Welcome to WordPress. This is your first post. Edit or delete it, then start writing!
Category: Uncategorized
-
Father To Son poem in Hindi Class 11th Chapter 8
मैं इस बच्चे को नहीं समझता
हालांकि अब हम साथ रह चुके हैं
बरसों से एक ही घर में। मुझे पता है
उसका कुछ नहीं, इसलिए निर्माण करने का प्रयास करें
कैसे से एक रिश्ता ऊपर
वह तब छोटा था। फिर भी मैंने मारा है
मैंने जो बीज खर्च किया या जहां बोया
जमीन उसकी है और मेरी कोई नहीं?
हम अजनबियों की तरह बोलते हैं, कोई संकेत नहीं है
हवा में समझने की।
यह बच्चा मेरे डिजाइन के लिए बनाया गया है
फिर भी वह क्या प्यार करता है मैं साझा नहीं कर सकता।
सन्नाटा हमें घेर लेता है। मैंने यह किया होता
उसे खर्चीला, वापस लौट रहा है
उसके पिता का घर, वह घर जिसे वह जानता था,
उसे बनाते और चलते हुए देखने के बजाय
उसकी दुनिया। मैं उसे भी माफ कर दूंगा,
दुख से एक नए प्यार को आकार देना।
पिता और पुत्र, हम दोनों को रहना चाहिए
उसी ग्लोब और उसी भूमि पर।
कहते हैं मैं नहीं समझ सकता
स्वयं, दुःख से क्रोध क्यों बढ़ता है।
हम में से प्रत्येक ने एक खाली हाथ रखा,
कुछ क्षमा करने की लालसा।
Content
- The Father To Son Chapter in Hindi Class 11th Chapter 8
- Summary of Father To Son Class 11th Chapter 8
- Hindi Summary Of Father To Son Class 11th Chapter 8
- NCERT Solutions of Father To Son Class 11th Chapter 8
- Extra Questions Of Father To Son Class 11th Chapter 8
tags: father to son class 11, father to son class 11 questions and answers, father to son class 11 summary, father to son class 11 pdf, father to son class 11 extra questions and answers, father to son class 11 mcq, father to son class 11 pdf ncert, father to son class 11 word meaning, father to son class 11 poetic devices, father to son class 11 theme, theme of poem father to son class 11, central idea of poem father to son class 11, summary of father to son class 11 english
-
Deep Water Flamingo Class 12th English Chapter 3
Deep Water
By William Douglas
Content
-
Extra Questions of Electoral Politics Class 9th Social Science Civics
Electoral Politics Chapter 4 extra exam Questions
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1. What are the choices that voters make in an election?
Ans. In an election, the voters make many choices :
(i) They can choose who will make laws for them.
(ii) They can choose who will form the government and take major decisions.
(iii) They can choose the party whose policies will guide the government and law-making.
Q.2. What is the check on the political leaders which makes them serve the people?
Ans. The check on the political leaders comes from the need to serve the people if they want to win the next elections. Regular electoral competition provides incentives to political parties and leaders. They know that if they raise issues that people want to be raised, their popularity and chances of victory will increase in the next elections. But if they fail to satisfy the voters with their work, they will not be able to win again.
Q.3. Why is there a provision of reservation of seats in the legislatures? [Important]
Ans. The constitution makers were worried that in an open electoral competition, certain weaker sections may not stand a good chance to get elected to the Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies. They may not have the required resources, education and contacts to contest and win elections against the more influential contestants. So seats are reserved for them in the legislature.
Q.4. Mention the provisions laid down under the Model Code of Conduct to regulate the election campaign.
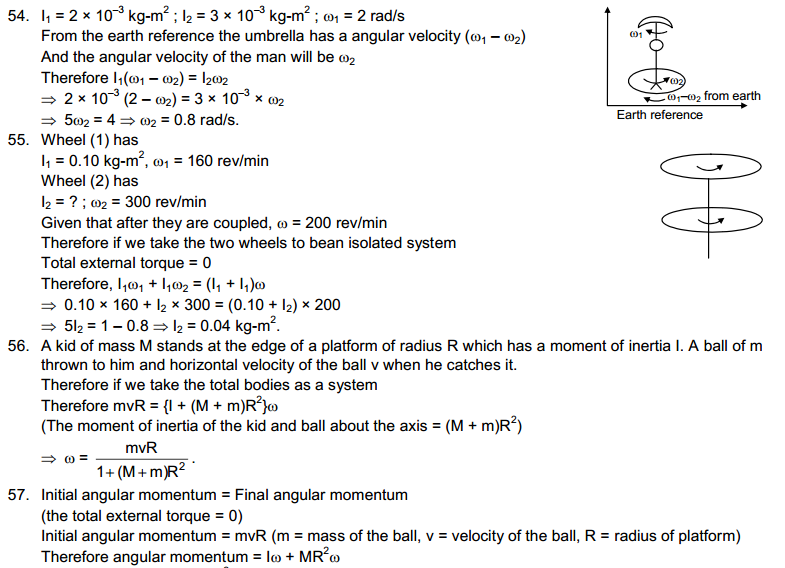
Ans. According to the Model Code of Conduct, no party can :
(i) Use any place of worship for election propaganda.
(ii) Use government vehicles, aircraft and officials for elections.
(iii) Once elections are announced ministers shall not lay foundation stones of any projects, take any big policy decisions or make any promises of providing public facilities.
Q.5. In which way does the Election Commission enjoy the same kind of independence as the judiciary?
Ans. The Election Commission enjoys the same kind of independence that the judiciary enjoys. The Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) is appointed by the President of India. But once appointed, he is not answerable to the President or the government. Even if the ruling party or the government does not like what the Commission does, it is virtually impossible for it to remove the CEC.
Q.6. What are the trends of popular participation in India?
Ans. The trends of popular participation in India are :
(i) People’s participation in election is usually measured by voter turnout figures. In India the turnout over all these years has either remained stable or gone up.
(ii) In India, the poor illiterate and underprivileged people vote in larger proportion as compared to rich sections.
(iii) Common people in India attach a lot of importance to elections as they feel that through elections they can bring pressure on political parties to adopt policies favouring them.
Q.7. Write about any three challenges which an ordinary citizen would have to face if he wants to contest an election.
Ans. An ordinary citizen would have to face some of the following challenges if he wants to contest the elections :
(i) Candidates with lot of money enjoy a big and unfair advantage over contestants.
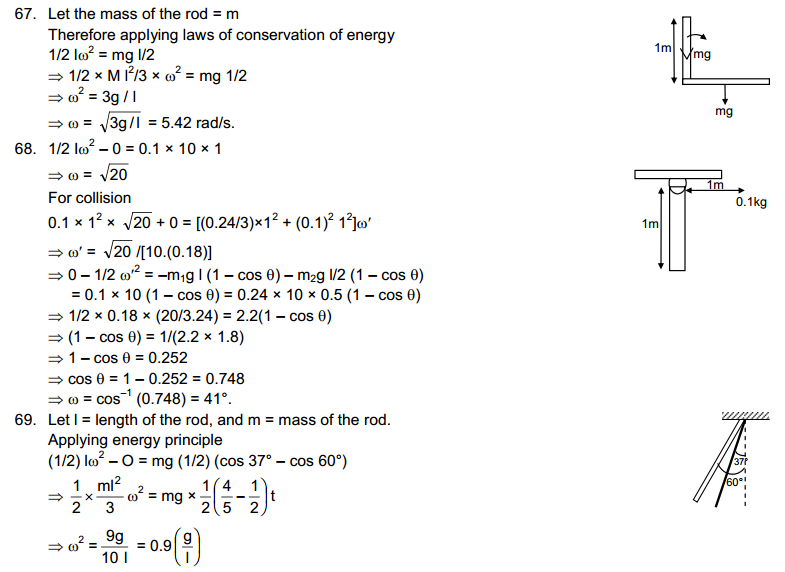
(ii) Sometimes candidates with criminal connections push others out of the electoral race and secure a ‘ticket’.
(iii) Some families tend to dominate political parties.
Q.8. Mention any three techniques of election campaign. [CBSE 2010]
Ans. (i) Candidates contact their voters
(ii) They address election meetings
(iii) Use newspapers and TV for publicity
Q.9. Discuss the importance of elections in a democracy. [CBSE 2010]
Ans. Elections give people a chance to choose the representatives the government and policies they prefer. The democratic way of selecting representatives can be had by holding elections. The voters can make their choice.
Q.10. Discuss the importance of an election manifesto. [CBSE 2010]
Ans. An election manifesto is a statement by a political party explaining its policies, saying what they will do if they win the election.
Q.11. What is a reserved constitueney? How does it strengthen democracy? [CBSE 2010]
Ans. In a reserved constituency only someone who belongs to the scheduled caste or scheduled tribe community can stand for election. In the Lok Sabha, 79 seats are reserved for SC and 41 for ST Communities. This reservation system makes our democracy a representative democracy.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1. What are the demerits of political competition? [V. Important]
Ans. The political competition has many demerits –
(i) It creates a sense of disunity and factionalism in every locality. Different political parties and leaders often level allegations against one another. Parties and candidates often use dirty tricks to win elections.
(ii) This pressure to win electoral fights does not allow sensible long-term policies to be formulated.
(iii) Some good people who wish to serve the country do not enter this area as they do not like to be dragged into unhealthy competition.
Q.2. With reference to ‘electoral constituencies’, state how the elections are held in India.
Ans. For elections, the country is divided into different areas called ‘electoral constituencies’. The voters who live in an area elect one representative. For Lok Sabha elections, the country is divided into 543 constituencies. The representative elected from each constituency is called a Member of Parliament (MP).
Similarly, each state is divided into Assembly constituencies. In this case, the elected representative is called the Member of Legislative Assembly (MLA).
Q.3. Why is there no educational qualification prescribed for the political leaders who hold such an important position of governing the country?
Ans. (i) Educational qualifications are not relevant to all kinds of jobs. Just as a cricketer needs an ability to play well, irrespective of educational qualification, similarly the relevant qualification for an MLA or an MP is the ability to understand people’s concerns, problems, and to represent their interests.
(ii) In our country, putting an educational qualification would go against the spirit of democracy as it would mean depriving a majority of the country’s citizens the right to contest elections. For example, if graduation is made a compulsory qualification, then 90 percent of the citizens will become ineligible to contest elections.
Q.4. How can you say that very few Election Commissions in the world have such wide ranging powers as the Election Commission of India? [Important]
Ans. (i) Election Commission takes decisions on every aspect of conduct and control of elections.
(ii) It implements the code of conduct and punishes any candidate or party that violates it.
(iii) During the election period, the EC can order the government to follow some guidelines, to prevent use and misuse of governmental power to enhance its chances to win elections, or to transfer some government officials.
(iv) When on election duty, government officers work under the control of the EC and not the government.
Q.5. Explain how the outcome of elections is a final test of free and fair elections.
Ans. (i) The ruling parties routinely lose elections in India both at the national and state level. In fact, in every two out of the three elections held so far, the ruling party lost.
(ii) In the US, an incumbent or ‘sitting’ elected representative rarely loses an election. In India, about half of the sitting MPs or MLAs lose elections.
(iii) Candidates who are known to have spent a lot of money on ‘buying votes’ and those with known criminal connections often lose elections.
Q.6. What are the main functions of the Election Commission of India? [CBSE 2010]
Ans. It takes decisions on every aspect of conduct and control of election. It implements code of conduct. It orders guidelines for the government to prevent misuse of power to win elections. It EC feels unfairness in polling it orders a repoll.
Q.7. Explain the term constituency. Give reasons why the system of reserved constituencies was introduced by our constitution makers. [CBSE 2010]
Ans. The country is divided into different areas for purposes of elections. These are called ‘constituencies’. The voters who live in an area elect one representative. For Lok Sabha elections the country is divided into 543 constituenes. The representative elected is called an MP. Similarly, each state is divided into a specific number of assembly constituencies. In this case the elected representative is called an MLA.
To give protection to the weaker section, the makers of our constitution thought of reserved constituencies. These are reserved for people who belong to SC or ST. The Lok Sabha has 79 reserved seats for SCs and 41 for STs.
Q.8. What are some of the activities undertaken by political parties to carry out election campaign? Mention any three activites. [CBSE 2010]
Ans. In election campaigns, political parties try to focus public attention on some big issues, e.g.. the Congress party led by Indira Gandhi gave the slogan of “Gharibi Hatao” in the Lok Sabha elections of 1971. “Save Democracy” was the slogan of Janata Party in the Lok Sabha election of 1977. Secondly, political leaders contact their voters, address election meetings, promise to remove the grievances of the people. Thirdly, support of media – TV Channels and newspaper columns – is also taken by the political parties to further their cause to gather more votes.
Q.9. Define elections. Explain the nomination process as practised in Indian elections.
[2011 (T-2)]
Ans. Every candidate who wishes to contest an election has to fill a nomination form and give some money as deposit. According to recent directive from Supreme Court every candidate has to make a legal declaration giving full details of assets liabilities, educational qualification & details of any serious criminal cases pending against them.
Q.10. Describe any four demerits of electoral competition. [2011 (T-2)]
Ans. An electoral competition has many demerits.
(i) It creates a sense of disunity and factionalism.
(ii) Different political parties level allegations against each others.
(iii) Long-term policies cannot be formulated.
(iv) Some good people who wish to serve, do not enter this arena.
Q.11. Explain any four conditions that make an election democratic. [2011 (T-2)]
Ans. (i) Every section of citizens should get equal representation.
(ii) Every one should get an equal opportunity to choose representatives.
(iii) Voters’ list which is revised every five year.
(iv) Election Photo-Identity Card.
Q.12. What is a reserved constituency? Why did India introduce this system? [2011 (T-2)] Ans. In a reserved constituency only someone who belongs to the SC/ST or weaker section can stand for election. This was done to give a fair representation to the weaker section who did not stand a good chance to get elected to the Lok Sabha.
Q.13. Explain any four challenges faced by election system in India. [2011 (T-2)]
Ans. (i) A few candidates may win purely on the basis of money money power sun four weans.
(ii) Are peoples preferences based on real knowledge.
(iii) Are the voters getting a real choice.
(iv) Is Election leally level playing field for everyone.
Q.14. Explain any four powers enjoyed by Election Commission in India. [2011 (T-2)]
Ans. (i) Election Commission takes decisions on every aspect of conduct and control of elections from announcement of elections to declaration of results.
(ii) It implements the code of conduct and punishes any candidate or party that violates it.
(iii) During Elections EC can order the government to follow some guidelines to use/misuse governmental power, its chances to win.
(iv) When on election duty, government officials work under control of EC.
Q.15. What is Secret Ballot System? Give three reasons why Secret Ballot System is good.
[2011 (T-2)]
Ans. A ballot paper is a sheet of paper on which the names of the contesting candidates along with party names and symbol are listed.
(i) The voter can vote in secricies
(ii) The voter feels secure, safe and fearless
(iii) The voter is free of threat and coercion.
Q.16. How does our Election Law regulate campaigns? [2011 (T-2)]
Ans. Election campaigns take place to have a free and open discussion about who is a better representative, which party will make a better government or what is a good policy. These campaigns take place for a two week period between the announcement of the final list of candidates and the date of polling. During this period, the candidates contact their voters. political leader address election meetings and political parties mobilise their supporters.
Q.17. What are the conditions which make an election democratic? [2011 (T-2)]
Ans. (i) The presence of an independent and very powerful Election Commission (EC). It enjoys the same kind of independence that the judiciary does.
(ii) The Chief Election Commissioner is not answerable to the President or the government.
(iii) It is virtually impossible to remove the CEC, once he is appointed.
(iv) When election officials come to the opinion that polling was not fair in some booths or
even in an entire constituency, they order a repoll.
Q.18. Enumerate any four challenges to free and fair elections. [2011 (T-2)]
Ans. (i) Inclusion of false names and exclusion of genuine names in the voters list.
(ii) Misuse of government facilities and officials in ruling party.
(iii) Excessive use of money by rich candidates and big parties.
(iv) Intimidation of voters and rigging on the polling day.
-
Rotational Mechanics HC Verma Concepts of Physics Solutions
Rotational Mechanics HC Verma Concepts of Physics Solutions
Rotational Mechanics HC Verma Concepts of Physics Solutions Chapter 10


































-
Constructions R.D. Sharma Solution Class 10th Chapter 11
Constructions R.D. Sharma Solution, PDF Download Full Solutions read Online Or download Free. RD Sharma Solutions Of Class Xth Construction Chapter.
Constructions R.D. Sharma Solution Class 10th Chapter 11
[gview file=”https://www.imperialstudy.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/5854204ce4b01bcaf6256353.pdf”]
-
Quadratic Equations R.D. Sharma Solution Class 10th Chapter 8
There Are Lots Of Students Find RD Sharma Solutions Searching On Google For Quadratic Equations R.D. Sharma Solution, But They Failed To Find Them Or The Solutions Are Paid But Here ImperialStudy Team Brought To You 100% Free And PDFDownloadable RD Sharam Solutions. Just Choose Chapter Read Solutions Online Like E-Book. For PDF Download Register On ImperialStudy And Get Access To Download All Solutions. We Post All The Solution By Collecting From Different Resources. Please Try To Read On Our Site only Which Give Profit To Us Also!
Quadratic Equations R.D. Sharma Solution Class 10th Chapter 8
[gview file=”https://www.imperialstudy.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/58541e15e4b01bcaf6256351.pdf”]
-
India’s top prestigious Distance University- NIMS UNIVERSITY
National Institute of Medical Sciences was established in Jaipur in 2008. The university is self-financed and is recognized by UGC and other apex regulatory councils. Over the years they have emerged as the largest university in North-India. The university has made exemplary efforts in the field of teaching and research and thus has recognitions from the statutory regulating bodies including the MCI, INC, PCI, AICTE, DEC, BCI, and the COA.
They have made a name for themselves in quality teaching and action oriented research. The university is located in the outskirt of pink city adjacent to Aravalli ranges. It is one of the top medical universities in India. They have transformed the education in the heath science to human sciences, engineering and management.
NIMS University offers degree, diploma and certificate programmes to the candidates at all the levels namely undergraduate (UG), postgraduate (PG) and doctorate (PhD).
The university is surrounded by lush green campus and has state-of-art-infrastructure with modern laboratory. The university is equipped with latest technology, interactive pedagogy and academics.
WHY NIMS?

- Simple online application and admission facility, for smooth and carefree admission.
- New and modified adaptive learning management system.
- Professional career driven programmes.
- The candidates get to apply their learning immediately which increases the impact of the studies.
- Simplified study material which is accurately designed for the working professionals so that they can study while working without any problem.
Courses
The courses offered by the distance learning institute.
- Management Programmes-
Master in Business Administration
The university provides young graduates opportunity to develop management skills even when they are working. The curriculum has been designed to lay a strong foundation for logical and analytical skills for working professionals. They have an intensive, stimulating and challenging learning experience in the management discipline to the aspirants.
The course is of 2 years of duration. Eligibility criterion requires the candidate to have a graduate in any field. The institute provides Finance, Marketing Management, Human Resource Management, and Operations Management options to the candidate.
Tuition Fees per annum 15,000/-
Lateral Entry Fees 5,000/-
More courses-
- PG Diploma in Hospital Health Management
- PG Diploma in Pharmaceutical Production Management
- PG Diploma in Intellectual Rights
- Information Technology and Computer Science Programmes
PG Diploma in Computer Application-
The programme is introduced to develop the knowledge about computers that can be used for developing business and scientific applications. The programme is of 1 year of duration and the graduates in any filed can apply for the course.
Tuition Fees per annum 14,000/-
- Traditional Programmes-
These are the conventional programmes to train the student in the various subjects like Mathematics, Physics and Chemistry.
B.Sc and M.Sc Mathematics-
B.Sc programmes has a duration of three years
Tuition Fees per annum 10,000/-
Lateral Entry Fees 2,000/-
M.Sc programme has duration of 2 years
Tuition Fees per annum 16,000/-
B.Sc and M.Sc Physics– The duration of the course and the fee structure is same as B.Sc and M.Sc Mathematics.
B.Sc and M.Sc Chemistry- The duration of the course and the fee structure is same as B.Sc and M.Sc Mathematics.
B.Sc General Science- The course is of three years and the fees is-
Tuition Fees per annum 10,000/-
Lateral Entry Fees 2,000/-
- Library and Information Science Programmes
Bachelor of Library and Information Sciences-
The main objective is to train library professionals to manage the libraries using Library Management techniques. The students are taught the fundamentals, for the application of Library and information system and activities. Through the programme the student will learn best practices and techniques of Library and Information Science.
The bachelor’s program is of three years of duration.
Tuition Fees per annum 5,000/-
Master of Library and Information Sciences
The master’s program is of two years of duration.
Tuition Fees per annum 7,000/-
- School of Paramedical Sciences
NIMS are the first private university that provides medical programmes in the distance learning education. These are the programmes which are provided by the university.
- Diploma, Bachelor and Master in Medical Lab Technology
- Diploma, Bachelor and Master in Ophthalmic Technology
- Diploma, Bachelor and Master Radiography
- Diploma, Bachelor and Master Occupational Therapy
- Diploma in ECG Technology
- PG Diploma in Geriatric Medicine
- PG Diploma in Maternal and Child Heath
- PG Diploma in Drug Regulatory Affairs
HOW TO APPLY

Buy a copy of the prospectus:
- The candidate has to buy a copy of the prospectus from the Office of Directorate of Distance Education, Nims University after the payment of Rs. 1000/- has been confirmed via Demand Draft (DD).
- DD can be made from any bank and the Prospectus is required to be made in favour of Nims University, payable at JAIPUR (Rajasthan). Once it is done then the prospectus will reach you.
Filling in the application form:
- Applicant should apply online by filling the application form.
- Please read the application instructions before applying. After reading fill the form carefully and also submit the form. The application will be submitted, please keep a print of the copy of the application form.
- Below are the required documents which need to be both self attested & attested by the competent authority or a Gazetted Officer with seal.
You also need to send the printed copy of the application form.
- Matriculation or equivalent certificate bearing testimony for the date of birth certificate.
- Detailed Marks Card of the qualifying exam that makes you eligible for the admission.
- Proof of Residence (Passport/ Driving License/PDS photo card/ Aadhaar Number/ UID Card/ PAN card Voter ID Ration /)
- Two Passport size coloured photographs which should also be attested.
- Demand Draft (DD) payable at Jaipur.
-
Multiple Choice Questions of Oh, I Wish I’d Looked After Me Teeth Class 9th.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Read the following extracts and answer the following questions by choosing the most appropriate alternative from those given below :
1. Oh, I wish I’d looked after me teeth,
And spotted the perils beneath.
All the toffees I chewed,
And the sweet sticky food,Oh, I wish I’d looked after me teeth.
(a) ‘Spotted’ means :
(i) invented (ii) noticed
(iii) thought (iv) discovered
(b) The poetic device used in these lines is :
(i) Simile (ii) Irony
(iii) Metaphor (iv) Alliteration
(c) “The perils beneath” in line 2 means :
(i) the danger of life
(ii) causes of a disease
(iii) hidden serious condition
(iv) taken care
Ans : (a) (ii) (b) (iv) (c) (iii)
2. When I think of the lollies I licked,
And the liquorice all sorts I pricked, Sherbet dabs, big and little,
All that had peanut brittle My conscience gets horribly pricked.
(a) The poetic device used in these lines is :
(i) Metaphor (ii) Alliteration
(iii) Simile (iv) Irony
(b) ‘Brittle’ here means :
(i) a sweet made from nuts and sugar
(ii) a bright coloured thing
(iii) hard but liable to break
(iv) a small creamy toffee
(c) ‘Sherbat dabs’ means :
(i) perfumed powder
(ii) a kind of tiny sweet
(iii) a kind of sweet dish(iv) a kind of children’s game
Ans : (a) (ii) (b) (i) (c) (ii)
3. Oh I showed them the toothpaste all right,
I flashed it about late at night,
But up-and-down brushin’
And pokin’ and fussin’
Didn’t seem worth the time I could bite!
(a) ‘Flashed’ here means
(i) occurrence of a sudden thought
(ii) moved in a particular direction
(iii) bright lights of traffic
(iv) the light of a camera
(b) ‘Pokin’ and Fussin’ here means
(i) peeping in someone’s room
(ii) making fun of someone
(iii) being fussy about something
(iv) checking carefully
(c) For the poet, taking care of her teeth meant
(i) being extra possessive
(ii) wastage of time
(iii) doing a worthwhile thing
(iv) setting up an example for others
Ans : (a) (ii) (b) (iv) (c) (ii)
Content’s
- Summary of Oh, I Wish I’d Looked After Me Teeth Class 9th.
- Hindi Summary of Oh, I Wish I’d Looked After Me Teeth Class 9th.
- Word Meanings of Oh, I Wish I’d Looked After Me Teeth Class 9th.
- Textbook Question of Oh, I Wish I’d Looked After Me Teeth Class 9th.
- Multiple Choice Questions of Oh, I Wish I’d Looked After Me Teeth Class 9th.
- Non-Multiple Choice Questions of Oh, I Wish I’d Looked After Me Teeth Class 9th.
- Short Answer Questions of Oh, I Wish I’d Looked After Me Teeth Class 9th.
- Long Answer Questions of Oh, I Wish I’d Looked After Me Teeth Class 9th.
-
Class VIII NCERT Text Book Of Maths | PDF Download
[gview file=”https://www.imperialstudy.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/NCERT-Class-8-Mathematics.pdf”]