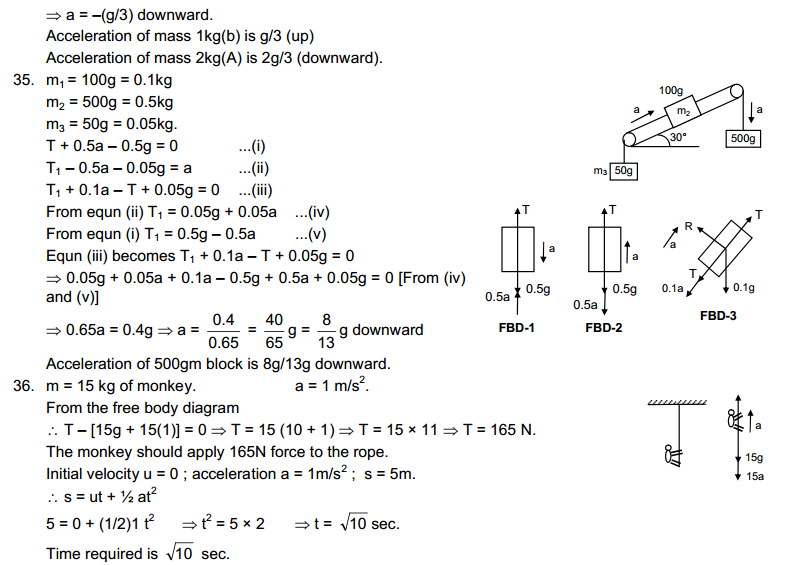



























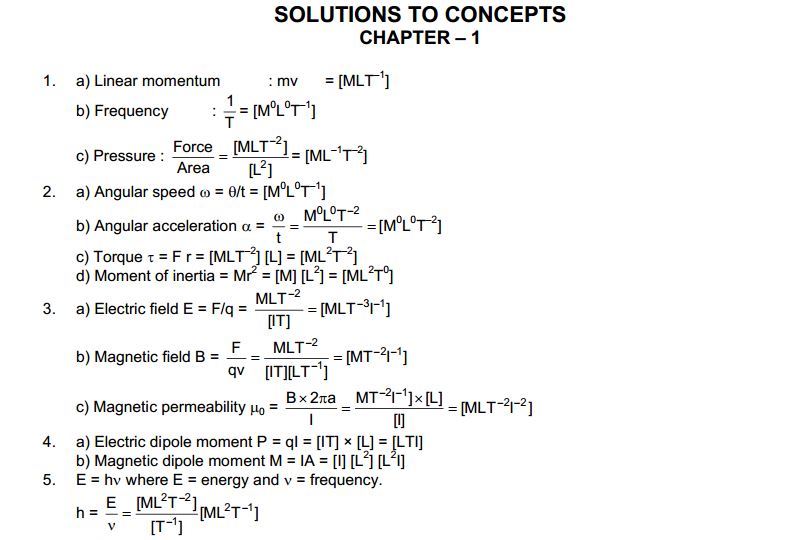





HC Verma solutions are for those who are studying and solving HC Verma. The answers to our are going to help you in learning and gaining knowledge. You also can refer HC Verma Solutions PDF while solving any problem of HC Verma book.
This Book is referred to every science studying of 11th and 12th. HC Verma concepts of physics are beneficial for those students who are preparing themselves for competitive exam. This book is consist of varieties of the question, of a different level. These all queries and solutions are very useful for the engineering entrance exam, Board exam and other exams too.
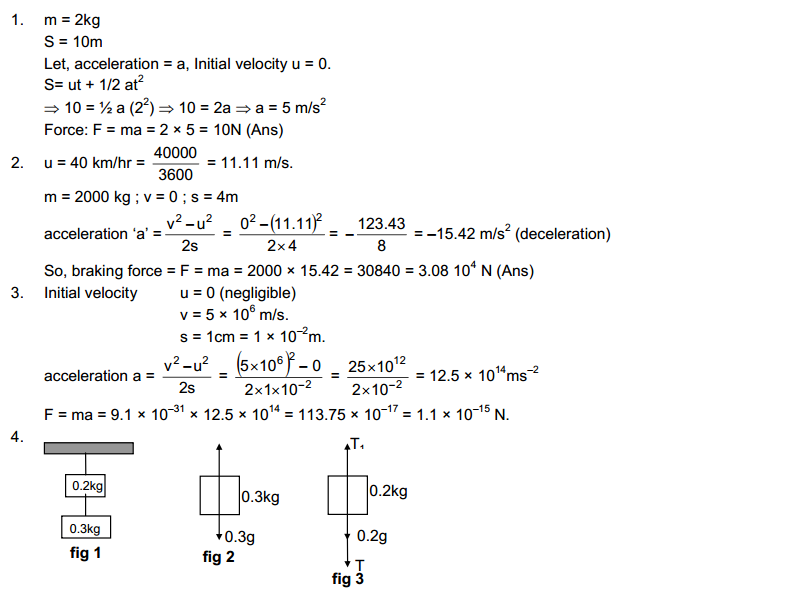
Sometimes maybe you faced a lot of problems while solving problems on HC Verma. Many times you tried to explain but you unable to solve one. Then you must refer to solution books or guides to get help and solve those. The aim of HC Verma solutions is entirely same, to provide methods to solve those problems on HC Verma.
The first book, HC Verma concept of Physics is wholly dedicated to 11th class science students. This book is consist of 22 Chapters and complete syllabus of an 11th student. These chapters cover solutions of rotational mechanics, kinematics, optics, and other topics. Those who are preparing themselves for engineering entrance exams can solve the HC Verma; It will be very beneficial for them.
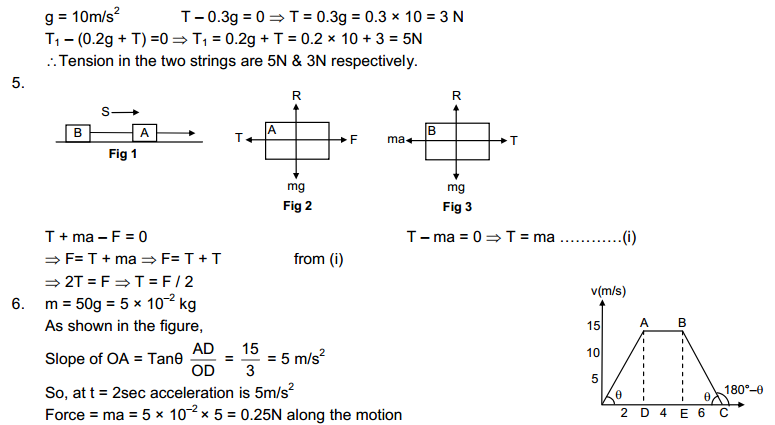
The second book, HC Verma concept of Physics Part 2 is wholly dedicated to 12th class science students. This part of HC Verma covers electricity, magnetism, semiconductors and other topics. The HC Verma solutions are going to be helpful for those Physics aspirants. There are objective types of questions and answers, as well as HC Verma Short Answer Solutions
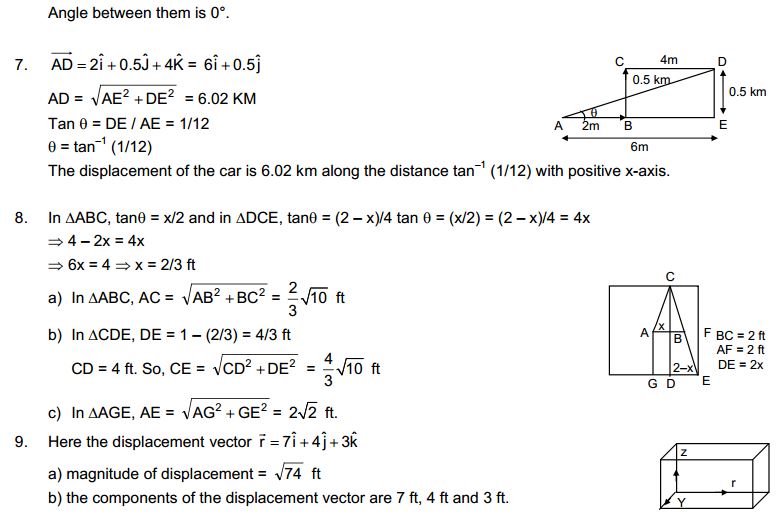
Content’s
Page No: 3
1. Which of the following are matter?
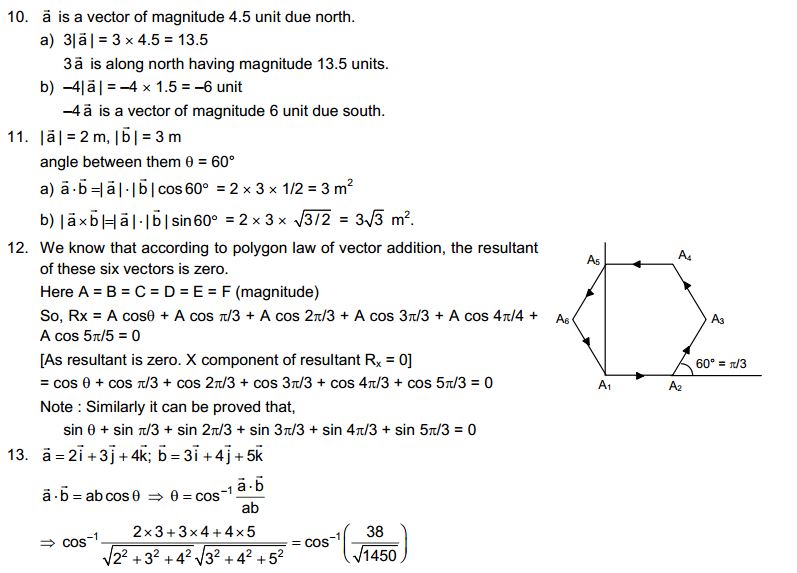
Answer
Chair, air, almonds and cold drink
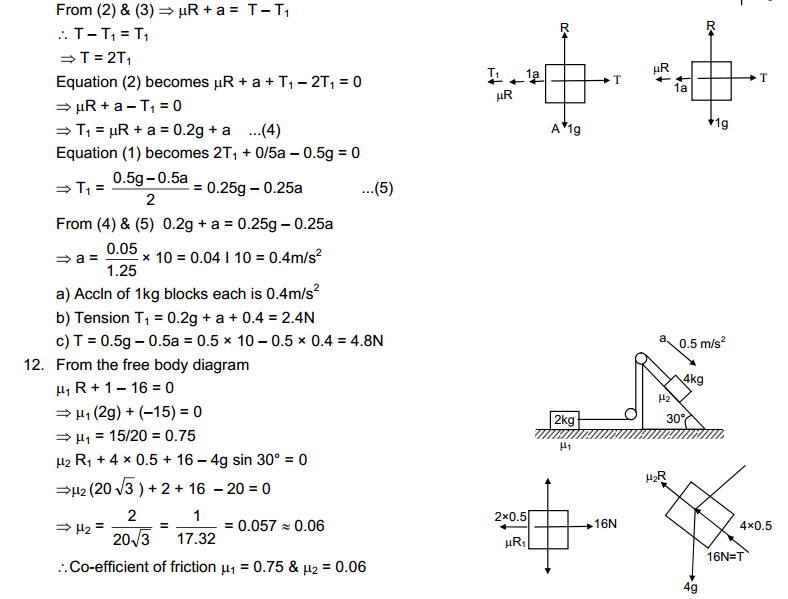
2. Give reasons for the following observation:
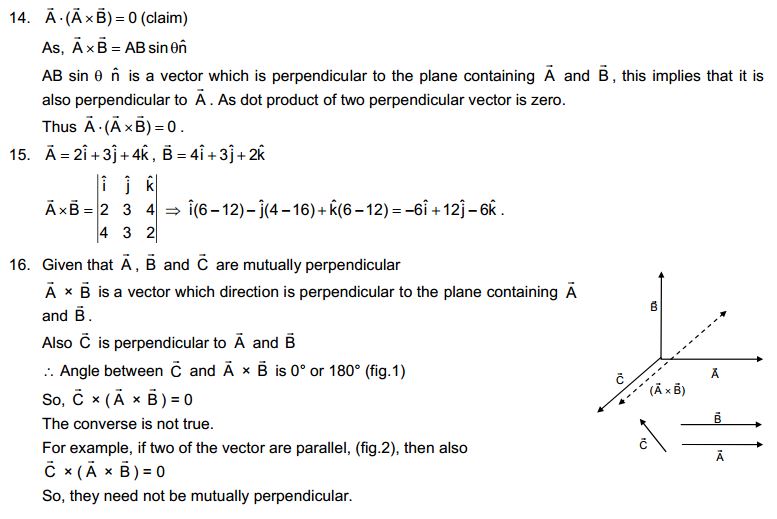
The smell of hot sizzling food reaches you several metres away, but to get the smell from cold food you have to go close.
Answer
Solids diffuse at a very slow rate. But, if the temperature of the solid is increased, then the rate of diffusion of the solid particles into air increases. This is due to an increase in the kinetic energy of solid particles. Hence, the smell of hot sizzling food reaches us even at a distance, but to get the smell from cold food we have to go close.
3. A diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool. Which property of matter does this observation show?
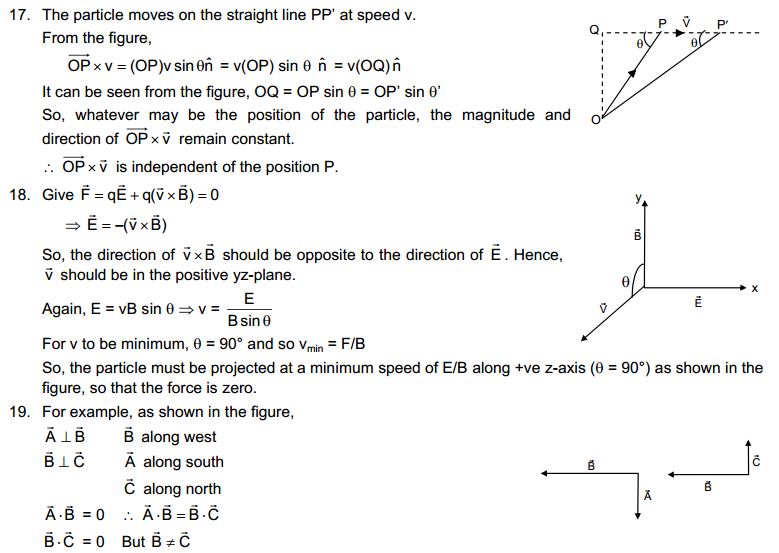
Answer
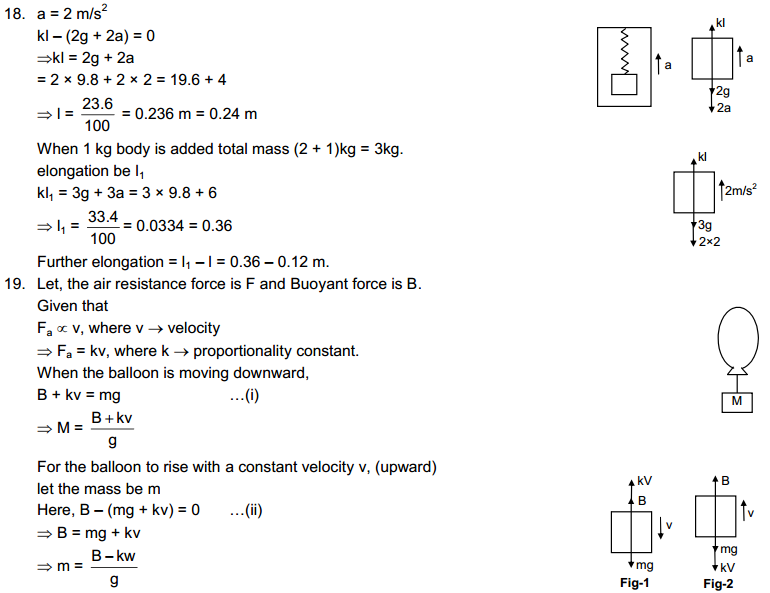
This observation shows that the particles of matter have intermolecular spaces. The intermolecular spaces in liquids is fair enough to let the diver pass through it.
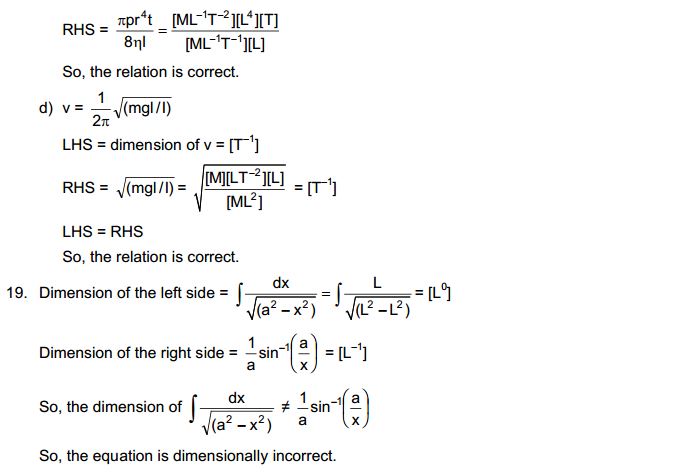
4. What are the characteristics of particles of matter?
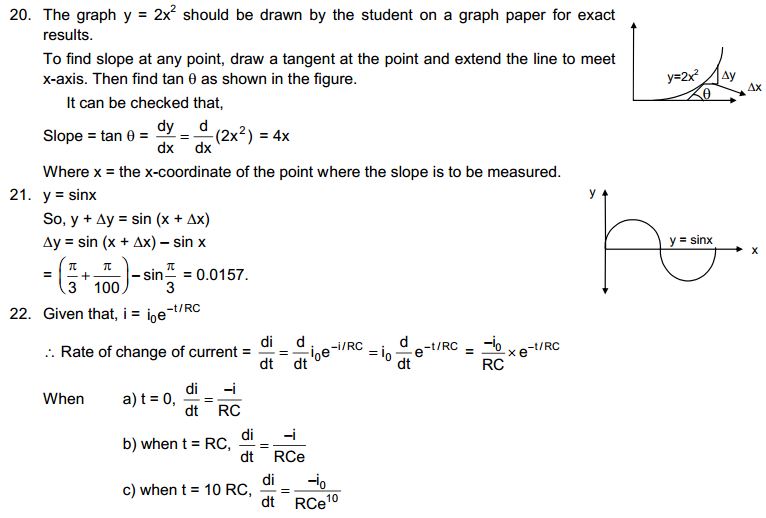
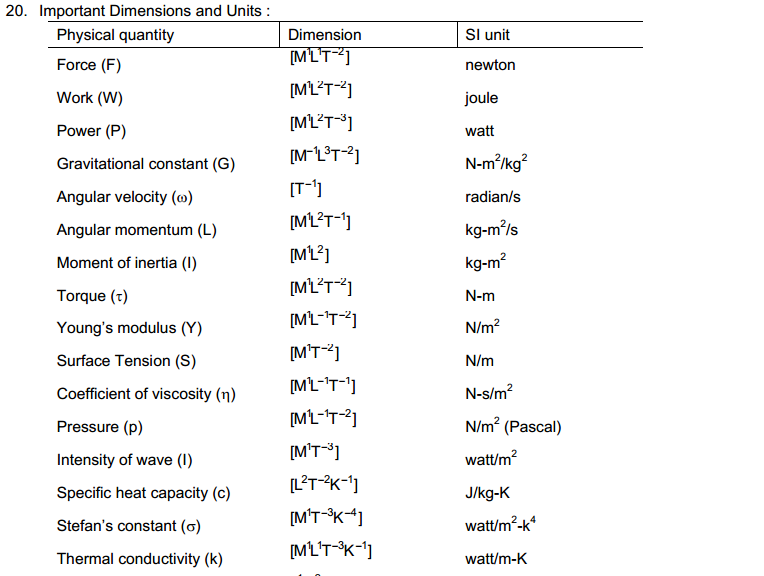
Answer
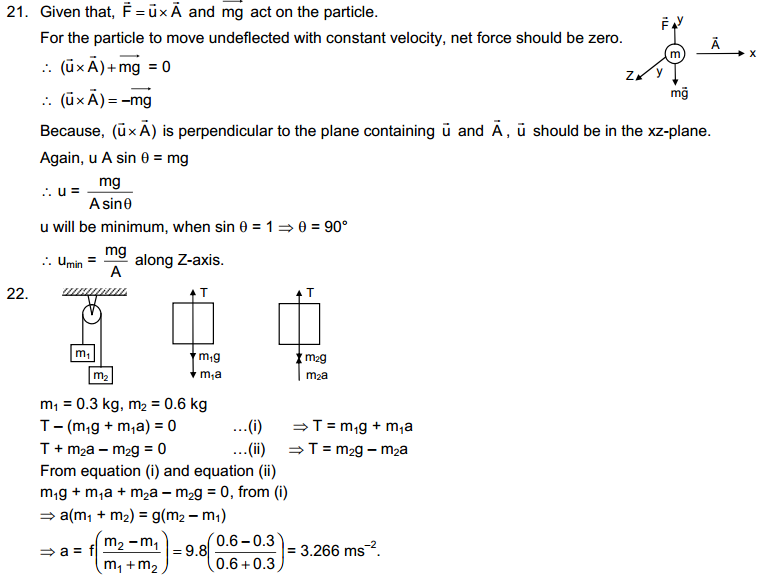
The characteristics of particles of matter are:
→ Particles of matter have spaces between them.
→ Particles of matter are continuously moving.
→ Particles of matter attract each other.
Page No: 6
1. The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density (density = mass/volume).
Answer
air, Exhaust from chimneys, cotton, water, honey, chalk, and iron.
2. (a) Tabulate the differences in the characteristics of states of matter.
(b) Comment upon the following: rigidity, compressibility, fluidity, filling a gas container, shape, kinetic energy, and density.
Answer
(a)
|
Property
|
Solid state
|
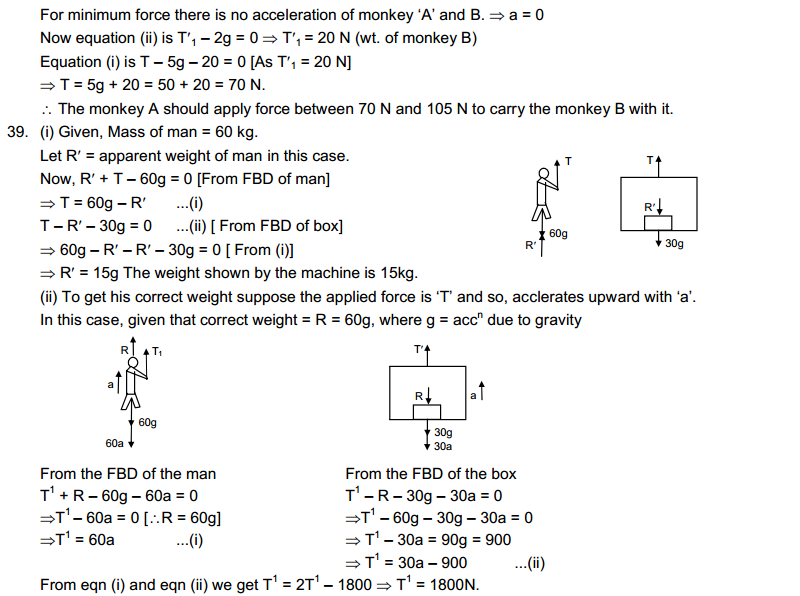
Liquid state
|
Gaseous state
|
| Definite shape and volume. | No definite shape. Liquids attain the shape of the vessel in which they are kept. | Gases have neither a definite shape nor a definite volume. | |
|
2.
|
Incompressible | Slightly Compressible | Highly compressible |
|
3.
|
Cannot flow | Can flow | Can flow |
|
4.
|
Particles don’t move freely | Particles move freely but are confined within the boundary. | Particles move freely. |
|
5.
|
Force of attraction between particles is maximum. | Force of attraction between particles is less than solid but more than that in gas | Force of attraction between particles is least. |
(b)
→ Rigidity: It is the property of matter to resist the change of its shape.→ Compressibility: It is the property of matter in which its volume is decreased by applying force.
→ Fluidity: It is the ability of matter to flow.
→ Filling a gas container: On filling a gas takes the shape of the container.
→ Shape: Having definite boundaries.
→ Kinetic Energy: It is the energy possessed by the particles of matter due to its motion.
→ Density: It is the ratio of mass with per unit volume.
3. Give reasons:
(a) A gas fills completely the vessel in which it is kept.
(b) A gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
(c) A wooden table should be called a solid.
(d) We can easily move our hand in air, but to do the same through a solid block of wood, we need a karate expert.
► Particles of the air have large spaces between them. On the other hand, wood has little space between its particles. Also, it is rigid. For this reason, we can easily move our hands in the air, but to do the same through a solid block of wood, we need a karate expert.
4. Liquids generally have lower density as compared to solids. But you must have observed that ice floats on water. Find out why.
Answer
Ice which is solid has vacant spaces between water molecules thus making ice lighter than water. Thus ice floats on water.
Page No: 9
1. Convert the following temperature to Celsius scale:
(a) 300 K
► 573 K = (573 – 273)°C
= 300°C
2. What is the physical state of water at:
(a) 250°C
(b) 100°C
3. For any substance, why does the temperature remain constant during the change of state?
During the change of state of any substance, the heat supplied or released is utilised in phase change. Such heat is called latent heat. So, the temperature of any substance remains constant during the change of state.
4. Suggest a method to liquefy atmospheric gases.
Answer
The gases can be converted into liquids by bringing its particles closer so atmospheric gases can be liquefied either by decreasing temperature or by increasing pressure.
Page No: 10
1.Why does a desert cooler cool better on a hot dry day?
Answer
A desert cooler increases the humidity of the surrounding air. The water particles in the air take the heat from the surrounding objects and evaporate. In hot and dry days the moisture level is very low in the atmosphere which increases the rate of evaporation. Because of faster evaporation, the cooler works well. That’s why desert cooler cools better on a hot dry day.
2. How does water kept in an earthen pot (matka) become cool during summers?
Answer
There are some pores in an earthen pot through which the liquid inside the pot evaporates. This evaporation makes the water inside the pot cool. In this way, water kept in an earthen pot becomes cool during summers.
3. Why does our palm feel cold when we put some acetone or petrol or perfume on it?
Answer
Acetone, petrol, and perfume evaporate at low temperatures. When some acetone, petrol, or perfume is dropped on the palm, it takes heat from the palm and evaporates, thereby making the palm cooler.
4. Why are we able to sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer than a cup?
Answer
A liquid has a larger surface area in a saucer than in a cup. Thus, it evaporates faster and cools faster in a saucer than in a cup. Thus, we are able to sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer than a cup.
5. What type of clothes should we wear in summers?
Answer
We should wear cotton clothes in summers as cotton is a good sweat absorber. Sweat is absorbed by the cotton and is exposed to the atmosphere making evaporation faster. During this evaporation, particles on the surface of the liquid gain energy from our body surface, making the body cool.
Page No: 12
Exercises
(For Conversion Process we must know,
Kelvin is an SI unit of temperature, where 0°C = 273 K approx.)
1. Convert the following temperatures to Celsius scale.
(a) 300 K
► 300 K = (300 – 273) °C
= 27 °C
(b) 573 K
► 573 K = (573 – 273) °C
= 300 °C
2. Convert the following temperatures to Kelvin scale.
(a) 25°C
►25 °C = (25 + 273) K
= 298 K
(b) 373°C
► 373 °C = (373 + 273) K
= 646 K
3. Give reason for the following observations.
(a) Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid.
(b) We can get the smell of perfume sitting several metres away.
Answer
(a) Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid because of they undergoes sublimation easily i.e., the change of state of naphthalene from solid to gas takes place easily.
(b) Perfumes have high degree of vaporisation and its vapour diffuses into the air easily. Therefore, we can get the smell of perfume sitting several metres away.
4. Arrange the following substances in increasing order of forces of attraction between particles– water, sugar, oxygen.
Oxygen, Water, Sugar.
5. What is the physical state of water at-
(a) 25°C
► Liquid State
(b) 0°C
► Solid State, can also be in liquid state(conditions required).
(c) 100°C
► Gaseous State can also be in liquid state(conditions required).
6. Give two reasons to justify-
(a) water at room temperature is a liquid.
(b) an iron almirah is a solid at room temperature.
Answer
(a) Water at room temperature is a liquid because it has fluidity also it has no shape but has a fixed volume that is, it occupies the shape of the container in which it is kept.
(b) An iron almirah is a solid at room temperature it has rigid and fixed shape.
7. Why is ice at 273 K more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature?
Answer
Ice at 273 K has less energy than water (although both are at the same temperature). Water possesses the additional latent heat of fusion. Hence, at 273 K, ice is more effective in cooling than water.
8. What produces more severe burns, boiling water or steam?
Answer
Steam has more energy than boiling water. It possesses the additional latent heat of vaporisation. Therefore, burns produced by steam are more severe than those produced by boiling water.
9. Name A, B, C, D, E and F in the following diagram showing change in its state.
Answer